Choosing the material from which a future house will be built is an important and very responsible task. Strength, comfort, durability and reliability in the future will depend on this. And it doesn’t matter whether they are frame partitions in a residential wooden house or load-bearing walls. If we consider partitions specifically, then, for example, for a lightweight frame it is extremely undesirable to make them from brick or concrete slabs. To understand what exactly you can choose, you need to understand the existing varieties, features and functions.
Features of the partition or how it differs from a regular wall
Vertical internal structures are walls that act as load-bearing structures and partitions. The first ones must be built strictly according to technology, since they are assigned, perhaps, the most important role - distributing the load of the house, including the roof on the base.
Partitions are not load-bearing structures; they only serve to divide the internal space into zones. Therefore, it is possible to use lightweight materials for their production. They will only affect the level of noise and sound insulation and are responsible for the aesthetic appearance.
When remodeling, people are often confused about the concepts of load-bearing and non-load-bearing structures. To bring at least some clarity and understand what can be demolished and what cannot be demolished, consider the following definitions:
- A load-bearing wall is a structure that takes on the weight of the roof or ceiling, and then transfers it to the base. Since they are responsible for the integrity of the house, they build them according to preliminary calculations. Mistakes here are fraught with grave consequences. It is strictly forbidden to demolish them yourself.
- Non-load-bearing walls are structures that, although they are laid out along the entire height of the house, transfer only the load of their own weight to the base and the roof is not based on them.
- Partitions are structures built from floor to ceiling. Compared to walls, the partitions of a frame house rest on a specially designed floor. They are not assigned a load-bearing function; they are intended only to delimit the internal space into rooms.
- The requirements for partitions are much lower than for walls. They can be demolished during redevelopment without the appropriate permission from the architectural bureau for these actions.
What tools are needed to assemble frame partition walls?
The installation of partitions in a wooden house with your own hands is carried out mainly on a base of lumber. Therefore, to process and install them you will need the following tools:
- electric or chainsaw, jigsaw, but you can get by with one hand hacksaw;
- drill, screwdriver;
- slick;
- axe;
- hammer;
- tape measure, square, float level, pencil;
- construction stapler.
It is convenient to mark the location of the structure using a laser level. You can also get by with dyeing thread or simple twine. They are fixed on opposite load-bearing walls, allowing you to designate the lines along which the partition will adjoin the floor and ceiling.
What requirements must they meet?
There are a number of requirements that must be met depending on the purpose of the rooms:
- In bathrooms, laundry rooms and other similar rooms, due to high humidity, the partition must be made of appropriate (moisture-resistant) materials. To prevent steam and moisture from penetrating into other rooms.
- For attic rooms, it is necessary to choose lightweight materials so that they do not create additional load on the base.
- In order to make the room inside brighter, it is better to choose light-permeable materials, for example, glass blocks, structures in which you can insert glass yourself.
- For laying communications: electrics, water supply and sewerage, stationary (special) partitions between rooms are well suited, albeit with increased thickness.
If the house has rooms with different temperatures and they need to be separated, then for this purpose it is better to use more massive structures with good thermal insulation.
Ordinary standard partitions cope well with most of the tasks. To improve sound permeability, you can make sound insulation yourself, rather than using factory-made ones.
Any of the interior partitions should be:
- Durable, stable, comfortable - in a word - so that it does not create interference, does not interfere with free passage, does not pose a danger to the health of household members;
- Meet the deadlines set for;
- The material must be chosen correctly so that the structure does not crack and is firmly and securely attached to load-bearing or non-load-bearing walls.
Sequence of installation of a wood-frame partition
Important! Often, partitions do not require special foundation preparation. However, if they are installed over significant spans of floors or a massive structure is installed, it may be necessary to strengthen its base. In this case, an additional beam is laid with its ends supported on the foundations of the walls.
Frame making
- The projection lines of the frame partition are marked along the ceiling, floor and load-bearing walls.
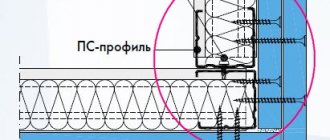
- Rigid fastening of the end beam is allowed only to the floor. The horizontal load-bearing element can be immediately installed on a thick damper pad, for example, made of felt; or fix it on steel brackets with a gap, which will subsequently be filled with foam.
- Vertical end beams are installed, securing them with temporary rigid connections to the walls.
- Two post beams are also installed at the location of the future doorway. Their vertical position is controlled by a float level, and temporary fixation is carried out by oblique struts to the floor.
- Install the upper horizontal end element. It is often made up of several parts connected by steel plates. The plates are placed on the upper and lower planes of the beams. It is recommended to calculate the locations of such connections in advance so that they are above the vertical posts.
- After assembling the frame of the frame partition, internal vertical posts are installed with a pitch of 600 mm. It is optimal for laying mineral wool thermal and sound insulation with a standard slab width of 610 mm.
- It is recommended to make horizontal jumpers from short bars inside the formed cells in a checkerboard pattern (taking into account the height of the cladding material, if it is sheet). This will not only make it easier to fix the lintels and sheets, but will also give the frame additional rigidity.
- At the location of the doors, a horizontal element is mounted to the vertical bars, limiting the top of the opening. It is strengthened with an additional short vertical post to the upper horizontal beam.
- Rigid temporary connections with walls are replaced with floating ones. They are made in the same way as for the frames of decorative wall cladding in wooden houses.
Important! Having a certain professional skill, you can avoid establishing temporary connections. The end vertical bars are initially secured with floating elements, similar to those shown in the figure below.
Infill and lining
- After the cells are filled with mineral wool, the interior partition made of wood is sheathed on both sides with a vapor barrier membrane (striped with a stapler). At the same time, it is important not to confuse the direction of vapor diffusion - it must be provided with an exit in the direction from the insulation, i.e. from inside the partition. The membrane strips are secured with overlaps, and the puncture sites with staples, damage and joints are taped with tape intended for this purpose.
- If the frame is sheathed with plasterboard, OSB or plywood, then their sheets are fixed with offset joints, which are then puttied. The resulting surfaces can play the role of rough or semi-finish and are subject to further processing in accordance with the selected technology. If lining or blockhouse is used as cladding, then they only need to be coated with paints and varnishes.
Purpose of partitions in a frame frame
Frame partitions are not erected immediately, but only after several months. During this period, the shrinkage of the structure should end. Partitions are made for the purpose of:
- Dividing space into rooms (zones);
- Creating an aesthetic appearance through decorative finishing;
- Performing sound insulation in created premises.
First you need to make partitions in a frame house, only then start cladding, using any modern material you like.
Construction of internal walls
For structural stability, the internal walls are framed - just like the external walls. As a result, empty space remains in the cavities of such frames formed by the cross-section of the posts and frame beams. Insulation is placed in these cavities in the external walls. The frame frames themselves are sheathed with sheet material that has increased strength, for example OSB sheets up to 12 mm thick. This is a necessary condition, since they are the main obstacle to mechanical impacts on the walls.
For interior walls, in most cases, neither insulation nor powerful protection is required. You can cover the walls with less durable, but lighter and thinner sheet material:
- Drywall
- Fibreboard boards
- OSB boards of the smallest thickness
- Plywood
- Chipboard sheets
- Lining and so on.
Such coatings easily lend themselves to a variety of interior finishing methods - from decorative plastering to wallpapering.
The cavities of frame cells can also be used.
The problem with interior walls is sound insulation. This problem also exists in capital city apartments, but the walls there are much thicker and more powerful than in private houses. However, not everything is determined by the thickness of the walls. Monolithic materials, on the contrary, can transmit sound waves better.
In this case, the internal walls are filled with material with good noise absorption. This can be mineral wool, which also acts as a heat insulator. Good results can be achieved by specially creating a layered layer for sound absorption. The so-called acoustic sandwich includes slabs of plasterboard and acoustic mineral wool.
The structure of the “acoustic sandwich”
Installation of interior partitions
The design of the partition between rooms is simple, so homeowners often do it themselves, using materials that they know how to work with, or that, in their opinion, are easy to install and process.
The basis is the frame. It can be made of wood, plastic or steel. Plastic is rarely used, but the fact is that it can still be used, for example, in an office, for arranging a screen. Basically, wooden beams and aluminum profiles are used.
The wooden beam that is most suitable for this purpose should have a cross-section of 40x60mm. Board – thickness not less than 30×50 mm. It is not advisable to make a frame structure from boards - it is unreasonable and uneconomical if they are not considered redundant after construction. That is, you don’t need to buy them specifically; you can use those for which you can’t think of a use.
Advice! If after building a house there is a board of 40-120 mm left, it can be cut in half, so you get two beams. This will save material costs.
The frame is assembled and secured with screws or nails. Sometimes, but very rarely, mounting plates are used for this.
The steel frame is made from a simple profile, which is used for plasterboard sheets. Or a profile with a stiffening rib. Once the frame is ready, it can be sheathed with any material that suits your financial capabilities. It could be:
- Plywood;
- GVL;
- The board is thin;
- GKL;
- DSP;
- Lining;
- OSB.
Sheet materials are prepared for finishing (finishing), the lining is sanded, sanded and only then covered with a finishing layer of decorative compounds or simply painted.
Advice! Frame partitions from lining must be assembled after the production of the subfloor, and not before. And after the ceiling is ready.
Construction of the internal frame of the house
Brick and block materials are not used in frame construction, as this significantly makes the structure heavier. The easiest way is to make frame partitions with your own hands. They are usually constructed from the same material that was used to build the house. For example, if the outer frame of a building is made of wood, then timber, boards, chipboard, and so on are used as the basis for the interior walls.
The internal frame of the house is a beam structure made of wood or metal with voids filled with thermally efficient materials, sheathing made of plasterboard sheets or, for example, chipboards. This technology for constructing walls allows you to save usable space, time and finances. In addition, the presence of insulation inside the structure helps to retain heat in the house.
Frame houses are mistakenly considered exclusively budget housing. But in fact, both economy-class and luxury houses are built using frame technology. It all depends on the materials used. The process of erecting walls using frame technology does not take much time. After construction is completed, there is not much construction waste left behind. At the time of installation of interior structures, there is also no rough work.
Useful: Isoroc - a wide range of insulation materials for domestic and industrial use
All types of partitions for frames
All internal partitions in a residential frame house, mounted on joists and beams, are divided into the following types, the so-called traditional:
- Frame-panel;
- Carpentry;
- Wooden;
- Solid.
The building materials market is constantly updated with new materials. This made it possible to produce the following types of partitions:
- Glass;
- Plasterboard;
- Designer ones.
Any design is not particularly complex, so you can do it yourself. Here you don’t need skills or experience working with the material – it’s a matter of desire, time and patience.
Design elements
Components of the partition:
- The racks are made of wooden or metal profiles, the thickness of which depends on the size of the entire structure.
- The strapping is done with a wooden beam.
- The cladding is made of chipboard sheets, plywood, and plasterboard.
- Insulation is placed inside the frame to increase sound insulation and heat conservation.
- Decoration is done with wood veneer, plaster, water-based paint, and wallpaper.
Racks are usually made of timber.
The racks are made of timber with a cross section of 50 x 100 mm or 50 x 60 mm. They are connected to each other by a horizontal lathing, which provides the partition with additional strength.
As thermal insulation, you need to choose environmentally friendly, non-flammable material. If the material has the ability to absorb moisture, it must be protected with a vapor barrier layer.
In areas where interior doors are installed and in places where heavy objects are attached to the wall, additional reinforcement is required.
Frame-panel view
It is considered the most economical and easiest to implement:
- The frame is made of timber with a section of 50×100mm;
- Beams are attached in increments of 50-60cm;
The connecting element here is the harness. It also gives strength and stability to the partition.
The frame is insulated with mineral wool or polystyrene foam 50-100mm thick. It is recommended to seal both sides using a vapor barrier material. It will protect the partition from moisture.
To give a perfectly flat surface, the partition can be sheathed with sheets of plywood.
The soundproofing properties that the partition receives as a result are much better than in any other form.
Construction of openings in internal walls
The presence of any opening - a door or window - violates the integrity of the wall and redistributes the load on it. Any violation of the post pitch weakens the entire wall frame. Methods for strengthening door and window openings were described in an article on our website. In general, they come down to the installation of additional racks, as well as the installation of crossbars - fastening elements that help create a uniform load on the racks.
Strengthening the wall frame with a crossbar
Carpentry and wood varieties
In this case, ready-made carpentry structures for internal partitions are used. They are ready for use, insulated and lined on both sides. The cladding, as a rule, is of high quality; it uses sheets or veneer from valuable wood species. Thermal protection and sound insulation in these structures leaves much to be desired. Most often you have to redo it yourself.
Advice! Where noise absorption and insulation are not needed, you can leave it as is. This could be a dressing room, zoning in the living room, arches.
The cost and thickness of a frame partition in a residential wooden house will depend on the financial ability of the buyer, the brand and the materials from which they are made.
Other features of internal walls and partitions
In addition to the fact that the walls carry the load from the upper part of the building in different ways, they can also differ in their structure:
- According to the degree of insulation. The main contribution to the insulation of the house is made by the external walls of the house. However, heat exchange occurs between rooms. Some rooms, such as storage rooms or utility rooms, may not be heated, while others, such as bathrooms or saunas, may be heated more than other rooms. Adjacent rooms must accordingly be protected from cold or overheating. However, insulation is not so important for interior walls.
- For sound insulation. It makes sense to additionally soundproof some rooms, such as a home cinema room or bathroom, or bedrooms.
- Based on the presence of openings. The walls can be blank, or they can have doorways or even window openings, for example, between the kitchen and the dining room. Openings thus affect the integrity of the structure. Their rigidity must be further strengthened.
- According to the loadability of the lower floor. Various heavy objects can be mounted on the walls - furniture cabinets, heavy household appliances, kitchen units - up to heavy air conditioners or a gas heater. All this affects the redistribution of loads on the lower floor and introduces additional requirements for the wall material.
Opening in the partition between the dining room and kitchen
Solid partition
This type of partition is made from the same material from which the structure was built. The system can be given rigidity using metal spikes (Ø 10 mm, length 100 mm). A frame of beams is assembled on them and secured in two ways:
- Nails directly to the load-bearing walls;
- Grooves are made in the supporting structure into which the beams are placed during the assembly of the frame.
The second is used when the structure has not yet completely shrinked.
Thermal protection and sound absorption systems are made from materials that the homeowner chooses himself. There are no priorities here; all modern materials are suitable for these purposes.
Features of installing supports for load-bearing walls
Since the load-bearing wall takes the load from the top of the building, it must be structurally sound. For its construction, the same beams and boards are used as those used to construct the external walls of the frame. As a rule, for standard frame houses, the racks are made of boards with a section of at least 100x40 mm.
Thus, the load-bearing capacity of the internal wall is not inferior to that of external walls. On the other hand, the external walls rest on the beams of the lower frame of the foundation, that is, the vertical loads from them are transferred to the most structurally strong parts of the foundation.
If the house is installed on a slab foundation, the arrangement of the internal walls does not significantly affect the overall load pattern of the foundation - the slab accepts all loads evenly. A different situation arises when using a strip or pile foundation. Here the loads must be transferred to the supporting planes and points through some additional elements.
Load-bearing walls cannot be installed directly on subfloor beams. Over time, no matter how light the wall may seem, the subfloor boards will certainly bend and the integrity of the structure will be compromised. In order not to place additional supports under sagging boards, it is necessary to take into account the location of load-bearing internal walls when constructing the foundation.
In strip foundations, additional concrete gutters are installed, and in pile foundations, additional supports are placed under the wall line.
However, often load-bearing walls do not necessarily rest directly on the foundation. The load is transferred to the support points by creating additional rigidity of the base using transverse joists. That is, the walls rest on the elements of the lower floor of the house, which transfer the load to the foundation.
There are three main ways to position load-bearing walls in relation to the lower floor beams.
On the beam. The partitions are installed directly on the lower floor beam and secured on both sides with bars. The cross-section of the bars must match the thickness of the floorboards.
Installing a wall on a beam
Between the beams. Additional support bars are installed between the floor beams. They are cut between the beams, and their ends are connected. Then a lag (bedding) is placed on them, on which the wall is already installed. For reliability, a groove is cut out in the bed, and a board is installed on the edge below.
Installation between beams
Across the beams. In this case, a transverse joist is placed on all beams - it is installed perpendicular to the beams. A board is installed on edge underneath it.
Installation across beams
From plasterboard
Such partitions are made very simply and quickly. This is a lightweight version that can be used in any room of the house, even in the bathroom. This system consists of:
- Profiles for gypsum boards. Rack-mount and horizontal guides are made from it;
- Thermal protection. You can use any insulation you like;
- Sealing. From any vapor barrier material;
- Sheathing material in the form of ordinary plasterboard for living rooms or moisture-resistant for bathrooms and toilets.
How to make a frame for drywall is discussed above. Plasterboard partitions are made before the flooring is laid, during the finishing of the rooms. The seams between the sheets are puttied, the partition is primed, and only then do finishing work begin: wallpapering, painting or applying decorative plaster.
Arrangement of compensation gaps
The provision of expansion gaps is an essential aspect of good construction practice. Such gaps are necessary to prevent deformation of the partition frame when the geometry and dimensions of the house box change over time. Professionals advise leaving 1 cm as a compensation gap on each side of the partition. The partition frame is attached to the house frame elements through sliding supports, i.e. supports that allow the partitions to move relative to the house frame elements when the latter is deformed. The joints of the partition with the walls, ceiling and floor are covered with plinths or profiled slats covering the indicated gaps. The plinth and slats are attached only to the floor, ceiling or walls, but not to the partition.
This design protects the partition from stresses when the size of the house box changes.
In established buildings that have already experienced shrinkage, the size of the compensation gaps can be somewhat reduced, since the period of the main deformations of the building is in the past. In such situations, it may be sufficient to lay a compensation tape made of elastic material around the perimeter of the partition. Filling the gap with polyurethane foam is also used.
In new buildings, the compensation gap is calculated by adding the amount of expected shrinkage to 1 cm of the upper gap.
Important! The greatest shrinkage is observed in log houses made of logs or timber. In the boxes of such houses, the use of sliding supports is necessary, regardless of the age of the house box. In addition, it is advisable to install partitions simultaneously with the installation of windows and doors, i.e. about a year after the frame is assembled.
Transparent partitions
Laying glass blocks can also be done independently, at the stage of finishing work, before the final finishing of the ceiling and walls. Installation of glass block partitions in a frame house is similar to brickwork. The difference is that bandaging is not necessary here.
- Glass blocks are laid on a cement screed.
- The thickness of the seam should be small, 1 cm will be enough.
- For masonry, you can use both cement-sand mortar and cement-lime mortar.
The connection of such a partition with the ceiling should be as strong and resilient as possible. Be sure to use cork gaskets in the connection. This is necessary to protect the glass from cracking, since glass is a fragile material and can easily be damaged if deformed.
Important! It is recommended to make the masonry from white sand or cement, so the seams will look neater.
Vapor barrier of internal walls and partitions
If in most cases there is no special need for insulation of internal walls (except for those mentioned above), there is no point in taking care of it. However, if an acoustic sandwich is installed, questions arise regarding the vapor barrier of the wall. After all, additional layers can accumulate moisture - this is especially true for acoustic mineral wool. Porous wool allows air to pass through well, and therefore water vapor. Under certain conditions, water vapor can condense into the mineral wool. This is an undesirable process - the material begins to become damp, conditions for the appearance of fungus and mold, and an unpleasant odor appear. The acoustic material itself becomes inhomogeneous and gradually deteriorates.
This is especially true for rooms with high humidity - kitchens, bathrooms, toilets. It is advisable to provide such walls with additional vapor barrier, which is known to us from the composition of the carcass “pie” of the side walls.
Frame pie devices
In addition, vapor barrier and waterproofing is necessary in places where communications are laid between walls - water pipes, heating pipelines and electrical wiring. It is necessary to carefully close such openings with hydro- and vapor barriers.
For a frame-type house, you can choose several options for partitions:
- single plank partitions
- double plank partitions with sound insulation
- frame-sheathing partitions.
In this article I will talk about the construction of frame-sheathing partitions. Because:
- This is the most economical and least labor-intensive type of partitions.
- The supports have already been partially installed in our house (see the article from the “We Build It Yourself” series about installing ceilings).
Note: Brick partitions for a frame-type house, of course, cannot be ruled out. But for this type of partition, a full-fledged strip-type foundation is required. And if, in our case, the house is wooden, then it makes sense to make the partitions from a homogeneous material. But such a decision is made by each owner individually, based on personal considerations.
Sound insulation requirements
The multilayer design significantly increases sound insulation due to the fact that the sound first encounters a solid barrier, is slightly muffled and touches the soft insulating material, dissolving into its structure.
Partition structure
Sound insulation standards according to SP 51.1330.2011 “Noise Protection”:
| № | Type of partition | Noise insulation, db |
| 1 | Apartment partitions | 52 |
| 2 | Between apartments and office premises | 52 |
| 3 | Between apartments and staircases | 52 |
| 4 | Partitions without doors between rooms in an apartment | 43 |
| 5 | Between the bathroom, toilet and room in the apartment | 47 |
| 6 | Between dorm rooms | 50 |
Installation of frame partitions provides high levels of heat retention and sound insulation. We must not forget to strengthen the structure in those places where the partition will be subject to additional load. Having studied the installation technology, the work can be easily done with your own hands.