They are divided into load-bearing (main, called structural), partition (belonging to the category of structural insulation), thermal insulation (additional, insulating the first 2 types of walls) and finishing (used for cladding the outside of buildings).
Each of the listed walls has its own thickness, specified in regulatory documents. You need to know it in order to determine the load-bearing capacity of the wall, correctly form the structure of the structure, and take into account the indicators in the calculations needed to determine the amount of consumables, reconstruction and repairs.
What requirements for the thickness of a wall made of panels relate to building codes, read more in this article.
Why is it important to correctly determine the indicator?
First of all, correct calculations of the thickness of a panel wall structure are necessary when reconstructing, repairing and remodeling residential premises.
Correct calculation helps determine the type of wall and the load it can withstand . A specialist should measure the thickness of the wall, but if you really want to, you can do it yourself.
Specialists make calculations more professionally and accurately. The obtained indicators are important not only for redevelopment, but also for the design of thermal insulation for walls, so that the insulating layers perform their functions fully.
Calculations help you choose the type of future insulation - external, internal or double-sided. Correct determination of indicators helps to save money when choosing panels for construction, which are carried out taking into account climatic and landscape features.
Also, the mathematical operations carried out help to determine the possibility of changing or decreasing the wall thickness, and look at the cost of consumables associated with an increase or decrease in their price. This approach will be one of the steps to save on heating systems for the premises in the winter.
Thickness, as an indicator, is considered one of the main parameters, the values of which must be determined before the start of construction work. It determines how comfortable the temperature in the house will be, and whether panels consisting of three layers can be used in construction (the efficiency is determined).
Briefly about the main thing
The ability to distinguish load-bearing walls from partitions is an important skill that will help you competently carry out redevelopment in an apartment, and then coordinate it with supervisory authorities. The rules prohibit demolishing or moving load-bearing structures, but in some cases it is allowed to make doorways in them (with the involvement of certified specialists).
You can find out the purpose of wall structures using a technical plan or by location and method of support. Measurements will also help to find out the truth: walls made of different materials have their own strictly defined parameters.
Question
Write in the comments what you think - is it worth looking for a diagram of a typical apartment based on the building series, since the series were often built with local modifications and may differ in parameters?
Regulatory documents
General requirements for the thickness of panel wall structures are regulated by the following technical documents, defining the basic conditions :
- GOST – monolithic wall panels.
- GOST 31310-2015 – reinforced concrete panels with three layers and insulation.
- GOST 11024-84 – external monolithic panels used for residential multi-apartment buildings.
- GOST 11118-73 – external walls of public monolithic buildings.
- GOST 33126-2014 – expanded clay concrete wall blocks.
- GOST 32603-2012 – sandwich panels.
- SP 31-105-2002 – private houses with wooden panels.
- GOST 33929-2016 – polystyrene concrete wall structures.
Monolithic panels have the most GOST standards. This is due to the fact that secondary multi-apartment housing, built from the beginning of the pre-war years to the 80s, was built in large quantities throughout the entire territory of the Soviet Union. If we draw a general conclusion on the thickness of the walls for all panels, the structural thickness of the products can have different sizes - 40, 60, 80, 140, etc. (mm).
When determining the thickness of a wall structure, be sure to pay attention to the dimensions of door and window openings. GOSTs are used here :
- 14624-69;
- 6629-74;
- 11214-78.
The documents indicate the requirements for their thickness, which directly applies to the wall structure where windows and doors will be installed.
Where to go if redevelopment affects load-bearing walls
Any redevelopment in Moscow that is not done according to a standard design is subject to approval by the Moscow Housing Inspectorate.
If the repair affects load-bearing walls, it is necessary to obtain permission from the authors of the house project. In particular, this is necessary when creating a new opening or moving it. Authors may be:
- MNIITEP - more than 70% of houses in the capital were built according to standard designs of this institute. For example, he designed houses of the II-49, P-44, I-209A, P-46, MG-601, I-522A, II-68, II-29, P-3 and others series;
- "Mosproekt". The Institute is the author of the KOPE series house projects;
- TsNIIEP. The Institute is the author of projects for individual houses for infill development and large residential complexes.
If the author of the house project is unknown, then a conclusion on the admissibility of redevelopment involving the load-bearing walls is obtained from the State Budgetary Institution “Expert Center”. Their standard conclusion costs about 70 thousand rubles, it all depends on the number of openings in load-bearing walls, the area of the room and the type of floors.
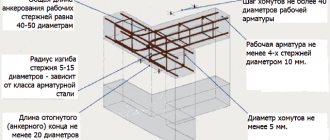
In addition, when creating a new opening in a load-bearing wall, it is necessary to reinforce it with metal structures. This can be done by a construction organization with SRO approval. This is what the reinforced opening looks like:
The work was carried out by a licensed APM-1 team. The opening is cut using diamond cutting. We talk about it in more detail here. The gain itself is calculated individually for each apartment.
We can help with the redevelopment project, and with obtaining conclusions, and with collecting documents, and we will also fully coordinate the redevelopment of a house of any series. Our turnkey legalization costs from 75,000 rubles.
If you want to carry out the approval yourself, we still advise you to contact us first to find out which walls in your apartment are load-bearing and what can be done with them. Send us the BTI plan:
- by email;
- on WhatsApp
- call us +7 (495) 181-13-09
In most cases, we immediately understand which walls are load-bearing and which are not. This way you will protect yourself from incorrect redevelopment, you will not have to redo the repairs and you will know where to start the approval.
Leave a request for a free consultation on apartment redevelopment
Zamyatin Dmitry Alekseevich
Zamyatin Dmitry Alekseevich
General Director of LLC "APM-1" Design workshop PEREPLAN.
Education: Higher technical (Master's degree from Moscow State University of Civil Engineering)
Specialization Coordination of redevelopment of commercial and residential real estate in Moscow and St. Petersburg
Standards for panel structures
The minimum general standards for the thickness of any type of wall, depending on the region, are for the southern regions - 25 (cm), central - 40 (cm), northern - 60 (cm). Different types of concrete have standards from 80 (cm). The optimal thickness is determined by taking into account the standard and thickness of the insulation, which can reach from 5 to 200 (mm).
The standard wall thickness by panel type is :
- Expanded clay concrete – 920 (mm).
- Monolith – 100-400 (mm).
- SIP – 125-220 (mm).
- Sandwich – 50-200 (mm).
- Wood concrete – 370 (mm).
- Polystyrene concrete – 50-150 (mm).
The presented standards are generally binding for structural (load-bearing) walls. In practice, thickness indicators, depending on the manufacturer, can be much greater. When making calculations, the thickness of all layers is always added to this indicator - waterproofing, insulation (by quantity, 1-2), plaster, finishing.
Internal walls can be made without insulation, so the calculation of their thickness is considered simplified, since it concerns only the layers of the panel itself.
For example, the arrangement of layers of buildings such as a garage and a bathhouse will also include sheathing, a foil layer, a ventilation gap (20 cm), finishing layers of plaster, brick or eurolining.
The thickness of the panel layers by the number of layers is equal to :
- single-layer – 300-350 (mm);
- multilayer – 380 (mm);
- internal partitions – 80-100 (mm).
The type of soil does not affect the thickness of the wall being built. It matters only for the foundation, which can be monolithic, strip or pile-screw.
For example, reinforced concrete panels are best erected on a monolithic foundation - this way the load-bearing load on the building structure is evenly distributed. For SIP, sandwich and other types of lightweight types of panels, a strip and pile-screw foundation is suitable.
GSOP (degree-climatic) indicators and heat transfer resistance, when determining the thickness of the wall layer, are important only when calculating the amount of insulation used.
This calculation should be entrusted to specialist engineers who will carry it out professionally, based on the table indicators from GOSTs applied to a certain type of panel products.
External walls of a panel house
These walls are the thickest and come in two types:
- single-layer external walls consisting of lightweight concrete
- multilayer walls consisting of reinforced concrete and, as a rule, polystyrene foam slabs
Single-layer panels
Most often, single-layer panels are made of expanded clay concrete with a thickness of 300-350 mm, depending on the climate zone. Expanded clay concrete is suitable for these purposes, both in strength and thermal conductivity.
There are single-layer slabs consisting of cellular concrete. The thickness of such panels also ranges from 300 to 350mm.
Multilayer panels
Most often, such panels consist of two layers of reinforced concrete (external and internal) and polystyrene foam (foam) slabs between them. The standard thickness of such a wall is 380mm.
The internal reinforced concrete layer is 80-100 mm (previously the layer was thinner). The outer reinforced concrete layer is at least 60 mm.
Expanded polystyrene is usually used as insulation, since mineral wool is too “soft” a material, and if it is used for the production of panels, it is very rarely.
Calculation rules
It is necessary to calculate the required wall thickness consistently according to all the rules, after familiarizing yourself with the technical diagram (drawing, plan) of the room. First of all, it is necessary to carry out calculations taking into account the thermal conductivity of the wall structure.
For example, a wall based on the building materials used is calculated using the following formula:
R=δ/ λ (m2 x °C/W), where:
- R – thermal resistance coefficient;
- δ – thickness of consumables used;
- λ is an indicator of specific thermal conductivity, calculated in (m2 x °C/W).
The passport of a product purchased from a trusted manufacturer always indicates the thermal conductivity coefficient. According to the established standard for the heat transfer resistance of load-bearing (external) walls, it must be at least 3.2 λ (W/m x °C).
In practice, calculations with R might look like this:
- The cellular concrete panel has an R of 0.12 W/m x °C. The required thickness for the region should be 300 mm.
- Using the formula R=δ/λ, we get: 0.3/0.12 = 2.5 W/m x °C.
The resulting figure is less than the norm in the GOST table, therefore, the wall needs insulation.
For this example, when deciding on the thickness of the wall that they want to equip with insulation, plaster and finishing, they use the same indicators as in the basic formula, but in reverse order:
δ = λ x R – formula for determining wall thickness.
For example : You need to calculate the thickness of a wall made of reinforced concrete panels. Given R= 2.04 W/m x °C (thermal conductivity coefficient). Using the formula, we get: 2.04 x 3.2 = 6.528 (m), rounded. The wall thickness of the panel according to the standards in this case is 6.5 (m).
If you check the thickness of mineral wool, according to the thermal conductivity coefficient specified in GOSTs, using the above formula, insulation with a layer thickness of 14 (cm) will correspond to λ (specific thermal conductivity) = 0.044 W/m x °C x 3.2 = 0, 14 (m).
Adding the resulting value to the thickness of the reinforced concrete panel will show the total layer of the main wall with insulation. Then additional layers of plaster (2-3 cm), waterproofing and finishing (sizes depending on type) are added, which will ultimately be the thickness of the entire wall structure.
The consequences of incorrect calculations are considered:
- Cold and damp in winter.
- High humidity in summer.
- Destruction of the structure (when the load-bearing structure is confused with the partition).
You can also use an online calculator for calculations.
Using the example of SIP
The calculations are also based on temperature indicators. The calculation for the SIP panel and the intended use of expanded polystyrene grade PSB S-25 100 (mm) can be carried out as follows:
Given:
- The atmospheric temperature outside is -26 °C.
- The temperature inside the house is +18 °C.
- R outside – 23 W/m x °C.
- R inside – 8.7 W/m x °C.
- SIP board is three-layer, has a total layer thickness.
- OSB 12 (mm).
R0 = 1:8.7+2 x 0.01:0.18 + 0.1:0.041+1:23=0.115+0.111+2.439+0.043=2.71 (W/m x °C)
The resulting indicator - 2.71 (W/m x °C) indicates that, according to a comparison of standards according to the GOST table, it should be more than 3, therefore the presented insulation thickness is not suitable, a higher one is needed.
We take polystyrene foam with a thickness of 150 mm, we get:
R0 = 1:8.7+2 x 0.01:0.18 + 0.14:0.041+1:23 = 0.115+0.111+3.415+0.0043 = 3.95 (W/m x °C)
The resulting value of 3.95 (W/m x °C) fully reflects the required standards for thickness, and is therefore ideal for SIP panels. That is, in this case, the panels must be insulated with polystyrene foam, with a thickness of 150 mm.
Exploring the possibilities
Even at the stage of buying an apartment, you should imagine the position of the walls, because in the future any redevelopment may be overshadowed by the presence of load-bearing structures in non-obvious places.
The apartment plan, which is included in the list of necessary documents on home ownership, will help you find out the purpose of the wall. The technical plan consists of text and graphic parts; the latter schematically displays the apartment, indicating rooms, partitions, window and door openings. There is no special designation for load-bearing walls; they are distinguished by color, shading, or a thick line.
Externally, structures are distinguished by characteristic features. You can find out whether a wall is load-bearing or not in a panel house in the following ways:
- Location. In addition to the external walls of the building, the load-bearing structures will be those bordering the staircase or separating neighboring apartments. But, of course, they cannot be moved or demolished.
- Method of supporting floor slabs. If the ends (short sides) of the floor slabs are on a given wall, then in front of you is a load-bearing element.
Source svoymaster.com
Other indicators
In accordance with the requirements of SNiP 23-01-99, which relate to the climatic characteristics of the region, when calculating, pay attention to temperature indicators. An example with these values can be seen in the section above.
The specified SNiP contains table No. 1. It contains a list of all settlements of the Russian Federation by region with an average annual temperature. The indicated indicators at the intersection accurately determine the number of days with low temperatures during the year.
Determining the degree-day for the entire heating season in order to calculate the required wall thickness along with insulation is an additional calculation. SNiP 02/23/2003 contains a formula that helps determine the indicator we need.
Thickness S is determined as follows:
S = R x λ
For example , cellular concrete panels have an R (thermal conductivity coefficient) of up to 0.14 (W/m x °C). The norm for the required thickness of a wall structure in the region should be 3.2.
We multiply the values together, we get 0.14 x 3.2 = 0.45 (m). That is, taking into account the climatic conditions of the region, its thickness according to the standard should be at least 45 (cm). This layer will help protect the room from freezing during the coldest time of the year.
Thickness Requirements
When developing technical documentation on the requirements for concrete walls, the following strength parameters were taken into account:
- for compression;
- when bending;
- for sustainability.
In this case, the coefficient of thermal conductivity relative to concrete walls was taken into account. These are the basic conditions for calculations
But additional data also needs to be taken into account.
Type of concrete partitions
As a rule, they focus on the winter season.
And if frosts in the area do not fall below 20 degrees Celsius, then a wall thickness of 250 mm is sufficient.
And with every ten degrees, another 100 mm is added to the depth. So, at an outside temperature of -40°C, the thickness of the concrete wall should already be at least 450 mm.
Availability of reinforcement
As a rule, all concrete structures are made with the participation of a metal frame. In construction this is called reinforcement. It is needed to increase the strength and reliability of the structure. Walls with reinforcement inside are much stronger than those poured from a single mortar.
But to protect the metal rod from corrosion and possible mechanical impacts, a layer of concrete is needed:
- 20 mm in dry and enclosed spaces;
- 25 mm at high humidity;
- 30 mm outdoors;
- 40 mm on or below the ground surface.
Location
The thickness of the external walls was mentioned above. The walls inside the room are divided into load-bearing ones, which help distribute the load from the floor slabs and just the partition. In the first case, ready-made reinforced concrete structures are used, the thickness of which ranges from 120 to 200 mm.
A simple partition has a standard thickness of 80 mm. If you use a homemade monolithic fill, then you are allowed to increase the size to 100 mm.
Purpose
Concrete partitions are erected not only in residential buildings.
One of them is a cellar, which acts as a vegetable storage area. When equipping an underground room, groundwater is taken into account.
If they are low and the soil is dry, then 150 mm is enough for the wall thickness. But with wet soil, the size increases to 250 mm. Otherwise, when freezing occurs, the load on the surface increases, and the wall may not be able to withstand it and collapse. But in both cases, vertical reinforcement is necessarily used.
But since the structure is constantly under increased load due to the water in it, the thickness of the walls should not be less than 200 mm. It is not practical to make partitions thicker than 250 mm.
For wells, special reinforced concrete rings are used. The thickness in such structures ranges from 70 to 120 mm.
Floor structures
When it is necessary to install ceilings between floors, this can be done in two ways. In the first case, monolithic floors are poured, which act as a lintel. The thickness of the slab must be at least 150 mm.
But you can use ready-made standard designs. Hollow reinforced concrete slabs with reinforcement have a thickness of 90 mm. This is quite enough for floors between floors. Because, unlike a homemade stove, factory panels are made in accordance with all GOST and SNiP standards.
Construction area
The method of constructing walls by pouring them out of concrete is approved for use everywhere. Even in areas with increased seismic hazard
And during construction, only the possible ambient temperature is taken into account. Changes in wall thickness with increasing frosts were discussed above.
Foundation type
When pouring a concrete strip foundation, you need to take into account that its thickness cannot be less than the depth of the load-bearing walls. But, as a rule, the dimensions of the base exceed these parameters
Therefore, knowing the requirements for future walls, it will not be difficult to pour the necessary foundation.
But there is a calculation formula that allows you to find out the dimensions more clearly:
Explanation of symbols:
- M – weight of all building elements;
- P – useful weight;
- C – snow load;
- B – wind force.
All exact data can be found in SNiP 2.01.07-85.
Soil type
Only low heaving soils are considered acceptable. Therefore, it is necessary to discard fine-grained and dusty soils from sandy soils.
They are extremely unsuitable for any construction. For the same reason, peaty soils are avoided.
GSOP indicator and heat transfer resistance
The relevance of this indicator applies only to residential or office premises. All current parameters of the degree-day of the heating period, as well as heat transfer resistance, can be seen in detailed tables by studying SNiP 2-3-79.
Types of reinforcement
A brick partition in a wooden bathhouse, as in a room for any other purpose, must be reinforced. Depending on the location of the elements, such strengthening can be:
- vertical;
- longitudinal;
- transverse.
In the latter case, a mesh is laid into the brick partition. The grille can be purchased or made independently. For this purpose, rods are used, which are connected to each other by the principle of welding or using wire. The side of the cells should not be more than 120 mm. There is also no need to increase the size of the mesh itself too much, as this will reduce the strength of the brick partition.
In order to protect the reinforcement, it is first placed in cement mortar, which will increase the thickness of the rod, as well as the width of the seam, which can be 14 mm. Partitions erected in 2; 1.5 or half a brick, must be reinforced every 4 rows.
Even if the partition is two bricks thick, but the structure is being operated in a region where there is a seismic hazard, internal reinforcement should be carried out vertically or longitudinally. Strengthening the wall using the latter method can be done outside or inside the structure.
Brick buildings – does the quality justify the price?
It is believed that living in a brick house is the safest from an environmental point of view. Especially if ceramic brick was used for construction - it absorbs and releases moisture, preventing the appearance of mold and fungi.
✓
Thermal insulation - a brick house is warm in winter and not hot in summer
✓
Service life, as with monolithic housing construction, is up to 150 years
✓
You can design the layout of rooms without regard to standard solutions. True, the customer must control the process from the very beginning.
✓
Sound insulation - among all possible options, brick has the highest performance.
However, an apartment in a brick building also has disadvantages:
✘
Long construction period
✘
Price: the construction of such a house uses manual labor, which cannot but affect the cost of housing
However, there is always a demand for such living space. Many luxury complexes are still built from brick.
Tools and materials used for laying foam blocks
Before starting work on constructing a partition from foam blocks, you need to prepare a set of necessary materials and tools:
- glue for foam blocks at the rate of 15 kg per 1 cubic meter. meter (with a layer of 2 mm);
- cement mortar for laying the bottom row;
- mounting foam for foaming the gap between the top row and the ceiling;
- foam gun;
- pins - self-tapping screws, metal embedded pins;
- spatulas and trowel;
- a drill with a mixer for mixing glue and cement mortar, a container for glue;
- a hammer with a rubber pad for leveling blocks when laying;
- construction laser or regular level;
- corner, wood hacksaw for sawing blocks;
- a plane or grater for foam blocks to level the surface before finishing;
- electric milling cutter or wall chaser for making holes and grooves in the partition;
- a large brush for sweeping away concrete dust from rows before applying glue.
After preparing everything necessary for the construction of a wall partition made of foam blocks, you can proceed directly to the beginning of work.
Technology for laying ondulin on the roof. You will read about this in our next article.
And here is an article about laying cork flooring.
Partitions
Partitions are subject to force impacts from their own mass within one floor, minor random force impacts during operation (when moving furniture, equipment, etc.), and non-force acoustic impacts. Partition structures, in accordance with the degree of fire resistance of the building, are designed with a fire resistance limit of 0.5-0.25 hours from fireproof or fire-resistant materials.
This low level of regulatory requirements for the fire resistance of partitions is due to the fact that their damage in a fire is usually local in nature and cannot affect the safety of the building’s load-bearing structures.
Low regulatory requirements for the strength and fire resistance of partitions allow them to be made from a wider range of materials than internal walls.
Partition structures are designed depending on the degree of fire resistance of structures made of brick, stone, concrete, gypsum concrete, wood and other non-concrete materials. The soundproofing ability of partitions is provided according to the principle of acoustically homogeneous or separate structures, depending on the selected material of the enclosing structure. The least industrial partition design is in the form of a thin wall, built manually from brick or small slabs; the most industrial is panel, single-row cut. Partitions made from small-sized products are outdated and even in houses with brick walls they are giving way to panel ones. In large-block and panel buildings, partitions are made from single-row cut panels (solid or with openings) the size of a room. Partition panels are formed from heavy or light concrete with a thickness of at least 60 mm or from gypsum concrete with a thickness of at least 80 mm. Inter-apartment partitions, as a rule, are designed to be acoustically separate, double, with an air gap between the panels of at least 40 mm. The designs of the partition panels and their fastening details are shown in Fig. 10.
Partitions made of non-concrete materials (Fig. 11) are designed, as a rule, layered in the form of frame or frameless (glued) panel-type structures or element-by-element assembly. The frame of such partitions is made of plank slats, aluminum or thin-walled galvanized steel rods of rectangular tubular or channel cross-section with double-sided lining with gypsum dry plaster and filling of the cavity with mineral or glass wool materials. The partitions are mounted along guides made of metal or wooden slats, fitted with dowels to the floor and ceiling. Vertical joints of partition panels are made into tongues and grooves onto spacer strips that fit into the grooves of the vertical strappings. Partition panels are made one floor high with a main width of 1.2 m and additional elements 0.6 and 0.3 m wide.
In buildings with a layout that can be transformed during operation, sliding partitions are used. Depending on the material used, a soft harmonious or hard folded structure (Fig. 12) of a sliding partition is used.
Rice. 10. Partitions made of gypsum concrete panels - general view of the panel; b - connection to the ceiling; c - connection to the floor; 1 - lifting loop; 2 - wooden slatted frame; 3 — door block; 4- lower wooden frame (support beam); 5 - metal clamp for joining with the ceiling
Rice. 11. Panel partitions made of non-concrete materials - adjacent to the ceiling; 6 - connection to the floor; c - connection to the wall; g - connection to the door frame; d - vertical joint; 1 - frame; 2 - casing; 3 - soundproofing layer; 4 - plinth; 5 - harness; 6 - butt rail
Standard length, width and thickness of bricks
The thickness of a brick partition will depend on such an indicator as the dimensions of the material used. Usually they are standard, but different masonry methods lead to changes in the size of the partition.
There are other sizes that differ in height, but this parameter does not in any way affect the dimensions of the partition. Builders highlight several options:
- masonry of 0.5 bricks - wall 12 cm thick;
- 1 brick masonry – thickness 25 cm;
- masonry of 1.5 bricks - 38 cm;
- masonry of 2 bricks - 51 cm.
When choosing the main material for construction, they take into account what the building will be used for, as well as where it will be located.