02.11.2020
The thickness of aerated block walls directly affects the warmth in the house. The thicker the aerated concrete walls, the more comfortable the room will be in winter. It would seem that it could be simpler: make the wall wider and forget about the cold. But there is also the other side of the coin: a large width of aerated concrete wall means the use of a large amount of building materials, which means increased costs.
It is necessary to decide what thickness of aerated block masonry should be at the stage of designing a home, when its main parameters are laid down. In this case, it is important to focus on the criteria on which the thermal conductivity of the walls depends.
Thermal insulation characteristics of aerated concrete
Aerated concrete blocks are included in the category of cellular concrete. They have low thermal conductivity compared to most other wall materials. This level is a guarantee that the room will be warm in winter and comfortable in summer.
Low thermal conductivity of aerated concrete blocks is due to their porous structure. During the production process of the material, gas bubbles are evenly distributed inside, thereby reducing its ability to transfer heat.
The porous structure, on the one hand, gives aerated blocks advantages, but on the other hand, it impairs their strength. The compressive strength of aerated concrete, depending on the brand, is 15–50 kg/cm2. Low density blocks, such as D200, have minimal thermal conductivity. However, such a gas block cannot be used for load-bearing walls due to the limited load-bearing load: as a rule, it is used as insulation.
When choosing the size of a suitable aerated concrete block for laying the walls of a house, attention is paid to both thermal conductivity and compressive strength.
When calculating the optimal thickness of the walls of an aerated concrete building, it is important to remember the effect of moisture on thermal conductivity. Wet blocks retain heat less well, so you need to protect them from precipitation with facade materials: brick, siding, plaster.
Wall strength
Aerated concrete belongs to the category of cellular concrete and its use in the construction industry is strictly regulated. The main recommendations to determine the required strength indicators of the walls being erected are as follows:
- it is imperative to calculate the permissible heights of the walls of the structure being erected;
- restrictions on the height of load-bearing walls erected from aerated concrete blocks are four to five floors;
- the strength indicators of blocks for the construction of five-story buildings are B-3.5, and for three-story buildings B-2.5;
- for the construction of buildings with self-supporting walls, it is recommended to use, depending on the number of storeys, blocks B-2.0 or B-2.5.
Reference Regulatory documents in the context of private housing construction are currently purely advisory in nature, and therefore may not be taken into account in low-rise construction, as well as in the construction of any outbuildings or garages.
Ecology
Among people unfamiliar with the production technology of aerated concrete (the second name is cellular concrete), there is an opinion that such material is harmful to human health. To understand this issue, you should study the components and method of manufacturing these blocks.
Components:
- quartz sand
, used to impart strength, absolutely harmless - 60%; - cement
, which is in a bound form within the block - 20%; - lime
baked at high temperature - 20%; - aluminum dust
- about 1%.
According to their structure, aerated concrete blocks for load-bearing walls consist of 50% air bubbles, which means that the substance content indicators must be divided in half. We get: cement - 10%, lime 10%.
In an ordinary wall, where every brick is covered with mortar on all sides, there is no less cement, but no one is afraid of it.
But that's not all:
- During the technological process, all components are mixed together in a wet form.
- Aluminum reacts with lime, hydrogen is released, which creates its own outlets from the mixture. These voids are filled with ordinary air, after which the composition is placed in an autoclave.
- Further processing takes place at a temperature of 190 o C and a pressure of 14 atmospheres.
- Under such conditions, quartz sand reacts with foamed cement and lime to form a homogeneous mass.
- After cooling, we obtain an artificial substance from which cement and lime can only be extracted if it is placed back under the same conditions.
Thus, the usual cement-sand mixture, from which dust flows in domestic conditions, is much more harmful. Aerated concrete for load-bearing walls, if not fed on it, is absolutely safe.
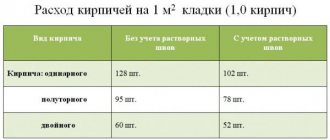
Characteristics of blocks 600x300x200
One of the most popular is a gas block measuring 600 mm in length and 200 mm in height. The width, due to which the wall thickness is formed, is 300 mm. The same blocks can also be used for laying internal walls with a thickness of 200 mm. In this case, the blocks are simply mounted on an edge, and the height of the row is not 200, but 300 millimeters. Blocks in this size can be purchased in several density options - both the strength class and thermal insulation with vapor permeability depend on it.
The exact characteristics of autoclave products are shown in the table:
| Block Density | Compressive strength class | Thermal conductivity coefficient (W/m*C) | Vapor permeability coefficient (mg/m*h*Pa) |
| D 300 | B 1.5-B2 | 0,088 | 0,26 |
| D 400 | B2-B2.5 | 0,117 | 0,23 |
| D 500 | B2.5-B3.5 | 0,147 | 0,2 |
| D 600 | B3.5-B5 | 0,183 | 0,16 |
What is the load-bearing capacity of an aerated concrete block 600x300x200
The porous structure of the block, coupled with its low mass, often raises doubts regarding the load-bearing capacity of the masonry for a developer who wants to build a house of 2-3 floors. Because of such mistrust, aerated concrete from the very beginning had difficulty making its way into the construction market, where stronger and more durable brick reigned for centuries.
- However, aerated concrete houses, which appeared in Europe in the second half of the last century, proved that the strength that the material is endowed with, albeit to a lesser extent, is perfectly balanced with thermal insulation characteristics. This made it possible for cellular concrete to launch on the world market.
- Over the past years, production technologies have improved, and some types of thermal insulation concrete (D300, D400) have acquired strength corresponding to the category of thermal insulation and structural concrete. So today, a two-story house, provided that a light beam floor is installed, can be built from blocks of lower density, resulting in warmer walls.
- Let's give an illustrative example: in the Russian standard 31359, according to which all autoclaved cellular concrete is produced in Russia, the minimum strength class for a stone density of 300 kg/m³ is set to B0.75. In fact, in mass production, the strength class of aerated concrete is twice as high – B1.5. And the best brands, produced mainly by subsidiaries of European companies operating in the country, even have a strength class of B2 and even B2.5!
- According to domestic standards, the strength of wall material for low-rise civil construction B1.5 is quite sufficient. Accordingly, blocks of individual brands even have a good supply of it, allowing them to embody a wide variety of architectural ideas.
- The strength class shows how much load in kilograms 1 cm² of concrete can withstand. B2.0 means: 20 kg/cm². The area of the bedded edge of a block with a width of 30 cm is 1800 cm² (width * length - 30 * 60 cm). We multiply by 20 kg, and we get 36,000 kg - this is the load-bearing capacity of the block.
Reinforcement of reinforced concrete monolithic belt
Reinforcement is placed in a monolithic belt.
| Reinforcement of a monolithic reinforced concrete belt |
To reinforce the belt, working reinforcement with a diameter of 10-12 mm is used. The reinforcement bars are connected (anchored) along their length, placing the ends on top of each other over a length of 40-50 bar diameters.
To fasten the roof Mauerlat, anchors are embedded into the concrete of the belt. It is also possible to secure the Mauerlat to the belt using spacer dowels.
Requirements for the walls of the extension
In construction, the thickness of walls (external and internal) is selected on the basis of thermal engineering calculations, taking into account the climatic specifics of the development region, soil category, wind load and other important parameters.
It is not always possible to cope with this task on your own, so you have to focus on the technical values of the strength class and energy efficiency of gas-block products:
- Depending on climatic conditions, aerated concrete with a thickness of 300-400 mm of grade D500 is used for laying the external walls of heated buildings.
- For internal walls, it is recommended to use blocks with a thickness of 200-300 mm of grade D400.
- Interior partitions are made from D300 brand blocks, which have the best soundproofing characteristics.
Blocks of these brands are characterized by excellent thermal insulation properties and allow the accumulation of internal heat. If we compare an extension built from classic brick and cellular concrete, in the latter option the savings in energy resources for heating is 40%.
External walls made of aerated concrete have height restrictions due to the low strength of the material. For this reason, the design of the walls of a one-story extension with a height of 2.5-3 meters provides for the installation of a reinforcing reinforcing belt laid along the entire upper perimeter of the external walls.
Device and features
If aerated concrete partitions are installed during the renovation and redevelopment of apartments or houses, markings must first be applied. The line is upholstered around the entire perimeter: on the floor, ceiling, walls. The easiest way to do this is with a laser plane builder. If it doesn't exist, it's better to start with a stream:
- Mark a line on the ceiling (two points on opposite walls). A painting cord, painted with blue or some other dry dye, is pulled between them. With its help they beat off the line.
- The lines on the ceiling are transferred with a plumb line to the floor.
- Then the lines on the floor and ceiling are connected by drawing vertical lines along the walls. If everything is done correctly, they should be strictly vertical.
The next step in constructing aerated concrete partitions is waterproofing the base. The floor is cleaned of debris and dust, waterproofing roll material is laid (any: film, roofing felt, waterproofing material, etc.) or coated with bitumen mastics.
Vibration dampening strips
To reduce the possibility of mother-in-law formation and increase sound insulation characteristics, a vibration-absorbing strip is laid on top. These are materials with many small air bubbles:
- hard mineral wool - mineral wool cardboard;
- polystyrene foam of high density, but small thickness;
- soft fiberboard.
The first row of blocks is laid on this strip with glue. Glue thickness is 2-5 mm, consumption for a thickness of 1 mm is 30 kg/m3. Next, the construction of partitions occurs using the same technology as load-bearing walls. Read more about the technology of laying aerated concrete walls here.
On short spans - up to 3 meters - no reinforcement is done at all. On longer ones, a reinforcing polymer mesh, a perforated metal strip, as in the photo, etc. are laid.
Aerated concrete partitions can be reinforced if desired
Connecting to a wall
To ensure connection with adjacent walls at the masonry stage, flexible connections are placed in the seams - these are thin metal perforated plates or T-shaped anchors. They are installed in every 3rd row.
Connecting the wall and partition using a T-shaped anchor
If a gas silicate partition is installed in a building where such connections are not provided, they can be fixed to the wall by bending them in the shape of the letter “L”, inserting one part into the seam.
When using anchors, the connection with the wall is rigid, which in this case is not very good: a rigid rod due to vibrations (wind, for example) can destroy the adjacent adhesive and the body of the block. As a result, the abutment strength will be zero. When using flexible connections, all these phenomena will not affect the blocks so much. As a result, the bond strength will be higher.
Flexible connections in the seams; if there are none, the plates are simply screwed onto self-tapping screws
To prevent the formation of cracks in the corners, between the wall and the partition, a damper joint is made. This can be thin polystyrene foam, mineral wool, a special damper tape that is used when laying heated floors, and other materials. To prevent moisture from leaking through these seams, after laying they are treated with a steam- impermeable sealant.
Openings in gas silicate partitions
Since the partitions are not load-bearing, the load will not be transferred to them. Therefore, there is no need to lay standard reinforced concrete beams over the doors or make a full-fledged lintel, as in load-bearing walls. For a standard doorway of 60-80 cm, you can lay two corners that will serve as a support for the overlying blocks. Another thing is that the corner should protrude 30-50 cm beyond the opening. If the opening is wider, a channel may be required.
In the photo, two metal corners (on the right) are used to strengthen the opening of a standard door; a channel is walled up in the opening on the left, for which grooves are selected in the blocks.
If the opening is not wide, and only two blocks are joined in it, it is advisable to select them so that the seam is almost in the middle of the opening. This will give you a more stable opening. Although, when laying on corners or channels, this is not the table: the load-bearing capacity is more than enough.
Doorways in aerated concrete partitions
To prevent the metal from bending while the glue dries, the openings are reinforced. In narrow openings, it is enough to nail boards; in wide openings, a supporting structure resting on the floor may be required (put a column of blocks under the middle of the opening).
Another option for how to strengthen a doorway in aerated concrete partitions is to make a reinforced tape from reinforcement and glue/mortar. A flat board is stuffed strictly horizontally into the opening, nailing it to the walls. Sidewalls are nailed/screwed to the sides to hold the solution.
The solution is placed on top of the board, and three bars of class A-III reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm are placed in it. Partition blocks are placed on top, as usual, making sure that the seams move. The formwork is removed after 3-4 days, when the cement “sets.”
Opening in a partition made of blocks
Last row - adjacent to the ceiling
Since floor slabs can bend under load, the height of the partition is calculated so that it does not reach the floor by 20 mm. If necessary, the blocks of the upper row are sawn. The resulting compensation gap can be sealed with damping material: the same mineral wool cardboard, for example. With this option, sounds from the upper floor will be heard less. An easier option is to moisten the seam with water and fill it with polyurethane foam.
What can't be done with aerated concrete?
Many people believe that aerated concrete is something like a construction set. In fact, this is not so, it has its own limitations in use, and you should always remember them. Let's present a list of cases in which this material will definitely not help you, as well as cases when it does not combine well with other materials.
- Laying pillars, especially load-bearing ones. With a small support area, its strength will not be enough. Use solid ceramic bricks. For pillars, it is one of the best materials along with reinforced concrete.
- Laying of bathrooms. You can make it from aerated concrete - just make sure that your partition does not get wet. Cement plaster is quite suitable for this.
- Aerated concrete is incompatible with acrylic paints on the outside. And if you decide to make a wet facade, choose a different paint, or even better, add pigment to the plaster.
- Construction of a house higher than two floors. In fact, aerated concrete can also be used in taller buildings - but only as an enclosing structure between two monolithic floors supported by columns. In this case, you can safely buy lighter brands.
- You cannot lay masonry from this material below the zero mark. Basement partitions are best made of brick.
- You should not leave the constructed box without a roof for the winter. If you do not have the funds to build a roof, cover the walls on top with waterproofing.
We hope you will take into account everything written above when you get ready to build your house from aerated concrete. And if you want it to last longer than 15 years, remember the proverb: measure twice, cut once.
We build from aerated blocks, observing the norms - we build for centuries
Topics have repeatedly appeared on our portal where authors asked for advice on what material to choose for walls.
We decided to build a house. What material is best to build from?
Hi all. We need your help, dear forum users. We want to build a one-story house with an attic in the spring of 2014, for permanent residence, land of 10 acres, the question is what material to build from? We are considering brick, foam block, gas block and other materials. There are geological surveys carried out in December 2013. I am attaching them to the topic. Please take a look and advise what house to build from what on what foundation, money 1,700,000. I would like a house of 100-120 sq. m. m of living space without any special frills, simple square, dimensions as it turns out. Foundation + frame of the house + gable roof and windows with doors, without decoration. Thanks in advance. Happy New Year 2014 everyone, happy construction to everyone.
I myself am not boom-boom in construction, so I apologize in advance if I write something wrong. My parents are planning to build a house and asked me to read what they write about wall blocks on the Internet. My father is conservative and tends to build with brick “the old fashioned way.” I am for everything new: foam blocks, gas blocks, etc. Everything is more or less clear about the merits of certain blocks. They are described in great detail on the manufacturers' websites. I would like to know what the disadvantages are. I googled this video. I would like to hear comments.
In all these branches, aerated concrete rightfully did not go unnoticed. We have already talked about this material more than once on our portal. You can read more about this cellular building material here: https://www.forumhouse.ru/articles/house/8979
Why have aerated blocks become so popular, and why do doubts arise at the stage of choosing a material? Let's first look at its pros and cons.
UDK
Rating: 4.8
The largest manufacturer of aerated concrete blocks in Ukraine is the UDK company. The company focuses on producing premium products. The manufacturer produces building blocks using autoclaved aerated concrete technology. Masa AG equipment is installed in the factory workshops, which has a positive effect on the geometry. The main raw material base is natural materials such as Portland cement, crushed quartz sand, and quicklime. A distinctive feature of the brand is a scholarship program for students that financially supports high-achieving students.
The manufacturer occupies third place in the rating for its precise geometry, affordability and care for the younger generation. The disadvantages include large waste and low strength.
Calculation prerequisites:
Load eccentricity.
When using slabs of different lengths, the load on the internal supporting wall from these slabs will be different, so the total concentrated load will be applied not at the center of gravity of the section, but with eccentricity eo. This means that in addition to the load itself, the wall will also be subject to a bending moment equal to M = Neо , and this moment must be taken into account when calculating. In general, strength testing is performed using the following formula:
N = φRF - MF/W (2.1)
where W is the moment of resistance of the cross section of the column.
General requirements for interior walls in a house
After the load-bearing walls, lintels and ceilings have been laid, the builders begin to think about laying the partitions planned for the project. First of all, they make markings on the floor, walls and ceiling, in accordance with the intended drawing, not forgetting the basic requirements for aerated concrete partitions:
- Structural strength. It is made in such a way as to withstand mechanical and external factors in the room, and fastening elements can be attached to it.
- Light weight. According to the project, the fence is planned without additional (extra) loads.
- Sufficient sound insulation. Interior partitions must meet the requirements of 43 dB. In apartment buildings this index is 52 DB.
- Thickness. Despite the fact that the septal cellular material comes in different thicknesses, the most optimal size is 100-175 mm. The presented indicator has sufficient strength and sound insulation.
- Environmental friendliness. The structure is made from environmentally friendly material, which is safe due to its mineral composition.
- Fire safety. The partition must prevent fire. The minimum fire resistance limit for aerated blocks is 0.25 hours.
- Availability of a quality certificate. Materials used in the work must have quality marks and markings provided by the manufacturer.
- Material density from D500 to D700. This requirement indicates the quality characteristics of the material, according to which the higher the D, the stronger the partition will be.
If the owner of the house wants to complete construction as quickly as possible, then experts advise using large-sized products for work, with dimensions in length and width of 750x625 mm.
For interior partitions, these blocks are the best option.
According to generally accepted standards, partition structures are directly dependent on height (h). So, for example, with h 2.5 m, a block with a thickness of 75 mm is used; at h 3 m – 100 mm; at h 3-5 m – 200 mm.
Reinforced concrete belt for supporting the roof truss system
Approximately half of private houses are built with an attic. To increase the volume of attic rooms, a house structure with attic walls is often used, which are a continuation of the load-bearing walls of the house on the attic floor. The height of attic walls is usually in the range of 0.7 - 1.2 m.
The roof truss system of a house with an attic rests on attic walls. To ensure the stability of the attic walls of the attic when exposed to roof loads, along the top of all load-bearing walls
perform a monolithic reinforced concrete belt. The Mauerlat of the roof truss system of a private house rests on a monolithic belt of the attic wall.
| Monolithic reinforced concrete belt of the attic wall of the attic. The Mauerlat and roof truss system are attached to the belt |
The design of a monolithic belt for supporting a roof is in many ways similar to a monolithic belt at the floor level.
The height of the monolithic belt is not less than 15 cm. The minimum cross-sectional area of the monolithic belt is not less than 250 cm2. A monolithic belt is often made across the entire width of the outer wall if the wall is insulated from the outside. If the wall is without insulation, then on the outside there is space left for laying a layer of insulation, which eliminates the cold bridge through the concrete belt.
For a hipped roof, the belt along the outer walls is made a continuous ring, as in the figure. If the roof is gable, then in the belt you can leave gaps in the gable walls for installing windows.