Load-bearing walls - these are walls that, in addition to their own weight, take the load from the overlying floors or coverings. In ordinary words, it is a wall on which something rests. Self-supporting walls - these are walls on which nothing rests and overloads appear only from their own weight.
Load-bearing walls are the outer walls of buildings on which floor beams or reinforced concrete slabs rest. But they are also often internal. It is difficult to say the thickness of the walls in our time, because due to the wealth of materials, the thickness of the load-bearing wall can vary from 150 to 510 mm, perhaps there are walls that are thinner or thicker. Self-supporting walls are usually much thinner than load-bearing ones and act as partitions inside an apartment or house. Their thickness varies from 50 to 380 mm. Unlike load-bearing walls, self-supporting walls can be made of another material, for example, plasterboard in a brick house.
Why is it important to know the difference between these walls? Because they play a very important role in the design of the building. Load-bearing walls in a Khrushchev-era building or load-bearing walls in panel houses are not just about the safety of you and your apartment, but also the floors above and below. Therefore, if you are planning a redevelopment, it is better to contact a specialist or, at a minimum, find out from the housing and communal services department which walls are load-bearing and whether it is possible to carry out the redevelopment.
The choice of wall building materials in the construction of civilian structures.
Load-bearing walls experience overloads from other parts of the structure and, together with their weight, act on the foundation. Self-supporting walls use a foundation as support, but load it only with their mass. Non-load-bearing walls are partitions (fences) that use the rest of the building as support and support only their mass.
The walls being erected must meet the following requirements:
- -have the required strength
- - have a long service life
- -be fireproof
- -be fairly soundproofed
The type of walls must be selected based on economic characteristics, also taking into account customer requirements. The wall thickness must correspond to static and thermal calculations.
Based on the materials used, the walls being erected are classified:
- stone
- woody
- combined
By construction method:
- masonry
- solid
- panel
Masonry is a system that is made from individual wall materials. The seams are filled with masonry mortars. To give the required strength, the layers of masonry are made with mismatch. Double-row and multi-row masonry systems are widely used. The thickness of the seams should not exceed 10-12 mm. For masonry, cement mixtures are widely used, which have sufficient plasticity and moisture retention. The main filler in such consistencies is quartz sand. Dry masonry mixtures are often used in modern construction. They are packaged in 25 kg bags and diluted with water specifically at the work site.
Recommendations for choosing material
When selecting building materials, the following rules should be observed:
- take into account your individual needs and budget;
- study individual characteristics of the product;
- calculate in advance the required amount of material.
Purchased building materials must be stored in proper conditions.
It makes no sense to purchase heavy-duty blocks for the construction of a simple partition. But for load-bearing walls, you need to choose a product based on its strength characteristics.
Important! Before installing heavy structures inside a built house, it is necessary to prepare the foundation. For apartments, it is necessary to choose lightweight materials that will not create excessive load.
The following types of wall stone are widely used in the construction of modern houses:
- sand-lime brick
- clay brick
- small wall blocks
Clay brick is a common wall material. It has the highest strength, is frost-resistant, retains heat, and has a good appearance.
Sand-lime brick, compared to other materials, differs in its recent appearance. But in terms of its properties, it is actually not inferior to clay brick. Development of production allows you to significantly reduce its cost. Also, sand-lime brick can have a huge number of different colors.
Small wall blocks can be used for the construction of load-bearing and self-supporting parts. They are widely used in the construction of houses with a height of no more than 3 floors. The use of blocks can significantly increase the speed of construction and reduce costs.
Silicate and gas silicate blocks are currently the most common in civilian construction. They provide unsurpassed regulation of humidity levels, have a long service life, meet all fire safety standards, and are not subject to smoldering.
Expanded clay concrete blocks. The main material in production is expanded clay. These blocks have the highest strength and light weight. Due to the porous structure, they provide sufficient sound insulation and thermal insulation. Compared to ordinary types of concrete, they have the lowest physical and mechanical characteristics, which limit the scope of their implementation.
How to determine a load-bearing wall and how thick it is
A load-bearing wall is a vertical surface that takes on the load exerted by elements located throughout the entire height and area of the building - internal partitions, floor slabs, flights of stairs and landings. This design transfers the weight of the building to the foundation, which distributes it along the ground. In construction, materials with different properties are used, based on which the thickness of load-bearing walls is calculated. These structures have special requirements regarding density, height and strength.
- What is a load-bearing wall
- Designations on the house plan
- Requirements for external walls
- Methods for determining load-bearing walls
- Load-bearing wall thickness according to GOST
Description of load-bearing and self-supporting walls and their comparison
The load-bearing wall is an important element in almost all buildings; their destruction leads to serious bad consequences. Therefore, during construction, it is important to find out in advance which system belongs to which type. Load-bearing and self-supporting walls work under overload, partly from weight, partly from other building components.
Energy efficient house
Construction of external walls
- 1. Load-bearing and self-supporting walls
- 2. Main types of wall structures
- 3. Application of external walls
- 4. Criteria for thermal insulation of walls
Load-bearing and self-supporting walls
Load-bearing and self-supporting walls perceive horizontal loads along with vertical ones, being vertical elements of rigidity of structures. In buildings with non-load-bearing external walls, the functions of vertical stiffening elements are performed by the frame, internal walls, diaphragms or stiffening trunks.
Load-bearing and non-load-bearing external walls can be used in buildings of any number of floors. The height of self-supporting walls is limited in order to prevent operationally unfavorable mutual displacements of self-supporting and internal load-bearing structures, accompanied by local damage to the finishing of the premises and the appearance of cracks.
A stiffening rod is a vertical hollow through rod spanning the entire height of the building, which is a load-bearing structure. The stiffening shaft is usually located in the central part of the building; Elevator, ventilation shafts and other communications are placed in the internal space of the shaft. In long buildings, several stiffening trunks are provided.
In panel houses, for example, it is permissible to use self-supporting walls with a building height of no more than 4 floors. The stability of self-supporting walls is ensured by flexible connections with internal structures.
The requirements for different types of walls differ significantly. In the first two cases, strength characteristics are very important, since the stability of the entire building largely depends on them. Therefore, the materials used for their construction are subject to special control. A structural system is an interconnected set of vertical (walls) and horizontal (floors) load-bearing structures of a building, which together provide its strength, rigidity and stability.
Main types of wall structures
Based on the material, there are four main types of wall structures: concrete, stone, non-concrete materials and wood.
According to the building system, each type of wall contains several types of structures:
- concrete walls - made of monolithic concrete, large blocks or panels;
- stone walls - hand-made, walls made of stone blocks and panels;
- walls made of non-concrete materials - half-timbered and panel, framed and frameless. About half-timbering and everything connected with it, see here: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fachwerkhaus, https://fachwerk-lehmbau.de/page.1.html;
- wooden walls - chopped from logs or beams, frame-sheathing, frame-panel, panel and panel.
What kind of walls are there in a building?
Properties do not affect the distribution of walls into groups. The placement of the element and its role in the arrangement of the building are fundamental. The indicated points are studied before the installation of floors begins.
Technical data sheets confirm the presence of the following varieties:
- Partitions. Structures vertically inside, for fencing. With support in the form of ceilings, to separate adjacent rooms. The most common definition.
- Curtain walls. Usually they are external, if the floor height does not reach 6 meters, they allow support on ceilings within the boundaries of the same structure. Protects the building from environmental influences.
- Self-supporting walls. With fencing function, also vertically. The weight is completely transferred to the side of the foundation. Serve for protection from the environment, only in the case of interior spaces. This is the main difference.
- Load-bearing wall. Towards a vertical plane, with the main functions of a load-bearing and enclosing character. The foundation will not only become a support for it, it will transfer the entire load to it with its weight and ceilings. Provides separation of adjacent buildings coupled with protection. Curtain walls are elements that differ from this group.
Load-bearing, self-supporting and load-bearing walls - what's the difference?
Self-supporting walls differ in their small width compared to their analogues. Thanks to this, the construction of the structure requires the least amount of material. The usual range is from 50 to 380 mm, depending on the initial material for construction. The panel house is no exception.
Non-load-bearing enclosing structures can also be erected when it comes to the construction of buildings of various types. Elements with a lower location do not transfer the load to the structures. Such products are also called pendant. Their construction is constantly taking place within the boundaries of the 1st floor. But structures become self-supporting if the floor height exceeds 6 meters. With all this, approaches to design and specific construction are changing.
Interesting read: Methods of attaching imitation timber to the wall
If the wall is self-supporting, it is a fence located outside. Provides additional protection, adjacent to the building from the main frame. The fastening goes from the side, along the entire perimeter of the floor. Self-supporting enclosing structures can consist of one layer, or several layers at once. When placed inside buildings, the main purpose becomes the function of partitions. For self-supporting walls, this is the same, only with some adjustments.
Self-supporting walls differ in their small width compared to their analogues.
Load-bearing walls 100 mm thick
There is a myth about the minimum thickness of load-bearing walls
- The minimum thickness of the load-bearing wall must be at least 380 mm (at least one and a half bricks);
- The thickness must be at least 250 mm (at least one brick);
- In any case, a load-bearing wall made of blocks cannot be thinner than 200 mm.
The myth is wrong (as a myth should be):
Load-bearing capacity is a function of design resistance (“strength”) and stability (shape, rigidity, method of loading). It depends on the flexibility of the wall, the conditions of support (central or offset), and the properties of the material. The thinner and higher the wall, the higher its flexibility and the lower its load-bearing capacity. However, the adequacy of the load-bearing capacity is checked by calculation (taking into account, among other things, random eccentricity). The load-bearing capacity must be sufficient. For something small, for example, a free-standing toilet or poultry house, according to calculations, a masonry thickness of 50-70 mm may be sufficient.
After calculating the load-bearing capacity according to our standards (SP 15.13330, clauses 9.16–9.20), the wall should be checked to see if the ratio of its height to thickness is acceptable.
For a flat wall made of B2.0 aerated concrete blocks β = H/h = 22 (with a free length l of up to 2.5 N).
If the distances between transverse stable structures connected to a flat wall are l≤ βН , the height of the walls is not limited and is determined by strength calculations.
Example: a flat load-bearing wall with a thickness of 150 mm can have a height of 0.15x22 = 3.3 m.
The next logical step: the everyday concept of “thin/thick” in relation to a wall is conditional. The plate is thin, but a box tube bent from it can be very stable.
Above is a simple graphic explanation of this idea. Practical conclusion: a flat wall 100 mm thick will be knocked over by a breeze or a horizontal bar suspended from a cantilever will break in half, but a tower with dimensions of 2x2 m can be raised by 30 meters, securing it as a mast from being blown away by the wind with guy wires.
The rationale for these thoughts and unexpected practical conclusions are presented in video format.
News
- YouTube congratulates you on the results of 2022.
- October 2022 Stream. Answers to paid questions.
- Frequently ribbed overlap VFD GG
- July 2022. Stream of the last Monday of the month (access via link)
- On the expected service life of load-bearing and enclosing structures made of autoclaved aerated concrete
Order a project / Buy a ready-made project
The main way we can be useful is house designs with a stone base.
I suggest:
— house designs optimized for construction and operating costs;
— optimization of finished projects for specific technologies and markets;
— consultations on construction in general and masonry in particular;
— construction of houses made of aerated concrete (and other stones) in the Moscow and Leningrad regions.
How to find whether a load-bearing wall is or not, design features
If you are interested in solving the issue, the selection of multifunctional walls will take place without any hassle. The easiest way to start is to study the structural plan of a particular building. The document is obtained by visiting representatives of the Department of Major Construction. Registration of technical passports for all buildings is mandatory. Finding suitable components is easy if you have the ability to read technical documentation on load-bearing, self-supporting and non-load-bearing walls.
The placement and width will tell you what the purpose of the structure is. Only old decorative materials from the surface of the walls should be removed in advance. The walls differ from each other in features. They try to pass on the plan to the masters.
- The use of bricks implies that the 28-centimeter thickness makes the wall load-bearing. The number of laying bricks and thickness increase immediately.
- With panels as a base, the load-bearing wall does not matter which wall is 14 cm or thicker. This causes difficulties with redevelopment.
- Thicker than 20 cm is a load-bearing wall located inside the monolith.
Studying the developer's construction plans is considered the most common solution. The frameless fastening method is also fixed there.
Registration of technical passports for all buildings is mandatory.
What actions can be performed with load-bearing walls
The construction industry places strict demands on load-bearing walls. It is important for owners to keep this in mind in order to avoid problems with regulatory authorities. A preliminary study of the documentation helps.
The prohibitions are as follows:
- Grooving for wiring or laying pipes;
- Transfer to other places;
- Demolition. The action leads to a decrease in the durability of the structure, even if the base is aerated concrete.
But there are also things that are completely permissible to do.
- Expanding and creating doorways.
- Use a drill for holes where the diameter is small. The use of self-supporting type of walls is also allowed for such work.
But even working with openings will require constant interaction with the administration. Damage to the wiring is very possible, so the question of its presence will be clarified in advance.
Even work with openings will require constant interaction with the administration.
How to recognize a load-bearing wall?
Knowing where the load-bearing walls are located in the apartment, you can understand whether redevelopment with the combination of rooms is feasible. The destruction of load-bearing walls or sections of them disrupts the power structure of the building, which in the future can lead to a weakening of the load-bearing capacity of structures.
In addition, if an inspection by the Moscow Housing Inspectorate reveals such illegal redevelopment, the owner of the apartment will have to pay a fine and, at his own expense, return the apartment to its previous condition.
Even the construction of new doorways in load-bearing walls can only be carried out on the basis of design documentation with a technical conclusion from the author of the house.
Therefore, before you begin remodeling an apartment, you should determine which walls in it are load-bearing.
This is especially relevant in light of the fact that the majority of standard housing in Moscow is represented by panel houses. A characteristic feature of this type of residential building is its structural design with a large number of transverse load-bearing walls.
Typical floor plan of a standard panel house (P-3 series). There are practically no curtain walls:
In block houses, a similar scheme is used, but load-bearing walls are spaced less frequently (floor of a panel-block house, series II-68):
An exception to this rule are panel and block Khrushchev buildings, as well as monolithic and brick houses, in which a significant part of all transverse walls are non-load-bearing partitions.
The Khrushchev-era scheme consists of three longitudinal load-bearing walls (two external and one internal), the stability of which is ensured by transverse rigidity diaphragms. In this case, the interfloor slabs can rest either on longitudinal main walls or on beams that lie on these walls. Most of the interior walls in such houses are partitions, which favors redevelopment.
How to find out if a wall is load-bearing or not?
Determining load-bearing walls in an apartment is not a difficult task today. If your house belongs to any common series, then on the Internet you can find plans for typical floors and sections, which usually have load-bearing walls. But the easiest way to find out which wall is load-bearing and which is just a partition is to measure its thickness.
The thickness of partitions in any modern standard houses is always insignificant and amounts to 8-10 cm.
It is quite easy to determine the load-bearing wall in a block house - they are 50 cm wide. It is difficult to confuse them.
The standard width of load-bearing walls in a panel house is 14, 16, 18 and 20 cm.
In brick houses everything is somewhat different. The partitions here are thicker from 8 - 10 cm (made of lightweight materials) to 12 - 25 cm (made of brick). Load-bearing walls in brick houses are 38, 50 and even 64 cm wide.
It is not always possible to determine load-bearing walls in a monolithic house: they may not exist at all (in monolithic frame buildings). Note that in monolithic buildings, as well as in brick ones, along with walls, there are various load-bearing structures, for example, round or rectangular columns (pylons). To find out where the load-bearing walls are, it is best to find the architectural plan of the developer of your home (if, of course, it is a new building).
It is interesting that sometimes in some houses there are 12-cm load-bearing walls. In addition, there are partitions whose thickness has increased due to layers of plaster, sound insulation, etc., and they can be confused with load-bearing ones. Therefore, the width of the wall is always measured without taking into account the finishing layers.
In such cases, when it is difficult to determine the load-bearing wall, an employee of the design organization conducts an engineering survey. A similar situation can arise in an apartment in a standard building, but most often this happens with old houses, as well as new ones built according to an individual project. Employees of the Moscow Housing Inspectorate may require to inspect and prepare a technical report for safety reasons - even for a wall about which the owner is confident that it is 100% non-load-bearing.
You can’t just go and measure a load-bearing wall with a tape measure. Measurements are taken only after the wall in the required place has been cleaned of the finishing.
Employees of APB No. 1 measure the pylon in their office
Self-supporting walls, the difference between the design and other types of walls
The overload of self-supporting walls that they accept differs from other types of structures. Nothing is allowed to be retained if it is an ordinary partition between rooms. The load is provided only by its own weight, which is where the name self-supporting comes from. Partitions become load-bearing if they work not only with their own weight, but also with part of the overload of other structures:
- Wall surfaces of the floors above;
- Beams on the ceilings;
- Overlapping on slabs between floors. The foundation doesn't matter.
It is prohibited to cut openings in load-bearing walls. The same goes for complete demolition operations. This increases the possibility that the house will completely collapse in the future. Only the function of separation and decoration is performed by self-supporting walls. As necessary, it is allowed to transfer them from place to place and enter configurations into the main system. The stability of the house will not suffer from such actions; the frame option will strengthen them.
Only the function of separation and decoration is performed by self-supporting walls.
Other operational features
An approximate project is drawn up for all houses and premises before construction, with self-supporting walls identified as the main operation. A separate check is organized for structures without a load-bearing function and parts with overload to check their strength. In the case of brick structures, data from several tables mentioned in SNiP are taken into account. Compliance is determined separately by the ratio of thickness and height according to these standards, with certain geometric parameters. The external structure also corresponds to it.
Fencing structures of this type allow the use of almost all materials. Example:
- Brick.
- Tree.
- Blocks.
But supports for structures require strength. The foundation part, together with the base, is poured at the same time, as the drawing says.
Flexible connections are used to connect self-supporting structures with adjacent objects. Rigid analogues lead to the fact that the overload will not be distributed moderately. Because of this, cracks and other types of deformations appear. Even the brick type of structures suffers.
An approximate design is drawn up for all houses and premises before construction.
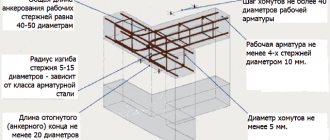
When laying self-supporting walls according to the standards, you cannot do without reinforcement. But, compared to loaded elements, the strengthening here will not be so serious in practice. Alloy rods are inserted through masonry rows, the break in quantity is large. The permissible diameter of the reinforcement is 1-2 mm.
If the buildings are not very tall, then the following materials are allowed:
- Large format blocks made of expanded clay concrete;
- Based on foam and aerated concrete;
- Made of ceramics;
- On wood concrete. Modern material.
Silicate and clay bricks are also intensively used.
When laying self-supporting walls according to the standards, you cannot do without reinforcement.
Evenness is typical for foundations made of brick and stone. In this case, the overload is moderately distributed from top to bottom. The lower the level, the greater the overload becomes. Additional stresses arise in the structure if some unnecessary element is used. The result is the occurrence of lateral shifts, a change in the density index. Damages also have systematization.
To get rid of excess stress, use the following solutions:
- Thickening of corners of buildings or structures.
- Removing unnecessary loads from window and door openings.
- Arched system.
Modern buildings prefer to be equipped with reinforcement, which also distributes the load in the best possible way.
Interesting read: How to fix a socket box in a concrete wall
Evenness is typical for foundations made of brick and stone.
Self-supporting walls are an economical option for arranging a space. But you need to keep in mind that they differ significantly from other fences in technical features. But they allow different design solutions for premises, regardless of purpose and location.
We demolish walls during redevelopment: what can be demolished and what cannot?
Many people, especially those living in Khrushchev-era apartment buildings, try to remodel their small and uncomfortable apartments using redevelopment. But it’s one thing to do it in an individual building, and quite another to change a doorway or move a partition in a high-rise building, where almost every wall is load-bearing. All this ensures the safety of residents in combination with the entire technical design of the house.
What is redevelopment? According to the Housing Code, this concept includes all changes in the configuration of the apartment that require inclusion in the technical passport. This:
- changing the location of load-bearing walls and partitions,
- relocation of window and door openings,
- re-equipment of vestibules and dark storage rooms,
- arrangement of internal stairs,
- refurbishment of bathrooms,
- division of large rooms,
- expansion of living space due to household premises,
- glazing of a balcony or loggia,
- replacing gas stoves with electric ones,
- moving a bathroom, kitchen or toilet.
All these types of changes in the apartment relate to redevelopment and require approval from the relevant authorities.
What cannot be demolished: a load-bearing wall
Most often, redevelopment involves the demolition of interior partitions. But not everyone knows which walls can be touched and which ones cannot. Reckless demolition of structures leads to a change in the action of forces on the remaining surfaces and rooms located below. In addition, ceilings left without support may not withstand the load and collapse at any time. Since, in addition to separating different rooms, the wall elements serve as ceiling supports for all similar structural elements located above.
The main (load-bearing) walls in practice are located perpendicular to the floor beams. If it is made of concrete slabs, then their ends rest on the surface of the supporting structure. Usually these are walls between apartments and blocks, or external ones. As a rule, only partitions are equipped inside the apartment.
How to find out which wall is load-bearing?
Is it possible to determine the purpose of the wall yourself? Certainly. By its thickness or the material from which it is built. In panel-type houses, internal blocks have a thickness of up to 120 mm. Therefore, they can be considered partitions (their thickness ranges from 80-120 mm). The load-bearing surface must have a thickness of at least 140 mm. Most often, in such houses, the external walls are made with a thickness of 200 mm. In brick houses, external, load-bearing structures have a thickness of 380 mm or more, inter-apartment structures - 250 mm, and partitions - 120 or 80 mm.
The material most often used for load-bearing walls in panel houses is wall or inter-apartment blocks made of reinforced concrete with various additives to lighten the structure and increase thermal protection. Internal partitions in 90% of panel houses are made of gypsum concrete panels. In brick buildings, the main material for all walls is red and sand-lime brick, which differ in size. Gypsum concrete panels can also be used as partitions.
Of course, no one is going to demolish the outer walls, but the partitions can be removed by obtaining the appropriate permission. To accurately determine which wall is load-bearing, it is best to use BTI data - a detailed floor plan. There, all main walls are marked with thicker lines, and partitions that do not have such functions are marked with thinner lines.
What is needed for demolition?
In any case, before starting work on demolishing a particular wall and moving it, you need to consult a qualified specialist. As well as a full calculation that takes into account the distribution of loads that must be transferred from old structures to newly erected ones. In addition, you may have to change the power supply circuit. In addition, it must be borne in mind that uncoordinated demolition of the walls of the premises may prevent its sale or the preparation of donation documents, etc. But that’s not all. Such actions are considered illegal and entail fines, summonses to court, and can even lead to confiscation of the apartment.
Therefore, approval of the redevelopment project is necessary in any case. What is needed for that?
- A plan developed by the BTI service specifically for this type of redevelopment.
- Drawing up a technical report for the demolition of the wall.
- Obtaining a positive conclusion from the housing inspection at the place of registration.
Wall types
There are several types of walls that are found in any high-rise or private building.
- A load-bearing wall is the main load-bearing and enclosing vertical system of a building, which rests on and transfers the load from the floors and the wall’s own weight to the foundation, separating adjacent rooms in the building and protecting them from the action of the external environment.
- A self-supporting wall is an external vertical enclosing system that protects the interior of a building from the action of the external environment, rests on and transfers the load from its own weight to the foundation.
- Curtain wall - an external wall resting on the ceiling within the boundaries of the 1st floor with a floor height of no more than 6 m. (at a higher floor height, these walls are considered self-supporting) and protect the building from the outside from the action of the external environment.
- A partition is an internal vertical enclosing non-load-bearing wall resting on the ceiling and separating adjacent rooms in a building.
Tips for improving sound insulation
To improve performance, it is recommended to choose building materials with the highest sound insulation rates. Also, soundproofing products can be mounted on an already erected structure.
To eliminate all external noise, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive sound insulation of all structures
When using aerated concrete blocks, which will later be finished with insulation and plaster, it is possible to obtain good sound insulation.
What are they?
The main distinctive feature of self-supporting walls, in comparison with loaded ones, is that they have a small thickness. Accordingly, less material is used during their construction. The thickness of the walls of this variety for us, depending on what they were built from, can vary between 50-380 mm.
During the construction of the rear, in addition to everything else, non-load-bearing enclosing structures can also be assembled. Such walls also do not take the load from parts of the house located above. In another way, structures of this type are called hinged. They are constantly erected within the boundaries of the 1st floor. But if their height exceeds 6 m, they can already be considered self-supporting. Their design and calculation are carried out in a suitable manner.
Self-supporting walls are basically just external enclosing structures. Such elements of the structure simply protect its interior from wind and precipitation, adjacent to the main skeleton. The ceilings are attached to such walls laterally on all floors in height. When building houses, both single-layer and multi-layer self-supporting enclosing structures can be erected. If walls of this type are located inside the building, they only serve as partitions.
How to determine whether a wall is load-bearing?
Question from Alevtina: Please tell me how to determine whether the wall in which we want to make an opening is load-bearing?
Answer: Alevtina, if we are talking about a load-bearing wall in a brick house, then punching an opening is possible. Please note that this opening requires structural reinforcement along the perimeter with a metal frame and an additional structural section will appear in the apartment redevelopment project, reflecting the components and details of this reinforcing frame. The cost of such a project will be higher.
If we are talking about punching an opening in the load-bearing wall of a panel house, then this is prohibited, and we do not formalize such projects.
In order to independently determine which walls are load-bearing, you can use the following recommendations:
- On the floor plan in the technical passport of the BTI, as a rule, the load-bearing walls in the apartment are depicted as large in thickness, and not the load-bearing walls (partitions) as smaller in thickness.
- We can assume that walls less than 12-15 cm thick in panel houses and less than 25-30 cm thick in brick houses are not load-bearing.
- You can see how the floor slabs lie. The walls on which they rest are load-bearing.
- In brick houses, most often the load-bearing elements are:
— external (facade) walls; - a wall dividing the house in the middle and running parallel to the outer walls; - inter-apartment walls;
— the wall between the apartment and the staircase.
- As a rule, all walls inside an apartment are not load-bearing, but there are exceptions.
- In panel houses, the load-bearing walls are all the same as in a brick house, as well as most of the internal walls perpendicular to the outer (facade) wall of the house.
Load-bearing walls in brick houses The thickness of the walls in brick houses is a multiple of the brick size (120mm): 120mm+10mm (thickness of the vertical mortar joint) +120mm and so on.. Thus, brick walls can have the following thicknesses: 120, 250, 380, 510, 640mm, etc. + finishing layers. Load-bearing walls in brick houses have a thickness of 380mm. In 90% of brick residential buildings, internal interior partitions are made of brick or gypsum concrete panels with a thickness of 120 and 80 mm. Load-bearing internal and external walls in brick houses have a thickness of 380, 510 and 640 mm. Thus, if the thickness of the wall in the apartment is less than 380 mm, then it is not load-bearing.
Load-bearing walls in panel houses In panel buildings, the thickness of the load-bearing walls varies from 140 to 200 mm, the thickness of the partitions - from 80 to 100 mm. In 90% of panel houses, the internal load-bearing walls are reinforced concrete panels with a thickness of 140, 180 or 200 mm, and the partitions are gypsum concrete panels with a thickness of 80 mm. In some old series of panel houses there are load-bearing walls with a thickness of 120 mm. Thus, if the thickness of a wall in a panel house is less than 120mm, then this means that it is a partition, and if it is more than 120mm, then it is a load-bearing wall. It should be noted that the finishing layers of walls (plaster, wallpaper) can make adjustments to its thickness, however, in panel houses they usually do not exceed 50mm and do not have a significant effect. If possible, it is better to remove the plaster layer for the purity of measurements.
Load-bearing walls in monolithic houses Monolithic houses are the most diverse in their architectural and constructive design. Residential monolithic buildings usually combine monolithic load-bearing walls, columns, pylons (columns of rectangular section), and beams. Often pylons are “recessed” into external walls and internal partitions. The thickness of monolithic load-bearing internal walls and pylons is usually 200, 250 and 300mm. The dimensions of the columns are even larger. Thus, if you measured the thickness of the wall and it turned out to be less than 200mm, then this is a partition. But, if the thickness of the wall is, for example, 200mm, then this does not mean that it is load-bearing, because in monolithic houses the partitions can be more than 200mm (for example, made of foam blocks). If you have a monolithic new building, then the easiest way to find out comprehensive information about the load-bearing walls of your apartment is to ask the management company or sales department for a plan of your floor from the architectural section of the building project (“worksheet”). Usually this is not difficult, and on the plan itself the internal load-bearing walls, partitions, and dimensions are clearly visible.
Calculation
Before starting the construction of any house, of course, its detailed design is drawn up. With all this, an operation such as the calculation of self-supporting, non-load-bearing and loaded walls for durability is also performed. For brick structures, for example, such calculations are performed taking into account data from several tables from paragraphs 6.16-6.20 of SNiP II-22-81. In any case, when calculating the resistance of a self-supporting wall, the correspondence of its thickness to height for a given geometry with standard values is determined.
How to coordinate redevelopment?
At the beginning of the article, we mentioned that any actions related to changing the layout of the apartment must first be approved by the relevant authorities. As a rule, such issues are dealt with by the Bureau of Technical Inventory (BTI). Consent is mandatory for two reasons.
Firstly, residents cannot always correctly determine the type of wall, so they begin to perform some prohibited actions with the load-bearing wall, mistaking it for an internal partition. Which, as has been mentioned more than once, can become a real threat to people’s lives.
Secondly, without official permission, any redevelopment is considered illegal. This will lead to fines and to the fact that such an apartment will subsequently be impossible to sell.
To conclude the topic, we invite you to watch the video for greater clarity. Remember that only you are responsible for the actions performed in your apartment. Therefore, treat redevelopment issues extremely carefully. Good luck to you and great achievements in your renovation!
Source
Individuality of construction
It is possible to build such enclosing structures from virtually all materials. Self-supporting walls are building elements that can be built from wood, brick, or blocks. In any case, such structures are assembled only on strong supports. Their foundations are poured immediately with the foundation of the building itself.
Self-supporting brick, block, etc. walls are combined with other types of enclosing structures only with the introduction of flexible connections. When using solid materials, due to the unequal degree of loading, the structural elements may subsequently crack and become deformed. Accordingly, living in the house will become dangerous.
Self-supporting walls are structures that, when laid with bricks or blocks, are required to be reinforced according to standards. But such enclosing parts of buildings are usually secured not as painstakingly as loaded ones. When constructing walls of this type, rods are inserted through a larger number of rows of masonry. According to the standards, reinforcement for such structures is allowed to be used with a diameter of 1-2 mm.
Lightweight brick walls
Characteristic
Lightweight brick walls , in which the brick is partially freed from heat-insulating functions unusual for it, by replacing part of the masonry with less heat-conducting materials, can significantly reduce brick consumption, thereby increasing material savings.
Classification
Lightweight brick walls are divided into 2 groups. The first group includes structures consisting of two thin longitudinal brick walls, between which thermal insulation material is laid, the second group includes structures consisting of one brick wall insulated with thermal insulation slabs.
Materials for high-rise buildings
When constructing high-rise buildings, self-supporting external walls can be constructed from:
- hollow, porous, solid clay bricks;
- sand-lime brick.
When constructing buildings of not very high number of storeys, blocks are also used from time to time:
- arbolite;
- claying;
- from foam or aerated concrete;
- expanded clay concrete and any other large-format.
The uniqueness of such materials in comparison, for example, with the same brick, is a relatively low degree of strength. Therefore, the use of their standards is allowed depending on the type when constructing houses with a height of no more than 3-5 floors.
Other building materials for wall construction
Blocks from different materials can be used to construct partitions. The budget solution is particle boards and plasterboard. In order to finally make a choice, it is necessary to take into account what role the structure will play and the loads it perceives.
Expanded clay concrete
A block building product consisting of expanded clay and cement. Among its advantages are:
- high strength;
- availability;
- durability (like brick).
Expanded clay concrete is not susceptible to mold, so the construction of structures can be carried out inside wet rooms.
Arbolit
Arbolite blocks are often used in the construction of low-rise residential buildings. In terms of price, building materials are a little more expensive. Among its main advantages are:
- environmental friendliness;
- durability;
- good thermal insulation indicator.
Before building a structure from wood concrete, you need to carefully familiarize yourself with its features.
cinder block
Cinder block is a material obtained by mixing blast furnace slag, cement, sand and broken bricks. Hollow samples can also be purchased on the market. Standard blocks are a suitable product for any building envelope.
Cinder blocks have minimal shrinkage after laying
During construction, it is necessary to ensure good waterproofing, as the product can absorb moisture, losing its performance characteristics.
See the walls and what this community looks like
Just as you are approaching the hour of choosing a private apartment, so when choosing an apartment in Novobudovo, it is important to understand what these other numbers mean – including the language about the appearance of the design and their composition. When designing a water vein, considering the necessary parameters, you will be convinced of the correctness of your actions. By choosing an apartment in Novobudovo, considering the culprit walls, you can independently evaluate the quality of the resulting inaudibility.
Definition
Having learned what a load-bearing wall is, you can understand how important it is to build this structure in strict accordance with all existing norms and rules. Such walls are a natural continuation of the building itself, the beginning of which is the foundation. To avoid great difficulties and troubles in the process of redevelopment, you need to know how to determine the load-bearing wall in an apartment. In most cases, it is enough to carefully study the technical documentation and determine the location of load-bearing walls on the building plan. However, it happens that there is no plan and you have to independently determine the quality and purpose of the erected structures.
To determine load-bearing walls in monolithic houses, it is enough to use a building plan, where all the structures of interest are highlighted in color.
The peculiarity of the construction of panel buildings is that reinforced concrete panels are used as a supporting structure in a monolithic house. Their thickness ranges from 100 to 200 mm. Structures made of gypsum concrete panels act as interior partitions, and their thickness does not exceed 80-100 mm. Thus, by measuring the thickness of the wall, you can recognize the load-bearing wall, the demolition of which in such a building is strictly prohibited. Failure to comply with the established rules will lead to inevitable deflection and collapse of the ceiling.
One of the most important indicators is the thickness of load-bearing walls in brick houses. To distinguish a load-bearing wall, you need to know its thickness, but it is better to have a construction plan on which all load-bearing structures are marked. Self-supporting walls in an apartment, as a rule, are much thinner than permanent structures. The thickness of the walls that bear the load from their own weight varies from 5 cm to 400 mm. Such a partition can be built from plasterboard, but more often it is a wall built from brick (half-brick masonry).
Related article: How to glue decorative stone to a wall
An experienced craftsman will tell you how to find out whether a brick house is a load-bearing wall or not, but the size of the structure will also help you understand this. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that the thickness of a brick wall is a multiple of this brick parameter, plus the thickness of the adhesive layer and finishing material. Thus, it is possible to find out which wall is in front of the builders. The thickness of the partition does not exceed 380 mm, and for a load-bearing wall this size is the minimum. The maximum thickness of a load-bearing wall in a brick house reaches 640 mm. The peculiarity of this structure is that an opening can be made in such walls. This is justified by the possibility of providing additional reinforcement to maintain uniform distribution of horizontal loads.
Their parameters will help you distinguish which walls can be demolished and which are strictly prohibited:
- from 80 to 380 mm - an interior partition that can be demolished if necessary;
- from 380 to 510 mm – internal load-bearing wall, subject to demolition subject to high-quality strengthening;
- from 510 to 640 mm – external load-bearing wall.
Brick houses or Khrushchev buildings were built according to a structural plan, the distinctive feature of which is the presence of 3 longitudinal load-bearing walls (green on the plan) and transverse walls called rigidity diaphragms (highlighted in blue).
Owners of apartments whose windows faced the front side of the house had the opportunity to build an extension or even make an additional window. You can get more detailed answers to all existing questions by watching the video.
Types of wall construction
Regardless of the surface area, there are three types of walls:
- nesuchi. Walls that absorb the strength of the supports of the ceilings of the upper surfaces of the building and convey their foundations. Their displacement is impossible, the stench of the greatest commodities;
- self-supporting. Such walls spiral onto the foundation of the building, but only carry the appearance of a thin layer of wool;
- not bearable. There are spaces in the middle of the walls that spiral onto other elements of the building frame. They only carry their own clothes and carry out their smallest labor.
Interesting read: How to install a triple socket in a wall
Let's take a look at the report of skin types.
Bearing walls - what is it
The load-bearing walls are the main vertical structure, which collapses and transfers moisture from moisture and water to the foundation to the foundation.
When installing a building, it is necessary to take care of a number of factors, in addition to the type of construction and the important type of care that load-bearing walls are subject to. Thus, non-bearing walls are divided into internal and external, and are subject to the following considerations:
- vertical;
- horizontal.
Vertical considerations for compressed structures under the walls and ceilings, as well as operational considerations. And horizontal extensions take into account the spread that is transmitted through the blood structure and the action of the wind. As the thickness of the wall increases, the range of permissible loads on the structure increases.
Changing the thickness of load-bearing walls or choosing the material of the thick frame is not the best idea when making a new home or new home. Acts of unscrupulous forgetters can profit from such a technique to make life cheaper. However, the moisture of the load-bearing walls is not only affected by the microclimate in the living areas, but also by the durability of the house. From this perspective, the economy is not worth it.
Self-supporting walls - what is it
Self-supporting walls – those that resist moisture from the walls, dry surfaces and wind.
Such walls are of thickness from 50 to 300 mm in depth depending on the material and thickness up to height. Self-supporting are economical structures; the material required for their construction is not so abundant. In contrast to the front type, self-supporting walls can be dismantled, retracted and expanded into their openings without any risk for restoration.
Non-bearing walls - what is it
A non-weight-bearing wall is one that does not receive attention and does not affect the durability of the building.
Such walls are spiraled on top of each other at the top, as they are no more than 6 meters wide. If it does not fit into the specified height, the wall is considered self-supporting.
As we can see, load-bearing walls are one of the most important parts of the future, and in more detail: what materials are tested when they are produced and what standards apply in Ukraine.
What is the difference
Walls are the main structural part of a building, but not all of them are able to withstand the load coming from the floors and roof. For this purpose, each building is equipped with load-bearing walls. Partitions that can only withstand the load of their own weight help to divide the space in a built house. Such walls are called self-supporting. The purpose of each non-load-bearing wall is to serve as a space delimiter, if necessary, to simply highlight a separate room.
Simply put, load-bearing walls are structures on which something rests. In every building, load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls play an important role, but if the load-bearing wall is a reliable support, a high-quality frame of the building, then the non-load-bearing wall is a partition, which, if desired, can be demolished during redevelopment without causing damage to the building. All walls are divided into load-bearing, self-supporting and non-load-bearing. Already by the name it becomes clear which of them are built in order to take on the main load.
Such a partition can be erected from:
I install monolithic slabs as self-supporting walls in panel houses. Such curtain walls can be used to create additional passage by cutting openings into them and installing doors.
Correctly recognizing which walls are load-bearing means that you can successfully carry out redevelopment without violating building codes and regulations, without risking creating a situation the end result of which will be the destruction of the building. To demolish a load-bearing wall means to change the distribution of the load, and this will lead to skewing of the building, collapse of the ceiling and cracking of the remaining permanent structures.
Load-bearing walls in a panel house ensure the safety of not only the apartment in which renovation is underway or redevelopment is planned. The safety of dwellings located on the lower floors depends on their quality and integrity. The main difference between load-bearing structures and self-supporting ones is the thickness of the walls. Knowing the differences is not enough; you need to be able to correctly determine which wall is load-bearing.
It is necessary to know exactly which walls can be demolished during redevelopment and which should remain untouched, at what thickness it is permissible to make an opening in the wall, and when it is too dangerous to carry out such work.
There are certain requirements that I impose on load-bearing walls:
- Strength and stability.
- Compliance with all fire safety standards.
- High level of heat, hydro, sound insulation.
The minimum wall thickness depends on the material used for their construction.
Another feature of the load-bearing wall, due to which such structures differ, is the uniform distribution of the horizontal load exerted by the floor slabs. An important criterion for strength, reliability and stability is the thickness of the load-bearing wall. This value is set for brick, monolithic and panel interior walls.
Strict adherence to established standards makes it easier to determine the load-bearing wall in any building or room.
Materials for the construction of load-bearing walls
Today, there are many types of building materials available on the residential market that are used for the construction of single-surface units, townhouses, cottages and large-scale new buildings. When erecting load-bearing walls in high-rise residential complexes, it is most popular to use concrete structures due to their value and sufficient thermal insulation properties. Dodatkovo, as well as in low-level everyday life, the following materials may be used:
- ; ; ; ; and others.
The internal non-bearing walls are additionally covered with only finishing materials. And the external axle is additionally reinforced and insulated with other materials. For example, with expanded clay concrete on the residential side, and on the side of the street - insulation and facing tiles.
When unfurling a dry wall, the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the dermatological materials is ensured. This parameter affects the operational properties of the wall, as well as the size of the payment receipt during the fire period.
Standard data for load-bearing walls
The national regulatory standards of Ukraine 2.6-31-2016 state that the construction of a block for load-bearing walls is required to ensure that the heat transfer coefficient is supported by the enclosing structures (R). The coefficient for external walls should be 3.3 sq. m*K/W (for 1st zone) і 2.8 sq. m*K/W (for 2nd zone). For growth, use the following formula:
- R – heat transfer support coefficient;
- d – quantity of material (m);
- k – thermal conductivity coefficient W/(m*K).
Another temperature zone of Ukraine lies in Odeska, Mykolayivska, Khersonska, Zaporizka regions and the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. All other regions are brought to the first temperature zone.
Totality of load-bearing walls
The thickness of the walls is due to fading without improvement, so it is necessary to carry out fading before applying plaster or anything else. Let's take a look at the fault of the wall of the non-knocked wall made of different materials.
Nesucha wall with targets
Half the thickness of the red target is 12 cm. This is the standard that the alarmists are guided by, and this is due to the multiple thickness of the wall. The outer non-bearing walls are made into a repeat of the target and more, so that the thickness is 38 cm (12 + 24 width of the target + 2 cm of the seam between them). With proper insulation, the thickness can be reduced to 25 cm (in one line + the seam between them is 1 cm), but not less. And the axis for inter-apartment walls is 25 cm - a great deal.
Nesucha wall with aerated block
In the 1st temperature zone of Ukraine, due to the expansion of the DBN, the thickness of the masonry without external insulation is up to 45 cm.
Nesucha wall made of timber
Exact cutting is carried out according to the norms of the temperature zones of the regions, but wooden beams wider than 22 cm are rare. So it is possible that the thickness of the wall should become 40 cm, but it will be difficult to fit. It will be necessary to install additional insulation in the middle or at the back.
Nesucha wall with panels
In booths with panels, load-bearing walls are thicker than 14 cm, which is often insufficient due to the conditions of the Ukrainian climatic zones. Moreover, apartments in panel buildings often require insulation. The partitions between rooms can be 10 cm apart, so when you buy an apartment in such a new building, you may want to consider soundproofing later.
As we all know, the performance properties and microclimate are affected by the durability of load-bearing walls. Having properly defined this parameter, a private or private booth will please the locals for many years. This problem is vital for potential owners of apartments in Novobudovo. It is better to clarify the importance of load-bearing walls in both cases in advance - for the sake of comfort and safety.
Chopped log walls
Characteristic
Log walls are a structure made of logs stacked on top of each other in horizontal rows and connected at the corners by notches. The thickness of the logs in the upper cut for the external walls of heated buildings located in the central zone of Russia is 22 cm, in the northern and north-eastern regions 24–26 cm. The diameter of the logs is chosen to be the same, with a difference between the upper and lower cuts of no more than 3 cm.
Technology
Each row of logs in a wall is called a crown . The crowns, laid sequentially one on top of the other from the bottom to the top of the wall, form a frame. The first lower crown is called the frame; it is made 2–3 cm thicker than the other crowns.
The crowns are laid with butts alternately in different directions and connected along the length by means of a vertical ridge (Fig. 10), and the joints of the crowns are spaced apart along the height of the wall. The crowns are held together using grooved grooves and insert tenons measuring 25x50x120.
The crowns are laid with the groove down , thereby eliminating the possibility of water flowing into it. Tow is placed in the grooves between the crowns to seal the seam and insulate it. Depending on climatic conditions, the width of the groove is taken from 12 to 15 cm.
Spikes are placed every 1.5–2.0 m along the height of the frame in a checkerboard pattern, rectangular (8x2 cm) or round (3–4 cm) cross-section, 10–12 cm high. In the piers, spikes are placed in each crown, one above the other in quantity of at least two and placed 15–20 cm from the edges of the wall.
Within 1–2 years after construction, the log house gives a settlement amounting to 1/20 of its height, due to shrinkage of the wood and compaction of tow in the seams. Due to the settlement of the log house, the nests for tenons should exceed the height of the tenons by 10–20 mm, and gaps of 6–10 cm are left above the openings, which are filled with tow and covered with platbands.
To reduce air flow, the seams between the logs In the corners of the building, the crowns are matched with a notch with the remainder in the bowl or without the remainder - in the paw. With the method of joining the crowns in the corners into a paw, i.e. without any residue, less wood is consumed, so this method is more appropriate. In Fig. Figure 11 shows a section of a chopped log wall from the cornice to the foundation.
Advantages and disadvantages
Chopped log walls are distinguished by high strength and good heat-shielding qualities , and durability under favorable operating conditions. Processing logs and building walls is a labor-intensive process that requires a lot of wood consumption.