Polycarbonate is in particular demand today. Many builders also choose it if it is necessary to build a transparent structure. Previously, glass would have been used for this task, but now that polycarbonate has appeared, there is no need to carry heavy glass that can break at any moment, and the work is not particularly enjoyable. What can you say about polycarbonate? Moreover, in addition to the fact that glass is fragility and heaviness, it also takes a significant toll on your pocket. Especially if the structure is larger than meter by meter. Due to the heavy weight, the structure turns out to be massive and greatly affects the main frame, making it heavier.
Areas of application of polycarbonate
Despite the fact that polycarbonate is a rather fragile material, it still has a number of advantages. First of all, it is quite cheap and available to a wide range of buyers. In addition, it has a small mass, which allows you to build large structures without weighing them down. In this case, glass is not the best choice, and its price is noticeably higher.
The advantages of polycarbonate sheet allow it to be used in various industries. Transparent roofs, greenhouses and greenhouses, partitions, doors and canopies made of polycarbonate no longer surprise anyone. In addition, this material is actively used in the production of stands and stands for advertising, as well as in exhibition halls and galleries.
The following examples of the use of monolithic polycarbonate can be given:
- glazing of various buildings;
- installation of partitions in office, retail or other premises;
- arrangement of greenhouses, attics and summer terraces;
- installation of noise-absorbing barriers on highways;
- blocking of pedestrian crossings and transparent security posts;
- creation of covered public transport stops and telephone booths.
These are not all cases of using the material. Over time, new ways of using it are found.
What could the cell structure be?
Stiffening ribs are the most important structural element of polycarbonate sheets. They determine the load-bearing capacity of the material. Moreover, their reliability may depend not only on their thickness, but also on the shape of the cells they form.
To create arched structures, a material with an orthogonal honeycomb structure is usually used. Such sheets are greatly deformed under load, but do not break and quickly return to their original shape.
Material with X-shaped and diagonal ribs is most often used to create rectangular greenhouses with a pitched or gable roof. Such sheets have low plasticity and practically do not deform. However, their maximum permissible load indicators are usually somewhat lower.
The fewer walls and partitions inside the sheet, the higher its heat-retaining qualities and the worse its strength. This should also be taken into account when purchasing material.
Whatever the shape of the cell, the dimensions of the polycarbonate sheets (width 210 mm, length 6-12 m), of course, will remain standard. The weight and thickness of the material may vary.
Types of Polycarbonate Sheet
Polycarbonate is produced in two main types:
- monolithic;
- cellular or cellular.
The simplest structure is that of a monolithic type of material. It is produced with a thickness ranging from 2-12 mm, sometimes it reaches 20 mm.
The properties of monolithic polycarbonate make it possible to use it to create structures with complex surface topography. It is convenient to hot mold, and the thickness of the material after processing remains the same over the entire area. Due to the high density of monolithic polycarbonate, it does not require an additional frame.
This type of plastic is characterized by high strength characteristics and anti-shock properties. You can purchase material of any color that remains transparent in any climatic conditions. In addition, such polycarbonate is very convenient to work with, and it does not weigh down the structure due to its low weight.
Dimensions of monolithic polycarbonate sheet
Monolithic polycarbonate is a cast sheet without cavities or voids, unlike cellular polycarbonate. It resembles silicate glass, but has a number of advantages over it:
- Flexibility
- High optical transparency (over 89% light transmission)
- Low flammability
- High impact resistance
- UV resistance
Standard sizes:
Width: 2050 mm. Length: 3050 mm.
Thickness. As a rule, we produce polycarbonate in the following sizes: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12 mm .
But if necessary, you can easily find imported samples (they are more expensive) with other sizes. For example, excellent thin-walled Israeli Palram 1 mm, 1.5 mm . Good Austrian Sabic Lexan 9.5 mm, 15 mm , high-strength Scandinavian Arla Plast 20 mm , etc.
Monolithic sheet polycarbonate is widely used in the construction industry, as well as in the production of furniture, medical equipment and household goods, in the automotive industry, in the computer industry, etc.
The thinnest monolithic polycarbonate is used to make billboards and signs. It is also easy to shape using cold or hot molding.
Polycarbonate with a thickness of 6 - 12 mm is widely used in the construction industry (it is used to equip bus stops, install telephone booths, anti-vandal barriers, etc.).
Simply put, a polycarbonate sheet is the same as glass, only unbreakable, easy to install, lightweight and relatively inexpensive.
Size scale and characteristics of various types of polycarbonate
The standard size of a polycarbonate sheet will differ slightly depending on its type.
The following sizes of polycarbonate are produced in production:
- monolithic - the width of the polycarbonate sheet is 205 mm, its length is 305 mm, the thickness ranges from 2-12 mm;
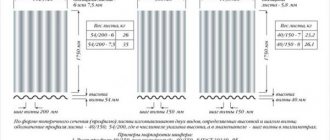
- The dimensions of cellular polycarbonate sheet are 6 or 12 meters in length with a typical width of 2.1 meters, and the thickness varies between 4-32 mm.
It is worth noting that in the case of a monolithic type of material, only its thickness affects the price, but in the honeycomb type, all dimensions of the carbonate sheet are important.
The weight of a typical sheet of solid polycarbonate can range from 1.8-14.4 kg, and the weight of one sheet of cellular polycarbonate 6 meters long is usually about 10 kg.
For comparison, let's look at the features of individual types of material.
Monolithic type of polycarbonate has the following properties:
- high impact strength - 10 times higher than that of plexiglass, and 250 times better than that of plain glass;
- ignites only at a temperature of 570 ℃, under the influence of fire it only melts, tends to self-extinguish;
- transmits light well - about 90%;
- maintains performance at temperatures from -40 ℃ to +120 ℃;
- does not react with most paints and oils, detergents and adhesives and other active substances;
- is highly soundproof;
- can be recycled;
- molded in both hot and cold ways.
Characteristics of cellular polycarbonate:
- small mass - 16 times lower than that of glass;
- the strength exceeds simple glass by 200 times, and acrylic by 8 times;
- impact and mechanical strength is higher than that of glass and acrylic;
- practically does not burn, does not emit toxins, prevents the spread of flame;
- able to withstand heavy loads and withstand considerable weight;
- resistant to temperature changes;
- transmits up to 86% of sunlight;
- Can be used at temperatures from -40 to +120 ℃.
Production of material
Raw materials for the production of polycarbonate
The production of sheet polycarbonate is considered a complex process in technical terms. High-quality products are obtained by following technology in combination with an established control system at all stages of production. They use a method of molding and processing thermoplastic polymers. Products are made by high pressure casting, sheets for construction are produced by extrusion, melt molding.
The production of cellular, profile and monolithic polycarbonate can be divided into 3 stages:
- preparation of raw materials;
- extrusion;
- cutting products to size.
The first procedure involves cleaning polycarbonate granules from dust and impurities using the cyclone method. The raw materials are placed in a container for melting at high temperature. During the process, various plasticizers and additives are introduced into the mass to improve quality. Heat-protective, water-repellent, and dirt-repellent additives are used.
In the second production period, the heated mass in a viscous state is supplied to a special extruder for extrusion. After passing through the conveyor, a belt of the required profile and cross-section is obtained. Next, a press acts to give it smoothness and the desired size in thickness.
The cooled tape is cut into standard size products, maintaining the standard length and width of the polycarbonate sheet. The panels are packed in film and sent for sale or to a warehouse.
Profiled polycarbonate
Profiled or wave is the most durable type of polycarbonate, reminiscent of monolithic, but with additional stiffening ribs. It is most often used for roofing and awnings. The wavelength coincides with the shape of the metal tile, which allows you to combine these materials (for more details: “What types of profiled polycarbonate are there - characteristics of the material, rules for installation on the roof”).
Specifications
For a long time, translucent structures were created using glass. However, it is fragile and unreliable. Any unfavorable atmospheric phenomenon (hail, gusty wind, snow) could result in damage to the structure. Polycarbonate outperforms glass in all performance characteristics, so it is more often used to create roofs of complex shapes. Strength and mechanical stability are influenced by thickness. Polycarbonate, selected for specific conditions of use, can last up to 25 years. Manufacturers claim the following properties of this material:
- A light weight. The sheet, in accordance with the thickness of the polycarbonate, weighs only 0.8-3.4 kg/m2, which makes it the lightest roofing covering.
- The minimum bending radius of the sheet is 0.7-5.7 m. The following trend can be observed: the thinner the material, the better it bends.
- The sound insulating ability of the sheet lies in the range of 15-36 dB.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient of polycarbonate is 1.4-4.1 W/m2xK. For cellular polycarbonate this figure is lower.
- Light transmittance is 53-95% depending on the thickness and structure of the material.
Material characteristics
Professional builders claim that polycarbonate is used to perform a wide range of jobs. It is suitable for constructing canopies, covering gazebos or terraces, building greenhouses, greenhouses, and outdoor swimming pools. In order for the material to serve for a long time, you just need to choose the right type, thickness and color of polycarbonate.
Installation rules
The laying of polycarbonate slabs begins with the preparatory stage, at which the ends are freed from packaging and protective tape.
There are two types of aluminum tape:
- perforated - for the lower part of the end;
- solid - for the upper part of the end.
The end that will not come into contact with air in the future can be covered with tape. There should be holes at the bottom end to drain condensed moisture.
It is very important to position the slabs correctly - the protective layer should face outward, as it will not deteriorate under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Marking is also done on this layer.
The slabs must be installed strictly vertically to prevent moisture from collecting inside. If you need to bend a sheet, then the deflection should be parallel to the stiffeners, and nothing else.
Profiles required for joining sheets:
- One-piece - used when the future structure will not experience heavy loads - come in a width of 4-10 mm.
- Detachable - needed for the best sealing and fastening of the slabs - there is no need for additional fasteners. Regarding the dimensions of the polycarbonate sheet - for a sheet of 8-10 mm thickness its width does not exceed 1050 mm, and for 16 mm - 1400 mm.
Please note that standard polycarbonate dimensions may vary slightly due to natural thermal expansion.
Indicators of changes in the dimensions of cellular polycarbonate are equal to:
- 2.5 mm/m – for transparent material and opal color;
- 4.5 mm/m – for other colors.
In hot periods, the slab must be mounted without departing from the lock of the joining profile, and in cold periods, a small gap must be made.
To secure the plates, you will need self-tapping screws, and:
- holes for self-tapping screws should be made 36 mm or further from the edge of the slab;
- the cross-section of the holes should be slightly larger than the cross-section of the screws;
- the spaces between the screws will be determined by the thickness of the polycarbonate: for a thickness of 8-10 mm - 400-500 mm, and for 16 mm - 600-800 mm;
- for slabs with a long length, from 7 meters, the holes are made oval;
- Do not damage the crossbars of the sheets with holes.
Sometimes an improved seal is made using construction silicone sealants or neoprene or EPDM tape. Soft polyvinyl chloride is not recommended, as it quickly degrades in open air.
To cut the material efficiently, you can use circular saws with high speeds and fine teeth. A band saw will also work.
Planning to build a greenhouse
If we do not consider a ready-made version of the greenhouse, the delivery package of which already includes all the necessary material, then the purchase of polycarbonate sheets for the designed greenhouse also remains with the owner. When choosing a material, the dimensions of polycarbonate for greenhouses are also taken into account.
The construction of a greenhouse involves bending a sheet. The most convenient option for construction is a 6-meter sheet. Based on the permissible bending limit of polycarbonate, this sheet can be bent to a radius of 3800 mm, which is the optimal value. The length of the greenhouse itself will depend on the specific project and the size of the site where the structure will be installed. Longer sheets of material will need to be cut, which increases the risk of error.
Relationship between panel sizes and transportation
Use in construction involves purchasing a large number of sheets. In order for the purchased material to reach its destination without damage, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to the selection of transport and loading. Otherwise, damage to individual sheets will not allow the work to be completed in full.
The ideal option for transporting the sheet is to lay it on a flat floor without exposure to protruding irregularities. Naturally, even a 6-meter sheet can end up hanging from the body. It should be taken into account that for thin panels - 4-8 mm - this is not allowed, and panels with a thickness of 10 to 16 mm can protrude beyond the platform no more than 1 m.
If there is not enough space in width, longitudinal bending of the panel is allowed for a short time based on the lack of space in width within 10%. If sheets need to be transported in a rolled state, then certain rules should also be followed:
| Sheet thickness, mm | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| Permissible panel bending radius, m | 0,7 | 1,05 | 1,5 | 1,75 |
To summarize, it should be noted that the purchase of polycarbonate sheets should be carefully calculated. Even at the design stage, you can not only use a certain amount of material, but also save a little. After all, the optimal number and size of doors and windows also optimizes the material that will need to be cut.
Selection of material and calculation of the number of sheets
First of all, you need to draw a plan and diagram of the future structure. This will make it possible to make a correct calculation of the required material. If you are not strong in drawing work, then it is better to entrust this stage to professionals. This way, you will avoid unnecessary costs and mistakes in the future.
Even if the polycarbonate design is as simple as possible, you cannot do without additional materials. Proper cutting of sheets and their installation will affect the service life of the structure.
Recommendations for material storage and transportation
If there is a need to store polycarbonate sheets, you need to follow the basic rules:
- sheets must be smooth, without protrusions of any origin;
- Before laying, the sheets must be cleared of debris;
- the stack of sheets should not exceed 250 cm;
- the room intended for storage should not be exposed to the sun and moisture;
- for outdoor storage, the stack will need to be covered with transparent or white plastic film;
- Sheets cannot be stored curled.
When transporting material, you also need to follow a number of simple rules:
- polycarbonate sheets must be folded on a flat, flat surface;
- The surface must also be cleared of debris before storage;
- the stack in this case should not exceed 200 cm;
- the stack must be secured to the body with tapes or ties, there must be at least two of them;
- When transported in a rolled state, the radius of the roll must exceed that of the bend of the sheet.
Why is the material width fixed?
So, 210 cm is the standard size of a polycarbonate sheet. It is clear how the width of this material is measured - based on one of the outer sheets. But why it is exactly like this and no other - this question already deserves more detailed coverage. And the point here is this: polycarbonate sheets, as already mentioned, are capable of greatly expanding at elevated air temperatures and contracting at lower temperatures. With a very wide material the difference in vibration would therefore be too noticeable. A narrow sheet is not particularly convenient to install. 210 centimeters, therefore, is the optimal option. A sheet of this size is convenient to install. The structures made from it are reliable and neat.