Heat escapes through the roof of a private house. Heat loss can account for up to 30% of the total. To reduce heating costs, it is necessary to choose high-quality finishing materials and insulate the roof of a private house.
Insulation not only reduces heat loss, but also reduces heating costs in cold weather. Reliable insulation for the roof of a private house allows you to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature at any time of the year.
The need for roof insulation
High-quality insulation of the roof of a private house reduces the percentage of heat loss inside it. An ideal temperature is formed, which is easy to regulate without significant losses in heating or cooling the air with electrical appliances.
Incorrectly selected thermal insulators lead to poor quality insulation of the roof of a private house. In winter, ice forms on it and icicles form. Icing can compromise the integrity of roofing elements by causing leaks.
A poor-quality insulating layer can lead to dampness in the roof space of a private house. High humidity leads to the spread of fungus and mold. The wooden truss structure suffers, which swells over time and becomes unusable.
conclusions
To make a high-quality warm roof, it is recommended to purchase basalt insulation or fiberglass analogues.
It is worth considering that glass wool has the property of absorbing moisture, albeit slightly. Fibrous materials for thermal insulation require the use of an additional layer of protective insulation against moisture from the outside, and a vapor barrier will be needed from the inside. And this increases the level of cash costs.
Please note: thermal insulation materials with a fibrous structure, due to their porosity, have high sound insulation properties, which prevents street noise from entering the house.
Another feature of glass wool or its basalt counterpart is its significant service life - over 50 years. It is perhaps not easy to choose an insulation material that will last as long as glass wool. In addition, this roll insulation does not burn, which means it can be used for finishing wooden houses
Which insulation can be considered the best, selection criteria?
The choice of thermal insulation material depends on the type of roof of a private house, which can be pitched or flat. The choice is made by analyzing the following parameters:
- Thermal conductivity. The lower the indicator, the higher the efficiency.
- Lifetime.
- Moisture resistance.
- Durability. How reliable are the insulation parameters?
- Environmental friendliness. No toxic substances should be used in the insulation.
- Frost resistance.
- Specific gravity. The best insulation materials have low density and do not weigh down the roof frame.
- Fire resistance.
- Soundproofing. Tile roofing requires high-quality insulation with maximum sound attenuation.
Good insulation keeps its shape throughout its entire service life, does not form voids and retains its thermal insulation properties for a long time, regardless of temperature changes.
Suitable for insulation
To insulate the roof of a private house use:
- Mineral wool . Fiber insulation is produced by combining molten and solidified rocks. It has excellent thermal insulation and sound insulation properties. Supplied in slabs or rolls, which are convenient to transport and install on site. During operation it does not shrink or change shape.
- Glass wool . Mineral wool is created on the basis of fiberglass. It is made by melting cullet or quartz sand. Keeps its shape perfectly, does not allow sounds to pass through, and retains heat. Can withstand temperature loads up to 500 degrees. It is sold in slabs or rolls.
- Polyurethane foam . Polyurethane foam insulation is a liquid that, during the production process, enters into a chemical reaction and foams. As a result, a solid substance with a porous structure is formed, which perfectly insulates the surface. Polyurethane foam has high thermal insulation properties due to its airtight surface coating. It is able to adhere firmly to any base and does not emit harmful and toxic substances.
- Expanded clay . Bulk insulation consists of porous clay granules that are light in weight and come in various sizes. It has a reduced thermal conductivity coefficient and a high level of sound absorption. It is environmentally friendly, non-flammable, therefore it is also used for insulating interfloor and attic floors.
- Penoizol . Properties are similar to polyurethane foam. The difference is that penoizol has slightly higher characteristics and a lower cost. It is easy to install and completely safe for health. To insulate with penoizol, it is necessary to use foam-forming equipment to reduce the weight of the structure. In addition, before spraying this material, you must first lay a vapor barrier layer to reduce the degree of moisture absorption.
- Foam concrete . It consists of cement, concrete, sand and a special agent that gives the material a porous structure. Foam concrete creates a strong and durable structure with low density. It retains heat perfectly and does not place high loads on the supporting frame. For laying, a mobile installation is used, which controls the thickness of the laid layer. Its size should not exceed 15 cm and not be less than 3 cm.
- Expanded clay . Bulk insulation, which is placed on floor slabs or on the outer surface of the roof. The heat insulator is pre-insulated and then covered with screed. Expanded clay creates a load on the foundation being laid, so its use must be carefully calculated and verified with the design documentation for a private house.
- Foam glass . Environmentally friendly insulator with high thermal insulation characteristics. Resistant to deformation and exposure to steam and moisture. Durable, non-flammable and can be used on any roofing materials. Polymer acetate glue is used for installation.
Not recommended for use
There are many roofing insulation products on sale that experts do not recommend using. This is due to their side effects. Their list is as follows:
- Ecowool . Good insulation with a huge drawback. Ecowool is made from a highly flammable component - cellulose fiber. Despite the treatment with fire retardants, its flammability is very high, and over time it shrinks and loses its original qualities. This material cannot be used to insulate the roof of a private house.
- Sawdust . Eco-friendly material, but not safe from a fire safety point of view. In addition, sawdust is a favorable environment for various microorganisms, small insects and even rodents. It absorbs moisture well, therefore creating an environment for rotting and mold growth. Over time, it shrinks, which leads to a decrease in thermal insulation properties.
- Expanded polystyrene . It consists of slabs that cannot withstand high temperatures above zero. Already at 80 degrees, polystyrene foam releases toxic substances that are dangerous to human health. It is allowed to lay this material only under plaster or screed made of concrete or cement.
Extruded polystyrene foam
It is based on the same polystyrene, but it is much denser and stronger. Its service life, according to experts, is much longer, as are its thermal insulating properties. Has complete vapor barrier. The main disadvantage in the eyes of consumers is the high cost of the material. The price is comparable to polyurethane foam spraying.
Therefore, its use is limited to projects where it is not possible to replace this material due to the characteristics of the soil, humidity, and pressure. In other cases, it is not economically profitable.
Comparison of the main characteristics of thermal insulators
| Insulation | Density kg/cub.m | Thermal conductivity W/(m*K) | Flammability |
| Minvata | 35 — 40 | 0,035 — 0,039 | NG |
| Glass wool | 15 — 20 | 0,035 — 0,042 | NG |
| Polyurethane foam | 60 — 80 | 0,023 — 0,032 | NG |
| Expanded clay | 300 — 500 | 0,09 — 0,1 | NG |
| Ecowool | 38 — 41 | 0,038 — 0,041 | G2 |
| Styrofoam | 10 — 37 | 0,033 — 0,041 | G1 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 26 — 32 | 0,028 — 0,031 | G4 |
| Sawdust | 0,10 — 0,25 | 0,07 — 0,09 | G3 |
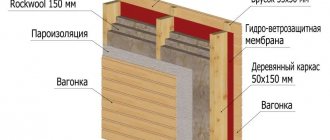
Insulation of a roof that does not have a counter-lattice, but has a vapor barrier
The difference between this version of the roofing pie device is that if the roof leaks, water will not get onto the insulation. In addition, if the vapor barrier has an anti-condensation surface, then it will “bind” part of the condensate that forms when the atmospheric air cools.
But this condensation, just like excess moisture in the insulation, must be ventilated from the under-roof space. And for this you need a conro-lattice with a vertical ventilation gap.
In this case, the waterproofing membrane can be attached a little easier than in the previous case:
- Between each pair of rafters, parallel to them, three or four slats are placed (depending on the distance between the rafter legs). The thickness of the rail is chosen equal to the size of the air gap (usually 4-5 cm).
- A waterproofing membrane is laid between the rafters. It can be laid either in one strip vertically or in pieces of panels horizontally with the top panel overlapping the bottom by 15-20 cm (installation must be done from top to bottom).
- The waterproofing membrane is stapled to each batten and along the rafter legs.
Thermal insulation material and vapor barrier are laid using standard technology.
The best insulation for an attic roof
For the attic roof of a private house, it is important to provide high-quality insulation to reduce heat loss. Good thermal insulation must have vapor permeability and low thermal conductivity to ensure high-quality air circulation.
Rockwool Light Butts Scandic
Light Butts Scandic is one of the lightest Rockwool insulations, with compression up to 70%. Elasticity is created by stone fibers running at the base of the slabs. Good elasticity and a high coefficient of compression allow the wool to easily fit between the rafters and naturally straighten after completion of work.
For your information! Excellently fills the space between frame elements and prevents cold air flows. Suitable for insulating pitched roofs and attic spaces, balconies, partitions and ceilings.
Rockwool produces Light Butts Scandic insulation in two size variations:
- Standard. 800*600 mm, thickness 550 or 100 mm.
- 1200*600 mm, thickness 100 or 150 mm.
Paroc eXtra
Mineral non-combustible basalt insulation produced in a slab. Its thickness varies from 40 to 250 mm. It is a kind of middle ground between stone wool and fiberglass, but Paroc eXtra fibers are much longer than classic materials.
For production, only high-quality and homogeneous raw materials are used, which ensures the elasticity and flexibility of the slab. During installation, mineral non-combustible basalt insulation does not break or roll into the structure; it is easily implanted into the spacer.
Paroc eXtra slabs are sold slightly pressed in sealed packaging. When it is opened, the shape of the plates is restored. It is not flammable and has high sound insulation ability.
Consumer Reviews
Review of Linerock “Light effect” insulation:
More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_1208058.html
Linerock Light effect
Review of ISOROC mineral wool thermal insulation:
More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_7134354.html
mineral wool ISOROC
Another review about ISOROC mineral wool thermal insulation:
More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_3951910.html
Review of Penoplex thermal insulation boards:
More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_3959072.html
Penoplex slabs
Penoplex slabs
Review of ISOROC mineral wool thermal insulation:More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_5193087.html
The best insulation for a pitched roof
For pitched roofs of a private house, high-quality and durable heat insulators are used. This is due to the need to protect the roof from loads and exposure to heat and moisture.
Isover C-000176898
Quartz-based mineral slabs are suitable for insulating attics and pitched roofs. The insulation has a special coating that ensures its shape remains unchanged. This also makes it possible to facilitate installation work, which is difficult due to the strong slope of the structures.
A special feature of Isover C-000176898 is that the material is suitable for insulating the roofs of a private house with different rafter spacing, is environmentally friendly and does not emit toxic substances when heated. When laying, it does not crumble and does not create dust. It has enhanced protection against moisture and steam, and also effectively absorbs noise.
HeatKnauf TR 037 Aquastatik
Created on the basis of basalt wool. The composition contains special fiberglass, which is mixed with components that provide the binder and water-repellent properties of the insulation. HeatKnauf TR 037 Aquastatik has low sound conductivity and a long service life.
It is convenient during installation, as it has excellent elasticity. This allows you to insert it into the spacer without distortion. It cuts and bends beautifully. It is non-flammable and safe for human health, as it is produced without the use of phenol-formaldehyde and acrylic resins.
HeatKnauf TR 037 Aquastatik is coated with water-repellent impregnation, which guarantees its reliability and durability.
Ecowool or cellulose
This type of insulation is made from recycled paper products.
Such material, paradoxically, may well comply with fire safety standards. During its production, special additives are added to the composition - fire retardants, which increase the resistance of the material to ignition.
Due to the fact that cellulose can be easily exposed to biological organisms, it is impregnated with antiseptic modifiers to increase its resistance to them. This allows you to obtain a lightweight, inexpensive, environmentally friendly material that has excellent heat and sound insulation functions.
The most recognized brands: a joint production of Canada and the USA - “Ecowoo”l, a product of cooperation between Russia and Kazakhstan - “Ekovata” and “Unizol” (Ukraine). Another advantage is that the material can be blown using a special installation, which makes it possible to achieve tightness without the use of seams. It is better to involve experienced specialists in carrying out such a procedure, since it is difficult to carry out independently.
The best insulation for a flat roof
The technology for insulating flat roofs of a private house differs from pitched roofs. Firstly, there is no need to nail the sheathing, which would form a ventilation gap for ventilation. Secondly, it is necessary to use products that are glued to the underlying base and coating.
TechnoNIKOL Carbon Eco
Extruded polystyrene foam is a heat insulator with evenly distributed and closed cells. This ensures high-quality insulation and long service life of such a coating. TechnoNIKOL Carbon Eco does not absorb moisture and does not swell. It does not shrink and is also resistant to chemicals and rotting processes.
Super strength allows for a smooth and at the same time rigid base during installation. This provides a guarantee of quality and operational reliability. The slabs are packaged in durable bases covered with stabilized film.
When insulating the roof of a private house, first of all you should pay attention to the roofing material. Based on this, you can choose the highest quality and most suitable insulation that meets the declared qualities. You shouldn't skimp. It is important to insulate the roof efficiently and for a long time to avoid heat losses.
Styrofoam
It has the most affordable price, and therefore is subconsciously perceived as the optimal solution. Along with this, as practice shows, its service life is very short. The material is susceptible to breaking under mechanical loads. This fact alone raises serious concerns about the strength of the structure behind the cladding, where it is difficult to control its current condition.
There is also difficulty in placing the foam between the rafters. This is a solid insulation and is not elastic, unlike mineral wool. Careful adjustment is required using a float; there may be gaps that need to be removed by foaming.
Compared to polyurethane foam, noise insulation is higher, since it is possible to cover the rafters by applying a layer in the counter-lattice.
To ensure fire safety, it will be necessary to provide a continuous fence from the residential area using non-combustible material. Rodents and birds love this material; they thrive there and destroy it. The structure must be hermetically sealed, but this is not easy.
Frequent errors that occur during installation
Lack of proper insulation installation technology can lead to the following negative consequences:
- The formation of “cold bridges” occurs when the integrity of the “roofing pie” is violated (for example, the cracks between the insulation are not sealed with moisture-resistant mastic),
- The formation of many icicles on the eaves in winter - this is caused by the penetration of warm air from the room through the roof of a private house, which leads to melting of snow,
- An increase in heat loss occurs when installing thermal insulation in a damp state or when carrying out work in a damp environment.
There are many materials on the market for insulating the roofs of a private house. The correct choice of insulation will ensure a comfortable temperature in the house, the absence of toxic emissions, reduced heating costs in winter and air conditioning in summer.
Content
We bring to your attention the video:
Let's put it this way: each technology has its pros and cons, and which insulation to choose for your roof depends on what you want to get in the end: environmental friendliness, manufacturability or durability? After all, each of us has our own priorities, and each product has its own buyer.
Thickness calculation
You can calculate the required thickness using the following formula:
αout=(R0in-0.16)·λout
In it, the symbol αout denotes the thickness of the insulator in meters, R0in. – reduced heat transfer resistance, λut – thermal conductivity coefficient.
Determining the thickness when insulating an attic
For horizontal floors and roof slopes, the insulation layer is taken more
The space under the roof can be used as residential or non-residential. For a non-residential attic, it is enough to insulate only the covering that separates the ceiling of the house from the room itself. In the case of residential attics, thermal insulation of side walls and slopes, if any, is required. In mansard roofs there are three types of enclosing structures - ceiling, slopes and gable walls. They require different widths of roof insulation. A thick layer will be required for the ceiling, and a small layer for the walls. Calculations for each surface are carried out separately.
Insulation of ceilings with a cold roof
If the attic is not used during the cold season, you can insulate the attic floor, leaving the roof without thermal insulation. Then the material is placed on top of the ceiling and covers the ends of the walls. If an insulating layer is installed inside the walls, heat will be transferred to the outside.
Calculation using online calculators
To reduce heat loss, insulation is combined in two layers
Many services offer construction calculators that allow you to make approximate calculations of the amount of materials, its thickness and the cost of the entire process. There are several options for calculating the size of roof insulation:
- Based on the total area of the building. It is necessary to enter the linear dimensions of the building, the number of floors, and the selected insulation. The result is a value with a large number of errors, since the characteristics of the house and climatic conditions are not taken into account.
- By project type. The architectural, structural and engineering plans of the building are taken into account.
- Universal calculator. It takes into account the type of floor, materials and other important features.
3 Expanded clay
To insulate attic floors, loose expanded clay insulator is often used. It consists of pebbles of a certain size with many pores inside. Expanded clay is used to fill the space between the joists, forming a continuous sound and heat insulating layer. The high popularity of expanded clay is explained by its affordable price and durability. This material is not afraid of moisture, it is not affected by mold or mildew, and mouse nests are not made in it. And the frost resistance of expanded clay allows it to be used in extreme climates. Since the insulation is made of clay, experts call environmental friendliness one of the advantages.
The disadvantages include the fragility of the granules; even when falling asleep, you must be careful. When expanded clay is damaged, its thermal conductivity deteriorates. And the scope of application of this insulation is limited to the floors of the house.
Basics Comparison Chart
When choosing insulation, the question immediately arises: which insulation for the roof is better? The price is different for everyone, as are the indicators. Let's compare the main types of insulation in the comparative table below.
| Insulation material | Flammability | Waterproof | Harmful to humans | Ease of use |
| Basalt | incombustible | partially permeable | harmful | medium light |
| Fiberglass | incombustible | partially permeable | harmful | medium light |
| Styrofoam | combustible | impenetrable | harmless | easy |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | incombustible | impenetrable | harmless | easy |
| Polyester fiber | incombustible | partially permeable | harmless | medium light |
Manufacturers
On the market you can find materials for insulation of domestic production, as well as insulation from the USA, Finland, Germany, France and other countries.
The following brands are available:
- TechnoNikol;
- Knauf;
- Isoroc;
- Isover;
- Paroc;
- Rockwool;
- Ruspanel;
- Soudal;
- Tytan;
- Ursa;
- Akterm;
- Penoplex;
- Penofol;
- Tepofol;
- Tilit;
- And others.
Go to any well-known online store and use filters to look at the characteristics of each individual product.
As you can see, there are very different methods of insulation, but price always remains an important issue.
Kinds
As already mentioned, all thermal insulation materials are divided into several types depending on their specific gravity.
The scope of its application depends on the latter. The table clearly reflects this:
| Density class | Density indicators | Scope of application |
| Lungs | 11–35 kg/m3 | Lightweight and elastic materials that are used to insulate roofs and roofing. |
| 35–75 kg/m3 | Wall insulation – thermal insulation of walls, partitions, frame structures. | |
| 75–100 kg/m3 | Wrapping of oil pipelines and heating mains. | |
| Average | 100–125 kg/m3 | External thermal insulation under a ventilated facade |
| 125–150 kg/m3 | Insulation of concrete and brick walls, interfloor ceilings | |
| Hard | 150–175 kg/m3 | Cladding of load-bearing structures |
| 175–225 kg/m3 | They are laid under the subfloor screed before finishing; they are durable and fire resistant. |
It is important that individual types of insulation have their own classification depending on their specific gravity. For example, according to GOST, foam plastic is divided into grades PSB 15 (density less than 15 kg/m3), PSB 25 (indicators 15–25 kg/m3), PSB 35 (specific gravity from 25 to 35 kg/m3) and PSB 50 ( 50 kg/m3 or more)
The classification of mineral wool by hardness is as follows:
- P-75 (material density, respectively, 75 kg/m3) is suitable for lightly loaded and horizontal surfaces;
- P-125 (the specific gravity of this wool is 125 kg/m3, but insulation with a density of 110, 120 and 130 kg/m3 also belongs to this type) wall insulation;
- PZh-175 (density indicators are clear from the name) - high-density material for external cladding;
- PZh-200 (specific gravity is 200 kg/m3 and above) - used for outdoor work, has increased fire resistance.
Description of slabs with different density levels
There are basalt slabs of various density levels. This is reflected in the following properties of insulation: vapor permeability, moisture resistance, resistance to high loads and response to compression of the material.
Table of parameters of basalt insulation
Based on density, slabs are divided into the following categories:
- Up to 35 kg/m3 – used for vertical and inclined insulation without load.
- Up to 50 kg/m3 - with the help of such insulation they increase the level of thermal insulation of interior partitions, attics or attics. Where there is no load on the surface.
- Up to 75 kg/m3 – lightly loaded surfaces, under floors when placed between joists.
- Up to 100 kg/m3 – external insulation of industrial and residential buildings.
- Up to 125 kg/m3 – arrangement of ventilated facades.
- Up to 150 kg/m3 – single-layer insulation of reinforced concrete or metal building frames.
- Up to 175 kg/m3 – insulation of heavy buildings with further plastering of the facade. Or it is located inside a three-layer cake.
- Up to 200 kg/m3 - insulation with such a density can withstand the highest loads. The soundproofing qualities of the material are significantly higher than analogues with a lower density level.