The number of layers that are laid on top of the base floor on the attic side is called the attic floor pie.
Correct installation of all layers of the cake, consisting of vapor barrier, insulation lathing, finishing materials and finished floor, extends the life of the ceiling on the side of the house.
Helps to equip an additional room as an attic, protects the main building from drafts and temperature changes, and further reduces the cost of alternative types of heating (by 20%).
How the layers of the attic covering cake are formed, what regulatory requirements are imposed on it, whether there are errors, how to eliminate them, as well as other important nuances, we suggest you learn from the presented article.
Vapor barrier of attic floor
Vapor barrier of the attic floor of a cold attic protects the wooden floor structures and insulation from steam entering them from the premises of the house. Steam condensing on beams can contribute to wood damage by fungi and mold, thereby reducing the service life of the structure. Condensing in the thickness of the insulation increases heat loss in the house, because Water itself is a good conductor of heat. In addition, water, freezing in the thickness of the insulation during the cold season, destroys the polymer bonds of the fibers and reduces the service life of the material.
Vapor barrier of a cold attic , when using foil materials, in addition to its main function, allows you to reduce heat loss and, accordingly, heating costs due to the creation of a heat-reflecting screen.
Attic vapor barrier materials are presented on the market in 2 main types:
- Film vapor barrier – does not allow steam to pass through (vapor barrier only).
- Foil vapor barrier - does not allow steam to pass through and reflects thermal radiation (vapor and heat insulation). This vapor barrier is installed with the foil side facing the premises.
, vapor barrier of attic floors with foil materials is most preferable when building a reliable and heat-efficient house made of aerated concrete, brick or monolith.
Choice of insulation
The methods of insulating the ceiling of the upper floor of the ceiling along beams in a private house are very diverse. When doing the work yourself, the insulation is placed between the joists and provides reliable thermal insulation and noise protection. There are many options for insulating a structure, the most common of which are:
- insulation with mineral wool;
- laying expanded polystyrene (foam plastic or penoplex) on wooden beams;
- filling with expanded clay;
- insulation with sawdust;
- filling the ceiling space with foam.
Each of these options has its own characteristics and advantages.
Insulation with mineral wool between joists
Mineral wool insulation
The material is available in two versions: plates and rolls. Insulating the attic floor with mineral wool has the following advantages:
- excellent heat-shielding characteristics;
- resistance to fire;
- low water absorption;
- resistance to chemical reagents and biological damage;
- long service life.
When insulating with mineral wool with your own hands, you must remember safety precautions: workers must have special clothing, masks and gloves to prevent particles of the material from getting on the skin and into the lungs. Rigid slabs are perfect for insulating the ceiling from above, and it is better to use rolled material to protect the ceiling from below. More information about protecting structures using this material can be found in the article “Insulation of floors with mineral wool.”
Foam plastic has become one of the most common materials for thermal insulation. It has earned its place in the top three thanks to its very attractive price. Using this insulation in an individual home provides the following advantages:
- high degree of protection;
- resistance to rotting and mold and mildew;
- low degree of water absorption;
- ease of installation and no need for complex tools and protective equipment;
- the light weight of the material prevents excessive load on the structure and allows for insulation from below.
The material is suitable for insulating the ceiling of the upper floor due to its low vapor permeability. Disadvantages include low strength and the risk of falling apart into individual balls when simultaneously exposed to moisture and low temperatures. In addition, polystyrene foam is a flammable material, which is not very desirable when constructing a wooden building. You can learn more about working with this type of material in the article “Floor insulation with foam plastic.”
Extruded polystyrene foam
More often this material is called a shorter word - penoplex. Being the closest relative of foam plastic, penoplex is devoid of most of its disadvantages. In the process of improving performance characteristics, the cost has increased. The material is produced fireproof, it has sufficient strength for use as a base for flooring and is light in weight for use in ceiling construction.
Do-it-yourself installation is quite simple. This issue is discussed in detail in the article “Floor insulation with polystyrene foam.” The text discusses options for using both penoplex and polystyrene foam for different types of floor construction.
For people who decide to build their own wooden house, the naturalness of the materials is usually important. Here penoplex, like foam plastic, loses to other types of insulation due to its artificial origin.
Expanded clay or sawdust
If you decide to use completely natural materials in your home, these two types of insulation will become indispensable helpers. They do not have high heat-protective characteristics, like previous types, but provide reliable protection from the cold with a sufficient layer thickness. Sawdust can be obtained almost free of charge; expanded clay is also an inexpensive material.
Insulation of the attic floor can be carried out by non-professionals and does not require special skills. The application is limited by the physical characteristics of these materials: they cannot be used for thermal protection from below.
You can read more about these types of thermal protection with your own hands in the articles “Insulating the floor with sawdust” and “Insulating the floor with expanded clay.”
Heat protection foam
Polyurethane foam insulation is a fairly new material in construction. When constructing a building yourself, this method can provide high speed work and reliable protection from the cold. You can read about insulating a building, including attic floors, with foam in the article “Foam for floor insulation.”
This provides a large selection of materials for insulation and significant savings on construction.
The insulation of a wooden floor is carried out between the joists, and therefore does not require high strength heat-insulating material: the main load from people, furniture and equipment will be borne by boards or timber.
A large percentage of heat losses occur precisely through the ceiling of the upper floor, which is why it is so important to choose the right insulation and follow the installation technology.
Vapor barrier for the attic “pie”:
- Attic floor (ladders) – necessary for maintenance, repair of the roof and attic space. In order to get to the attic, provide an attic ladder with an insulated hatch (Thermo). To exit from the attic to the roof, we recommend installing blind or glazed exit hatches (Velux, Vilpe, etc.) on the roof.
- Para- or super-diffusion moisture-proof membrane - for effective removal of steam from insulation.
- Insulation - mineral wool slabs. Recommended thickness for the Moscow and Leningrad region is 300mm. 200 mm are laid in the space between the beams, the remaining 100 mm are laid perpendicular to the laid layers - counter-insulation. For comparison, building codes in Finland determine the thickness of insulation from 400 to 500 mm. It is recommended to delay the installation of insulation as much as possible - no earlier than 6 months after the completion of the construction of the house frame. Because For the construction of floors, timber with natural moisture is mainly used. The timber must dry thoroughly, otherwise there is a high probability of wood being damaged by fungi and mold, which entails additional costs for dismantling/installation work and treating the wood with bleaches and antiseptics.
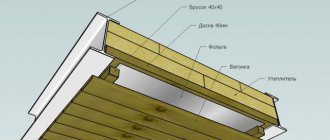
- Counter grille and ventilated gap. For effective ventilation and removal of steam from the surface of the moisture-proof membrane.
- Floor beams. As a rule, in private housing construction a 50x200mm board or 100x200mm natural moisture timber is used.
- Lathing is the basis for laying insulation. It is recommended to use a 100x20 (25) mm board as lathing and lay it in increments of 70-80 mm. The resulting cracks will form an additional air thermal layer under the insulation. That. The insulation slabs (mats) will not lie on a vapor barrier film, but on a rigid base, already under which there will be a vapor barrier. This solution eliminates the possibility of accidental damage to the vapor barrier or its pushing through when laying insulation, during maintenance and repair work of the roof and attic. In this case, you can begin interior decoration of the premises, and postpone the installation of insulation as much as possible (see above).
- Vapor barrier of the attic floor on wooden beams - is attached using a construction stapler from below to the rough ceiling (lathing), which allows you to cut off vapors from the entire floor structure. It is necessary to overlap the vapor barrier rolls by at least 15-20 cm and carefully glue them with aluminum adhesive tape. It is necessary to form overlaps on the walls of 15-20 cm and carefully glue them (place them under plaster and other wall finishing). Carefully seal the places where chimneys, ventilation pipes and other utilities pass through the attic floor using special hoses. The best material for vapor barrier is high-density polyethylene film of 200 g/m² and above.
- We close the attic - the finished ceiling is attached to the vapor barrier . The finished ceiling (OSB, gypsum board, etc.) is installed along the sheathing and guides. For the best fire protection, it is recommended to “sew up” the ceiling with 2 layers of plasterboard sheets.
Styrofoam
Insulating an attic space with polystyrene foam is a good option for converting it into an attic, suitable for year-round use. This material has low thermal conductivity, as it is produced in the form of foamed air granules pressed into slabs.
During installation, the foam must be cut so that the plates fit tightly between the attic floors. Any gaps and cracks become “bridges” for the penetration of cold, and thereby significantly worsen the quality of insulation.
In this case, it is necessary to maintain a distance between the foam board and the waterproofing film of at least 2-3 cm. It is recommended to use it as insulation with a thickness of 70 mm, and in regions with a harsh climate - 100 mm.
Attention! When installing a vapor barrier film, you need to pay attention to the fact that it faces the insulation with the required layer, according to the instructions. Otherwise, the opposite effect will be produced: all the steam will be directed towards the insulating material
Why do you need a vapor barrier?
- protect the insulation from moisture vapor entering it along with warm air from the heated room;
- prevent the creation of conditions for structural materials to get wet;
- protect living spaces from mineral wool particles entering them.
And if the last point is aimed at providing comfortable conditions for humans and is a consequence of the properties of the material, then the first two are mandatory according to current standards.
The entire structure of the “pie” of the insulated ceiling of a cold attic must meet the requirements of SP 23-101-2004, which regulate the design standards for thermal protection.
According to clause 8.5 of the general provisions, technical solutions must ensure reliable waterproofing of thermal insulation materials and limit the penetration of water vapor into them as much as possible. And the relative arrangement of the layers should eliminate the prerequisites for the accumulation of moisture and create conditions for its weathering.
Installation rules
Wooden ceilings are beams filled with boards or panels of the rough ceiling on the side of the room. This device determines the specificity of the order of layers. If on a concrete floor the vapor barrier is laid on a slab under the insulation (the same as when insulating a flat roof), then in this case it must still protect the wooden elements of the structure.
The sequence of layers and installation of vapor barrier will be as follows:
- They arrange the ceiling - a rough ceiling is attached to the beams (number 8 in the diagram).
- On the side of the room, the false ceiling is covered with a vapor barrier film (number 9 in the diagram). If it is a reinforced vapor barrier (with a two- or three-layer structure) or heat-reflecting vapor barrier, then the anti-condensation rough surface or metallized layer should face the inside of the room.
- The overlap between the panels, regardless of the direction of laying, is 15 - 20 cm.
- The edges of the vapor barrier layer along the perimeter are brought out onto the walls and fixed to them.
- The joints of the canvases and the perimeter are taped with vapor-proof tape.
- A gap is required between materials with an anti-condensation or reflective surface and the finishing of the ceiling. It is provided by stuffing the slats with a thickness of 4 - 5 cm.
depositphotos
Insulation of the ceiling of a cold attic is carried out as follows:
Between the beams, mineral wool (in soft mats or in rolls) is laid on the surface of the false ceiling. The insulation layer is calculated so that the total reduced heat transfer resistance of the entire floor structure is not less than the standard value.
In accordance with the requirements of clause 8.20 of SP 23-101-2004, waterproofing of insulation is required along the perimeter of a cold attic for a width of 1 m or more. In private houses, with a relatively small building area, the procedure is simple - a waterproofing membrane with a high vapor permeability (superdiffusion) capacity is laid over the entire surface of the heat-insulating layer. The vapor permeability of waterproofing is needed to ventilate excess moisture from the insulation when the temperature and humidity level of the atmospheric air changes.
The membrane is laid without tension close to the thermal insulation with the white side. Attached to floor beams and around the perimeter. The overlap between the panels is 15 - 20 cm.
Counter slats 4-5 cm thick are placed on the beams (number 3 in the diagram), which is ensured by the ventilation mode of the heat-insulating layer.
The floor is laid along the counter slats.
The procedure for constructing a roof
The construction process includes the following stages:
- laying the Mauerlat;
- arrangement of the rafter system;
- construction of a roofing pie.
Before constructing the roof, you should order a design for the roof of the house. After completing the construction of the walls of the building, waterproofing (roofing felt, roofing felt) should be laid on top of them (under the Mauerlat). When arranging a gable (single-pitched) roof, it is laid on two walls on which the rafter legs rest. When a hipped roof is being built, the Mauerlat is installed along the entire perimeter of the building. Waterproofing is also installed on all walls.
Next, the Mauerlat is attached, which is installed at the level of the inside of the walls. To distribute the load evenly, its top should protrude a few centimeters.
After this, the floor beams should be installed. The ends of the beams should protrude to the planned width of the cornice (usually within 0.4-0.5 m). First, the outer beams are laid, then the remaining ones are installed (the pitch depends on the pitch of the rafters, usually 0.6 m). The beams are secured to the mauerlat with nails or self-tapping screws. Boards are laid on top (not secured).
The “skeleton” of the roof in a frame house has been assembled Source izoluks.ru
Further construction work includes the installation of racks, for which a 50x150 board is used. They are fixed using spacers, and their height depends on the design of the particular roof. First, the outer racks are installed, after which the rest are installed. The ridge beam is attached to them with self-tapping screws.
When installing rafters, it is important to maintain uniform load distribution. They are fixed on the ridge, as well as below (on the floors)
Crossbars with racks are installed under them.
The pediment frame is built and covered with inch boards. Then the entire cornice is installed. The ends of the ceiling are covered with a front board, and 2 belts of boards are attached below. Gutter holders should be installed.
A waterproofing membrane is attached to the rafters. A counter-lattice is installed on top, and then the sheathing is installed. Roofing material is laid on it.
The roof is insulated from the inside using modern heat insulators. Mineral wool is most often used for this. More expensive ones (sheet, sprayed polymer insulation) are used less frequently.
Insulation of the roof of a house with an atticSource euroace.org
The heat insulator is closed with a vapor barrier (special membrane). The material protects the insulation and the entire wooden structure from moisture.
The entire process of installing the roof and roofing is clearly and step-by-step in the following video:
What you need to know to prevent dripping from the ceiling
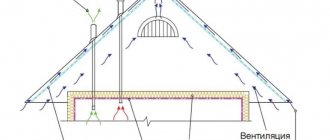
Insulation of an unheated attic can only be carried out if it is ventilated (clause 8.19 of SP 23-101-2004).
- For a continuous pitched roof, ventilation openings must be at least 0.1% of the floor area.
- On a pitched roof made of piece roofing materials, you can do without ventilation holes - there are enough gaps between the roofing elements.
You can turn on the heating only after the insulation of the floor and the vapor barrier of the ceiling have been completed in full.
Ceiling vapor barrier in a cold attic
If an apartment or private house has an unheated and, accordingly, cold room above the ceiling, homeowners may encounter an unpleasant problem - the formation of condensation on the ceiling surface. To avoid this disaster, in a cold attic, a vapor barrier on the ceiling is essential. What it is and how it can solve the problem will be discussed in this article.
Why can't you insulate your apartment from the outside?
All the methods described above are suitable for owners of private houses, but in multi-apartment buildings they are usually not applicable. Why, after all, it would seem possible to carry out work on the technical floor above the apartment? It's simple.
Communications are laid on the technical floor of the house, to which repair teams from housing maintenance offices must have unhindered access. There are also fire safety rules that must be followed to avoid putting yourself and your neighbors at risk.
That's all, dear reader. I hope the information was useful to you. And don't forget to tell your friends about us on social networks. Good luck with the renovation work and see you next time!
What is it and why
Vapor barrier is a specially laid material that does not allow moisture to penetrate into the structure protected from it. To put it simply, it is a thin film through which water cannot penetrate. In a ceiling situation, it prevents warm, moist air rising from leaving the room. To create a vapor barrier layer in different situations, you can use different materials:
- Plastic film or glassine
- Special films with membrane effect
- Liquid mastics and varnishes designed to create a vapor barrier layer
- Foil types of insulation
Some of them simply create an impenetrable barrier and prevent water from entering the insulating layer or settling on the cold surface of concrete floors. Other vapor barriers are capable of allowing some air to pass through, but retain moisture. Films with a layer of foil applied prevent moist air masses from passing through them and have another function - they reflect some of the heat back into the room.
Required Tools
To carry out thermal insulation work, you will need tools such as: fasteners (screws, screws, dowels, anchors, liquid nails), construction staples, tape measure, hammer drill for working with concrete, screwdriver, hammer, construction knife for cutting sheet products.
The material used is insulation, vapor barrier film or membrane, metal profiles to create a frame, wooden blocks 3x3 cm or 5x5 cm.
Polyethylene and glassine
These insulating agents create a barrier that is impermeable to moisture. However, they not only prevent water from getting into the insulating layer or getting on cold floor structures, but also prevent air circulation. Therefore, in a room with polyethylene or glassine as insulation from moisture on the ceiling, it is necessary to install a ventilation system to ensure normal air exchange.
Installation of ventilation systems- Pipes for internal sewerage
How to choose a window sill?
There are not too many advantages of such insulators, but to be precise, there is only one thing - price. Both polyethylene and glassine are very inexpensive. At the same time, polyethylene lasts quite a long time, while glassine is characterized by fragility and rapid wear.
Membranes
These are special materials with limited breathability. They allow air to pass through, but retain moisture. The most common and popular vapor barrier of the Izospan brand has a characteristic feature - a fleecy surface on which tiny drops of condensate accumulate and evaporate quite quickly.
The cost of such materials will be higher than that of polyethylene with glassine, but the efficiency of moisture removal is much higher, and air exchange remains within the normal range. At the same time, there are certain features of the installation of such membranes - to remove moist air vapors, a ventilation gap is necessary. Therefore, the installation of a decorative ceiling covering on the side of the room is carried out on a sheathing or frame, which will create the necessary space for ventilation.
Liquid coatings
A fairly new solution, created thanks to the achievements of chemists. Looks like regular varnish or mastic. It is applied to the surface in the same way as conventional paints. After drying, a special coating is formed that can allow air to pass through, but prevent the passage of water vapor. Such materials are often used to vaporize the ceiling on the cold attic side.
In addition, this will be a very effective solution if flat roofs are treated in buildings that do not have an attic. In this case, a suitable insulation is laid on top of the applied insulation and the entire structure is waterproofed. In some cases, such materials may be harmful to health and can only be used in non-residential premises. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of the selected paintwork material.
Insulation technology
How to insulate the attic floor so that there are no problems in the future? In general, the technology for do-it-yourself thermal insulation is almost the same. But the methods of its installation depend on the specific situation.
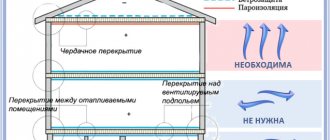
Insulation of the attic floor is carried out in the presence of a cold attic. Thermal protection of the structure is carried out from above, since in this case the thermal insulation is most competent. But in some cases, another scheme is used - protection from warm air.
The answers to the question why insulation from the ceiling side of the upper floor is undesirable can be the following disadvantages of thermal protection from below:
- the insulation only protects the ceiling, and the ceiling remains cold;
- doing work from below with your own hands is quite labor-intensive;
- the point of condensation moves inside the floor pie, which can lead to rotting of the structure along the wooden beams.
It is also important to maintain the correct order of all related materials.
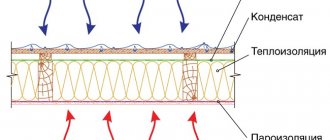
When insulating, you need to remember one rule: the vapor barrier is always located on the warm air side, and the waterproofing on the cold air side.
Incorrect placement can lead to the following problems:
- insulation getting wet;
- condensation on the ceiling surface;
- rotting of the ceiling of a cold attic along wooden beams.
Whether vapor barrier and waterproofing is needed depends on the chosen insulation.
Cold attic design
When building the roof of a house, many people think about making a cold attic or attic underneath it? The easiest way to organize a roof is with a cold attic space. Construction of an attic will cost several times more and require more labor.
. Although, it is undeniable that the attic will significantly expand the living space.
Cold attic roofs have the following main components in their pie:
:
Installation of PVC windows- Covering the drain hole with your own hands
- How to lay flexible tiles on the roof?
- roofing;
- attic external walls (applicable for gable roofs with gables);
- insulated ceiling between the living space and the attic.
Ventilation is provided by eaves and ridge vents. The air passing through the eaves openings is called supply air, and the air leaving through the ridge is called exhaust air. Additionally, ventilation can be done through dormer windows on the gables or roof slopes. The windows are equipped with louvered grilles to allow the ventilation intensity to be adjusted.
Dormer windows are located on opposite slopes of the roof so that there are no unventilated areas.
Dormer windows can be rectangular, triangular and semicircular in shape. Their lower part should be at a height of no more than 0.8-1.0 m from the floor of the attic, and the upper part should not be lower than 1.75 m from the floor in the attic. They can also serve as an exit to the roof of the house to inspect the roof, ventilation and chimney elements.
Possible mistakes
Before you build a roof on a house, you should consider the following nuances:
it is important to correctly determine the dimensions of the floor spans; if the building has a sufficiently large width, then it is necessary to choose a rafter leg of the maximum cross-section; in order to prevent deflection of construction legs when using rafters of small cross-section, the truss must be equipped with additional support posts and other elements; when calculating the roof, wind loads should be taken into account; for this, the rafter legs must be secured with brackets; The density of the sheathing (sparse, solid) depends on the type of roofing.
Steam and thermal insulation of a cold attic
For a roof with a cold attic, it is most important to minimize heat loss through the attic floor
. For both wooden and reinforced concrete floors, a vapor barrier is mandatory. It is laid on the ceiling itself and protects the insulation from vapors that can condense in the heat insulator after passing through the ceiling of the living room. Slab and bulk materials can be used as insulation. The ceiling pie consists of a vapor barrier, floor beams and insulation.
The following types of heat insulators are often used in ceiling coverings:
:
- expanded polystyrene and foam boards;
- mineral wool slabs or mats;
- expanded clay granules;
- fuel or granulated slag;
- sawdust with lime or clay;
- pumice.
The thickness of the required insulation layer is selected depending on the estimated winter temperature using the table below.
How to properly lay a vapor barrier on the ceiling?- Is it possible to glue wallpaper on whitewashed walls?
- Imitation of a brick wall made of gypsum plaster
Winter temperatures are calculated according to SNiP 2.01.01-82 (building climatology and geophysics) or selected by regions of the Russian Federation from the corresponding climate maps.
The insulation is laid between the joists or ceiling beams, and a boardwalk is made on top for the attic passages. Joists are usually 50 mm thick, and decking boards are 25-35 mm thick.
For ventilated attic spaces, soft or semi-solid heat-insulating materials are considered the most optimal.
Attic waterproofing device
Waterproofing roofs with a cold attic, according to many experts, is a controversial issue. Some say that waterproofing must be present under the roofing material, while others categorically recommend that it be abandoned. Here, a lot depends on the type of roofing material and the angle of inclination of the roof slopes.
Metal roofs are most susceptible to corrosion, which occurs due to possible small leaks or condensation
.
Therefore, we once again draw your attention to the fact that ventilation plays one of the main roles in the fight against condensation.
.
For flat metal roofs, experts recommend installing superdiffusion membranes. It will prevent moisture from entering the outside of the roof when snow or rain blows in. No matter how well the roof is laid, there is always the possibility of minimal leaks. That is why, by paying a little extra, you will receive additional protection from moisture getting on the insulation in the ceiling of a cold attic.
Possible leaks or condensation entering hydrophobic insulation materials significantly reduce their thermal insulation properties.
If, for example, slate is used as a roofing material, then waterproofing can be abandoned. There is also corrugated sheeting with an anti-condensation coating on the market, which can hold up to 1 liter of water per 1 m2. For our part, we recommend always using waterproofing membranes, because this is the cheapest and easiest additional way to protect your roof from possible leaks
.
When installing waterproofing membranes, a counter-lattice is used. It serves as a fixing strip and, due to its height, provides the necessary clearance for ventilation of the under-roof space. The installation of lathing in a cold attic is no different from insulated roofs. The dimensions of the sheathing and its pitch determine the type of roofing being installed.
Cold attic temperature
To prevent ice and icicles from forming on the roof, it is necessary to maintain the correct temperature and humidity conditions in the attic. If the thickness of the thermal insulation material is insufficient, significant heat losses occur through the ceiling. Warm air, heating the roof covering, causes snow to melt and ice dams to form. By choosing the right insulation layer, this can be avoided.
The effectiveness of a heat insulator can be assessed by measuring the temperature of the top layer of insulation. The electronic thermometer is immersed in insulation by 10-20 mm. The temperature readings taken should correspond to the values in the table below.
As you can see, the design of a cold attic pie is not particularly complex in design. The main task is to ensure the necessary intensity of ventilation and the thickness of the thermal insulation layer in the ceiling.
We will install copper roofing quickly and efficiently
Ventilation options in a private house
Ventilation of the room is necessary in order to create optimal conditions for people’s lives and the existence of furniture and equipment located in the house.
If in apartment buildings everything has already been done by the specialists who erected the building, then during the construction of private real estate this issue is often overlooked.
Sometimes the installation of ventilation ducts is considered a waste of time and money. However, they are an obligatory part of the project implementation, ensuring favorable living conditions and long service life of building structures
This is a fundamentally erroneous opinion. Musty air, sweaty windows, unpleasant odors from bathrooms and the aromas of fried food, along with fumes, will enter all rooms and even the bedroom. Without a properly designed and assembled ventilation system, the comfortable life of the inhabitants of the house will be at risk.
Ventilation in a private house can be:
- natural;
- mechanical;
- mixed.
The first type is based on the natural process of circulation of air masses. No mechanisms are used to pump air into the house. It comes from the street, penetrating through micro-ventilated windows or supply valves arranged in the most suitable places.
In rooms of the house that do not have valves installed, air circulates through doorways and through cracks between the door and the floor.
Exhaust air also leaves the house naturally through ventilation shafts located in one of the walls of the house (+)
With the mechanical type of ventilation device, fans and special supply equipment are used. The required volume of clean air is supplied to each room of the building, and exhaust air is discharged outside. This is a more complex system used for large country houses and cottages.
The mixed ventilation option involves the use of the first and second types. This could be the installation of mechanical supply valves in combination with a natural exhaust system for removing air through ventilation shafts in the bathroom and kitchen. Or vice versa - the influx is natural, and mechanical equipment is used for removal.
A mechanical ventilation system with forced air movement consists of equipment that requires periodic repair or replacement. Most often you need to change filters (+)
The main advantages of the natural type:
- energy independence;
- the cheapest cost;
- does not require repair;
- minimal maintenance;
- you can organize it yourself.
In addition to the positive aspects, this type of ventilation has significant disadvantages. If everything were perfect, then other arrangement options simply would not be used. The main disadvantages are dependence on air temperature and weather conditions, limited service area.
In other words, with natural ventilation in the hot season, you can forget about the existence of a ventilation system in the house
The mechanical system is easy to use, because it can serve any area of the house/cottage and is completely independent of the weather. Moreover, it can be controlled at your discretion, maintaining a comfortable temperature in the rooms.
Many forced ventilation systems that have sensors to monitor the state of the microclimate in the room are controlled using a remote control
Additional opportunities for heating the incoming air, ionizing and humidifying the air masses of the room, etc. can be organized by installing appropriate equipment in the ventilation system.
The main disadvantages of the mechanical ventilation method:
- higher cost of equipment;
- the need for repair and periodic replacement of individual system elements;
- dependence on electricity supply;
- Professional installation and configuration of equipment may be required.
Considering the positive and negative qualities of ventilation types, a mixed type is most often used for country houses and cottages. This is justified from an economic point of view and is quite doable with your own hands.
Ceiling vapor barrier in a cold attic
- Features of the design
- Types of materials
- Film vapor barriers
- Foil materials
- Liquid products
- Adviсe
A vapor barrier is a practical solution to the problem of ceiling condensation in homes with a cold attic. The material prevents the penetration of moisture, protects floors from condensation and further destruction, and also prevents the appearance of mold and mildew in insulation boards.
Variety of roofs
A non-specialist can easily confuse a hip roof with a hip roof. Source bazaznaniyst.ru
A complicated version of a gable roofSource yandex.ru
Sloping roof for a house with an atticSource biznes-stroi.ru
Conical roof on the rounded part of the houseSource stroi-remontirui.ru
A combination of old and new - a gable roof on a house in modern style. Source fasad-master.com.ua
A complex multi-tiered roof looks very impressiveSource mirstrojka.ru
A few more beautiful and practical types of roofs in the following video:
Features of the design
A cold attic includes the surface of a gable roof with roofing material and an insulated ceiling that separates the living space from the attic. To ensure ventilation, the attic is equipped with dormer windows, without which the air exchange in the attic will be disrupted, which will lead to the formation of condensation on the roof.
The floor of the attic is the ceiling, which also serves as the ceiling of the living space. When street temperatures drop, the ceiling becomes susceptible to condensation, the formation of which is caused by the temperature difference between its lower and upper parts. To prevent droplets of condensation from penetrating into the ceiling, the top is covered with special materials that do not allow water to pass through.
In addition to protecting the base from moisture, the material performs an important thermal insulation function, preventing warm, moist air from rising upward. This technology significantly reduces heat loss in a living space and allows significant savings on heating. Vapor barrier must be performed on all types of foundations, including concrete and wooden floors. Isover slabs, glass wool or bulk materials can be used as insulation.
Types of materials
Before the advent of modern polymers, high-fat clay was used to vaporize the ceiling in a cold attic. Its disadvantage was its rather large weight and labor costs during installation. Today, the construction market offers a large selection of vapor barriers, differing in release form, installation method, properties and cost.
Film vapor barriers
Film vapor barriers are the most popular and sought-after type, which is represented by polyethylene and polypropylene films and membranes:
- Polyethylene is the most widely used. This inexpensive and practical material reliably prevents the penetration of steam, but has limitations in use. It is recommended to use this type of film only in warm climates under moderate temperatures: under the influence of extreme influences, it quickly loses its performance properties and is destroyed. The disadvantages include the low strength of polyethylene, which can lead to ruptures of the material even at the installation stage. Glassine, often used as a vapor barrier, is very similar in its properties to polyethylene: it also retains moisture well, but does not allow air to pass through at all.
- A more practical type of vapor barrier is polypropylene . This film tolerates thermal shocks well and is highly resistant to ultraviolet radiation. The service life of this material is several times higher than that of polyethylene. Modern technologies make it possible to produce film with the addition of viscose and cellulose. This significantly increases the strength and hygroscopicity of the material. A prerequisite for using such a vapor barrier must be the presence of good ventilation.
The water accumulated and retained by the pores of the material must evaporate freely, otherwise the properties of the material will be disrupted, which will lead to moisture in the ceiling.
- The most modern and practical type of vapor barrier material is membranes. The insulator is designed in such a way that the ability to pass steam is possible only in one direction. Thanks to this property, moisture is quickly removed, and air is exchanged between the ceiling and the attic room. In the domestic construction market, the most famous is the Izospan model, the fleecy structure of which is capable of retaining condensate droplets and quickly evaporating them. Installation of a membrane coating requires the formation of a ventilation space designed to provide room for liquids to evaporate.
Foil materials
This type is intended for operation in conditions of high temperatures and is used in the construction of baths as a vapor barrier for wooden floor beams. The insulating material is a film covered on one side with a thin layer of foil. Thanks to this structure, the material is able to reflect thermal radiation and retain steam well. There are several varieties of it:
- The most budget option is foil kraft paper. The material fits well, but during long-term use it is susceptible to the appearance of mold and mildew. The disadvantages include its low hygroscopic properties.
- Dacron-coated kraft paper can withstand temperatures up to 140 degrees. This allows it to be used as a vapor barrier material in the construction of baths. The disadvantages include low resistance to chemical compositions of detergents.
- Foil fiberglass fabric is considered the highest quality vapor barrier, and is characterized by increased strength and long service life. The downside is the high cost of the material.
Liquid products
Liquid means for providing ceiling vapor barrier are represented by varnishes and mastics. The compositions are applied to the surface of the ceiling and, after complete drying, form a thin film that can retain moisture and allow air to pass through. This promotes good ventilation of the floors and significantly reduces the likelihood of mold and mildew.
Some liquid products are intended only for use in non-residential premises and, if in contact with them, can cause harm to health, therefore, when using them, personal protective measures should be observed
Basic requirements for arrangement
In order to correctly carry out the work of creating a reliable layer on the attic floor, which will perform a protective and insulating function for the main premises of the building, you need to purchase and use only high-quality materials from trusted manufacturers . They must have labeling, instructions for use and a quality certificate, and also meet the following technical requirements:
- Possess high strength and density properties.
- Be manufactured in an industrial environment from environmentally friendly and high-quality raw materials.
- Comply with the declared characteristics from the manufacturer.
- Be resistant to water and repel condensation formed due to changes in atmospheric temperatures.
Protect from noise and extraneous sounds.- Be non-flammable and resistant to fire for 1.5-2 hours.
- Lay according to the spacing between the beams, with a minimum distance of 4 (m).
- Comply with the thickness specified in the work project.
- Must withstand a certain load.
- They are easy to install, as they adhere to any surface.
- Create a level surface over the subfloor.
- Shouldn't be expensive.
The installation of a pie in the attic is primarily based on compliance with the technical part. All work is subject to general regulatory documents , which provide references to all lower standards. This:
- GOST 4981-87;
- SNiP II-26-76;
- GOST 17177-94;
- SP 31-105-2002;
- GOST 31309-2005;
- GOST R 52953-2008;
- GOST 31913-2011;
- SP 17.13330.2011;
- GOST 32603-2012;
- GOST 26434-2015;
- GOST 12767-2016;
- SP 17.13330.2017.
The higher quality and better the finishing layers for the floors are made, in compliance with the technology and sequence of work, the longer the coating will last in a cold or warm attic.
Insulation, vapor barrier, waterproofing and finishing help create additional space for arranging additional space, which is useful for any purpose.