When manufacturing a single interior detail or implementing an entire renovation and construction project, you should adhere to precise technology. Each manufacturer of relevant materials, mixtures and parts provides a number of recommendations for the use of their products, adhering to which you can achieve the expected effect during operation and fit within the guaranteed period of use of the final product. Knauf system partitions can be considered one of the most striking examples in the construction products market, where the above axiom really works.
Types of partition structures
Why Knauf? This brand is known to many, but when renovating, not everyone decides to purchase materials from this brand, as they are afraid to go beyond their budget. Having examined the construction of partitions made from Knauf sheets, you will understand whether this method is for you, why it is remarkable, and how much repairs using this system will cost.
To understand the essence and differences of these partition structures from other options, it is worth getting acquainted with their types.
There are four types of such structures:
- Partition model W111;
- Partition model W112;
- Partition W113 (fireproof);
- Security wall W118.
Each of these types has its own characteristics.
Installation of partitions using the Knauf system - W 111
This structure consists of a frame, which is covered on both sides with sheets of plasterboard. A layer of sound insulation must be placed inside the structure.
Guide profiles are fixed to the ceiling, walls and floor, using dowels. After covering the gypsum plasterboard, the joints are sealed with a special compound “Uniflot”. The places where the walls come into contact with the ceilings are sealed.
It happens that the structure reaches a length of 15 m, in which case movable seams will have to be made in it. Thanks to them, the partition will be able to expand linearly. To do this, two posts are placed at the seam.
An insulating material is always placed between the profiles, and a metal profile with an elastic liner inside is placed in the spaces between the plasterboard sheets.
You can also consider special cases of such partitions made of gypsum plasterboard:
- For example, a rack profile has a size of at least 75 mm, then the installation of a moving seam has such a feature - it is placed between two additional racks. They will be smaller in size than the main racks, the difference will be about 25 mm. Then the plasterboard sheets will have a thickness of 12.5 mm, this will compensate for the difference.
- If this room also has a suspended ceiling, then in order to mitigate the possibility of subsidence of the ceiling structure, the partition is attached with a movable connection.
Dependence of sound insulation of a partition on its design
Next, you can consider the differences between other types of Knauf partitions
Finishing
The formed partition plane is a rough surface and is subject to facial finishing. Wallpapering, painting with water-based paints or tiling can be used as cladding.
In any case, the entire surface will have to be puttied and leveled to the level of the seams. Before puttying, it is advisable to treat the entire surface with a primer, and after it dries, putty the screw heads.
Wallpaper
The putty is applied in a thin, even layer. The starting layer will be sufficient for subsequent wallpapering with preliminary priming with wallpaper glue according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Painting
Before painting, the wall must be brought to perfect condition. To do this, a finishing gypsum solution is applied over the dried starting layer. After drying, sanding with a float and the obligatory primer are carried out. If you neglect the primer before painting, the paint on the seams and between them will be absorbed unevenly, resulting in stains.
Tile
For facing wall tiles, an ideal surface is not required and you can limit yourself to only a starting layer of putty. It should be borne in mind that tiles are usually used in damp rooms, and these are favorable conditions for the growth of fungi. Therefore, before puttying, the primer should be made with a special composition containing a fungicide.
Before laying, the wall is covered with a special waterproofing compound intended for subsequent laying of tiles. The composition is applied with a brush, preferably in 2 layers. The tiles are laid after the waterproofing has dried using tile adhesive, just like on other surfaces in damp rooms.
Partition W112
It also consists of a metal frame and plasterboard sheets, with which the frame is sheathed on both sides. Between these sheets there is a soundproofing layer. The height can also be different, depending on the design objectives.
Installation techniques are similar to those above. The subtleties in which the differences lie are that the structure is sheathed on both sides with additional gypsum boards. This is done in order to improve the soundproofing qualities and increase the fire-resistant properties of the device.
Fasteners
Profile connection work is performed using the following elements:
- Multi-level transverse connector for PP profile (60×27). It is sold flat, so it must be bent before installation.
- Single-level cross connector "Crab".
- One-way cross connector. The upper side clings to the supporting profile.
- A rotating multi-level connector that allows you to connect the supporting profile at any angle.
- Longitudinal single-level connector. It is used when it is necessary to increase the supporting profile.
- Universal connector. Necessary in order to connect the supporting profile in one plane at any angle.
Connectors
The work of installing the frame on the Knauf ceiling is carried out using the following elements:
- Straight U-shaped suspension.
Important! Not everyone knows that U-shaped hangers are produced under the profile and under the beam. Although they are similar in appearance, they have different nominal sizes after folding the side strips. For wood it is 50 mm, and for a profile – 60 mm.
- Anchor suspension with adjustable clamp, quick suspension. They are similar due to the presence of a fastening rod. Its length can reach 1500 mm, which allows you to adjust the required ceiling gap in a wide range. The disadvantage is that the load is limited to 25 kg. This is considered a low figure, since all average calculations in the Knauf technical map are based on a load of 40 kg.
Vernier suspension
- Adjustable vernier suspension. It is a telescopic structure made of two parts. Designed for a load of 40 kg.
- A combined suspension, in which there is both a rod and a retractable element of the vernier suspension.
- To connect metal elements, you need an LN screw (with a sharp tip) and an LM screw (with a self-tapping tip).
- Installation of a heavy profile in the P131 system is carried out using FN self-tapping screws.
- Installation of guides to the wall is carried out with metal or nylon dowels.
- Installation to hollow structures in a sheet of Knauf plasterboard is performed with multifunctional dowels or butterfly dowels.
- Installation of attachments to the sheets is carried out using a dowel with a screw thread.
- Drywall is screwed with TN screws (in a standard profile) or TB (in a thick sheet profile). The MN screw is used for screwing into a gypsum fiber sheet.
Partition W113
The partition includes the same metal frame, which has a three-layer gypsum board sheathing. There is a non-flammable sound insulation layer inside the device. It is laid between sheets of drywall.
Since the design is distinguished by a three-layer cladding, the distance between the fixation of the guide profiles will be no more than 500 mm.
The surfaces of air ducts pass through such partitions; they must have reliable fire protection. This is often an enclosure with a fire resistance rating greater than 0.5 hours.
PDF instructions KNAUF
You can view and download the technologies described above in PDF KNAUF instructions here (https://yadi.sk/i/P71YZKJ13P35fD) (Yandex.Disk) or here (https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BxOOL1biI_jQS2hLczlQTVlRQk0/view ?usp=sharing)(Google Drive).
The instructions include the following technologies:
- C625 Metal frame with single-layer cladding, weight 16 kg/meter;
- C626 Metal frame with two-layer cladding, weight 27 kg/meter;
- C612 Parallel grooves for facing curved structures without a frame and on a frame;
- C612 V-shaped corners;
- C611 Frameless system KNAUF-sheet with glue.
Gipsokart.ru
Security wall W118
This type of device is reminiscent of the design features of the W113. But W118 differs in that a galvanized sheet half a millimeter thick is placed between the sheets of drywall. The installation of this structure requires strict compliance with the requirements prescribed for fire walls.
This type of partition has a reinforced frame, which is made of PS 100 metal profile. The thickness of this profile is not less than 0.6 mm.
Security wall
Factors influencing the choice of the type of complete partitions
The manufacturer of German construction products offers its consumers a large selection of kits for installing plasterboard partitions. Today there are more than twenty types of partitions. They are marked with the letter “C” with a prefix of the corresponding number (for example, C 111, C 115.2, etc.).
The specific type that should be applied to the room will depend on several factors:
- total height of the room;
- permissible noise level;
- expected additional load on the wall;
- condition and type of material of the base mounting surface;
- the need to store/hide communication systems in the box;
- presence and type of door (pendulum, swing, sliding);
- required partition height;
- humidity and temperature levels;
- type of room and its functional purpose.
Partition selection
Application area
In accordance with the requirements of current regulatory documents on fire safety, fire partitions are provided in the following cases:
- for common corridors, halls, foyers, lobbies and galleries in public and administrative buildings with a height of more than 28 meters;
- for airlocks;
- to separate the volume of a multi-light space from adjacent rooms and corridors in buildings of functional fire hazard classes F1.1, F1.2 and F2-F4, for example, for placing open staircases, escalators, atriums, etc.;
- for separating storage rooms and control towers in airport buildings;
- for dividing hospital buildings into sections depending on the number of storeys and with a standardized area;
- for the placement of sleeping quarters intended to accommodate families with children in the buildings of holiday homes, campsites, motels, boarding houses, sanatoriums, recreation and tourism institutions (with the exception of hotels);
- on evacuation routes to separate corridors longer than 60 meters into a section of shorter length;
- to provide smoke protection on smoke-free staircases of type H2;
- for organizing safe evacuation through staircases of type L1 in industrial, warehouse and agricultural buildings of categories G and D;
- for separating lobbies with type 2 staircases from corridors and other rooms;
- to organize safe evacuation through staircases that are designed for evacuation from both above-ground floors and from the basement or ground floor;
- to divide corridors into sections no longer than 42 meters in ward buildings of medical institutions;
- for separating corridors connecting stairwells in three-story buildings of preschool institutions;
- to organize safe evacuation through one staircase of buildings of classes F1.2, F3 and F 4.3;
- for separating escape routes in buildings with a height of 28 meters or more of classes F1.2, F2, F3 and F4;
- in corridor-type multi-apartment residential buildings to divide corridors into sections less than 30 meters long;
- for separating cross passages from shelving structures in buildings of class F5.2;
- for the construction of stairs connecting basement or ground floors with the first floors of buildings of functional fire hazard classes (except for buildings F1.3 over 5 floors);
- for the allocation of catering units, as well as parts of buildings, groups of premises, or individual premises for production, storage and technical purposes (laundries, ironing, workshops, storerooms, electrical switchboards, etc.) in buildings of class F1.1 and F 1.2;
- for the arrangement of public built-in and built-in-attached premises in the basement, ground, first, second (in large, largest and super-large cities and third) floors of multi-apartment residential buildings;
- for dividing multi-apartment residential buildings into sections, as well as constructing inter-apartment walls and partitions;
- for dividing technical, basement floors and attics into sections with an area of no more than 500 m2 in non-sectional multi-apartment residential buildings;
- when installing solid fuel storage rooms on the ground or first floors in residential buildings with stove heating;
- to allocate a waste collection chamber in multi-apartment residential buildings, as well as administrative buildings;
- for the allocation of premises for production and technical purposes (premises for technological maintenance of the demonstration complex, workshops, restoration rooms, kitchens, electrical switchboards, etc.), warehouse premises (storerooms for flammable goods and goods in flammable packaging, book depositories, etc.) at cultural facilities - entertainment purposes;
- when arranging premises for stage lighting in auditoriums;
- when installing projection rooms in extensions, designed to be equipped with film projectors with incandescent lamps, in buildings of cultural and entertainment facilities of IV and V degrees of fire resistance
- when constructing an orchestra pit in buildings of cultural and entertainment institutions;
- for dividing into sections with an area of no more than 600 m2, storage and book depositories of libraries;
- for the allocation of premises (except for premises of categories B4 and D) for production, storage and technical purposes (kitchens, bakeries, pre-cooking, cutting, storage of flammable goods and goods in flammable packaging, etc.), including from the hall for visitors with an area 250 m2 or more in buildings of classes F3.1 and F3.2;
- for the allocation of premises (except for premises of categories B4 and D) for production purposes (laboratories, premises for the preparation of medicines, workshops, etc.), as well as storage facilities (storerooms for medicines and medicinal materials, storerooms for equipment, flammable goods and goods in flammable packaging etc.) and technical premises at facilities of classes F3.4, F3.5, F3.6;
- to allocate a complex of premises for built-in baths (saunas) built into buildings for other purposes;
- for the allocation of premises (except for premises of categories B4 and D) for production and warehouse purposes, technical premises (laboratory premises, rooms for labor training, workshops, storerooms of flammable materials and materials in flammable packaging, library book depositories, server rooms, electrical switchboards, etc. ) on objects of classes 4.1, F4.2, F4.3;
- for separating administrative extensions of I and II degrees of fire resistance from industrial buildings of I and II degrees of fire resistance;
- for separating inserts and build-ins from industrial premises of categories B1-B4, G and D in industrial and warehouse buildings of I, II and III degrees of fire resistance classes C0 and C1, III degree of fire resistance class C0;
- when constructing premises of categories A and B with a total area of no more than 300 m2 In one-story buildings of IV degree of fire resistance, fire hazard class C2;
- to separate premises of different categories A, B, B1, B2, B3 from one another, as well as these premises from premises of categories B4, D and D and corridors in industrial buildings;
- in industrial buildings to divide basements with premises of categories B1-B3 into parts with an area of no more than 3000 m2 each, as well as to separate these premises from corridors;
- in warehouse buildings and areas under sheds for storing petroleum products in containers, for dividing into compartments (rooms), as well as for separating these rooms from other rooms;
- for separating rooms for valve units from rooms for pumps in oil and petroleum products warehouses;
- to separate the premises of food pumping and storage facilities for storing petroleum products in containers and tanks of the consumable warehouse from other premises;
- in cable basements and cable floors of basements, in case of their protection with volumetric fire extinguishing means, for division into compartments with a volume of no more than 3000 m3;
- for the installation of exit chambers from inter-shop cable tunnels of production facilities;
- in tunnels intended for laying oil pipelines, to divide them into compartments no more than 150 meters long;
- in cable tunnels for division into compartments no more than 150 meters long, and with oil-filled cables - no more than 120 meters;
- in places where pedestrian galleries adjoin reloading nodes in the structures of production facilities;
- in places where closed cable and combined galleries meet, as well as in places where they adjoin production premises, structures and buildings;
- for the installation of premises of gas distribution substations;
- in places where galleries and overpasses adjoin buildings and premises of categories A, B and C, transshipment centers of timber warehouses;
- for separating built-in and roof boiler rooms from adjacent rooms and the attic;
- for separating boiler rooms built into buildings from production premises;
- for separating the above-bunker fuel supply galleries of boiler rooms from boiler rooms;
- for arranging exits from built-in and attached boiler rooms through common staircases;
- in single-apartment residential buildings, including blocked ones, to allocate parking spaces;
- when placing premises in the parking lot for car service (maintenance and repair stations, diagnostics and adjustment work, washing, etc.) for their separation;
- in underground car parks for cars, to separate car storage rooms from car park maintenance rooms, including service rooms for duty and maintenance personnel, fire extinguishing and water supply pumping stations, transformer substations (only with dry transformers), storage rooms for customer luggage, rooms for the disabled ;
- for the installation of separate boxes in buildings of above-ground parking lots of closed type cars of I and II degrees of fire resistance;
- in buildings of refrigerators of I-II degrees of fire resistance class C0, to separate the premises of the machine and equipment rooms of ammonia refrigeration units from other premises;
- for separating built-in production, administrative and household premises from other premises of refrigerator buildings;
- to separate the premises of the control units of water and foam fire extinguishing installations from the premises they protect;
- for separating the premises of pumping stations of water and foam fire extinguishing installations from other premises;
- to separate the premises of fire extinguishing stations of gas fire extinguishing installations from other premises;
- in buildings of children's institutions, dormitories and public catering establishments with stove heating for the installation of partitions within the setback;
- to separate rooms intended for ventilation equipment from other rooms;
- to separate the premises of fire pumping units and hydropneumatic tanks for internal fire water supply from other premises of the building;
- enclosing structures of elevator shafts located outside stairwells and elevator machine rooms;
- for separating central and local heating points built into buildings and structures from other premises;
As you can see, this is an incomplete list of places where fire barriers should be installed. Requirements for the placement of fire partitions are also established by numerous departmental standards and design rules for various facilities.
Advantages
On the territory of the post-Soviet countries a couple of decades ago, the word “European-quality renovation” was strongly associated with the exotic material “plasterboard”. This and other related products of its production were first launched on the market of new generation building materials by the German company Knauf. At the same time, the leading specialists of the enterprise developed detailed instructions for the construction of suspended, frame and frameless structures lined with plasterboard sheets. High quality products combined with a properly selected set of marketing techniques allowed the company to quickly become a leader among its competitors.
Today, the Knauf company produces a whole range of kits for the manufacture of partitions, which, depending on the purpose, have different configurations. A step-by-step and detailed explanation of the installation process allows you to install Knauf system partitions with your own hands, without wasting time studying the building materials market and independently searching for the required structural components.
Also, the convenience of such kits lies in the ease of calculating the cost of one square meter of the finished product. In addition, determining the consumption of materials is also not difficult.
One of the important advantages of the set is the elimination of the “forgetfulness” factor. All necessary basic and additional parts are included in the kit.
Drywall sheets
The plasterboard used for installing Knauf system partitions has several types.
Depending on the conditions of use, as well as the properties of this cladding material, the following are distinguished:
- ordinary sheets (gypsum board);
- fireproof (GKLV);
- moisture resistant (GKLV);
- combined (GKLVO).
In addition, externally the sheets differ from each other in the type of edge, depending on the method of processing technological joints:
- PC – straight edge;
- ZK – rounded edge;
- UK – edge, thinned on the front side;
- PLUK - an edge that has a thinned and semicircular edge on the front side.
- PLC – round edge on the front side.
Depending on the area of application and the required dimensions of the final product, plasterboard of various dimensions is used for installing partitions:
- Length: from 2000.0 mm to 4000.0 mm.
- Width: 600.0 mm and 1200 mm.
- Thickness: from 6.5 mm to 24.0 mm.
Drywall sheets
Finishing work
At the end of the cladding, the manufacturer proposes to enhance the properties of gypsum fiberboard by additional surface treatment with water-repellent compounds (Tiegenrgund primer) and Uniflot or Fugenfüller putty.
If all requirements and recommendations are met, the installation of partitions, walls or ceilings using Knauf materials will be successful and durable. But remember when installing gypsum boards: the smoother you set the profile structure, the smoother the surface will be in the end.
Source
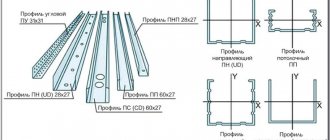
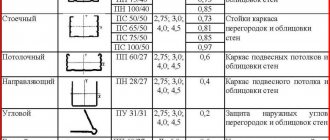
Metal profiles
They are metal products made from a sheet of rolled steel with a galvanized coating. Used to construct a frame for plasterboard partitions. The standard length of these elements varies from 2750.0 mm to 4500.0 mm.
The parts have grooves on top, giving the finished structure additional rigidity.
To install the base under drywall, two types of profiles are used: guide (NP) and rack-mount (SP). They must have comparable cross-sectional dimensions.
A feature of Knauf guide profiles should be considered the presence of holes in them for fastening, which makes it possible to reduce the deformation coefficient of the part and, to a large extent, reduce the time for installing the frame.
The functional task of these metal elements is to hold the rack profiles in a given direction, as well as to impart rigidity to the plasterboard partition as a whole. In addition, it is used to make lintels inside the structure.
Metal profiles
Purpose and content of the technical map
If for an amateur GOST and SNiP are a “dark forest”, then for a professional the technological map is a universal guide on how to technically and quickly assemble a frame and screw drywall.
- This instruction will save the master from studying these very norms and requirements and will speed up the delivery of the work to the customer. If you follow all recommendations, the work will comply with fire and environmental safety standards, GOST, SNiP requirements.
- The Knauf technological map contains tables with ready-made initial data of the main components of the frame structure for the ceiling.
Ceiling Knauf
Important! If the work is performed under a contract, then when placing and submitting an order you cannot do without the recommendations of the Knauf technical map for drawing up project documentation.
- The manual specifies the required material and algorithm for assembling a frame of one type or another, and describes methods for performing individual design tasks.
The latest current Knauf technological map (series 1.045.9-2.08.1) is comprehensive on how to design and install a suspended ceiling structure under plasterboard and gypsum fiber boards. All work is divided into separate sequential stages, so understanding the technology will not be difficult.
Rack profile
The cross section of the part is C-shaped. The joint venture is installed vertically.
Fixed by a guide profile using one of three methods:
- end-to-end;
- nozzle method;
- using the “cut-off with fold” method (used most often).
The side walls of the rack profile have holes designed for easy installation of electrical wires.
Rack profile
Wood slats
Designed for the manufacture of a wooden frame for a plasterboard partition. These elements, as a rule, have a square cross-section. Just like a metal frame, a wooden one has guides and rack parts. Vertical frames must be installed at the same distance from each other (as a rule, the spacing of the racks is 30.0 or 40.0 cm).
Knauf specialists strongly recommend treating the bars with special means that protect the frame from external factors and impart fire-resistant properties to the product.
The moisture content of the material used for the wooden base should be within 10-12%.
Additional components
In addition to the listed main elements of the Knauf system partitions, various fastening elements are also used, the type of which will depend on the difference in the general level of the base plane, as well as the material from which the fastening surface is made and the degree of its wear.
To improve the soundproofing properties of the partition, the voids in the frame must be filled with appropriate material. The German manufacturer recommends using mineral and fiberglass fillers that meet sanitary and epidemiological standards with a high noise absorption index.
Fasteners
Installation technology
Installation of this design is certainly similar to standard installation. But still, the technology has its own characteristics that I would like to focus on.
Features of installation of partition structures using the Knauf system:
- Knauf designers have developed some recommendations that must be followed at all stages of installation;
- Knauf partitions are supplied with guides (upper and lower), as well as racks; their width depends on the weight of the structure and the height of the room;
- The guide profiles need to be attached to the ceiling with dowels, the pitch will be equal to the pitch of the risers, they need to be fixed in at least 3 places;
- Rack profiles will be fixed at a distance of 600 mm from each other, sometimes it can be less;
- The racks need to be secured using the “notch-and-bend” method; Knauf self-tapping screws can also be used;
- If structures are to be attached to a suspended ceiling, the fire resistance class is always observed;
- As for sound insulation (and the partition should be like a wall, soundproofed), mineral wool is most often used as an insulating layer;
- The peculiarity of the installation of sheets is that they must be installed end-to-end without a gap;
- The sheets should be laid in such a way that cross-shaped seams are not formed.
The installation of the frame also has its own peculiarities - the joints of the gypsum board partition above the doorway should not be on the racks to which the frame is attached. The seam should be placed on an intermediate guide that is installed above the horizontal beam. This, in turn, is the upper limit. These measures are necessary to ensure that the service life of the structure is long.
Obviously, without using plasters and other “wet” repair elements, the cost of construction work is reduced. Therefore, the difference between these materials and materials in the lower price segment is compensated by savings on the same plaster.
Partition walls are devices made of plasterboard sheets that change the appearance of the room. These walls, built on your own, allow you to zone the apartment, divide rooms into functional parts, and at the same time be a separate decorative element. Knauf specialists are constantly searching for new technologies and studying the market demand for construction products. Thanks to the use of modern production methods and the desire to expand the sales market, complete partitions of the Knauf system have remained a leader in their field for many years, annually offering consumers more advanced new products.
Putty joints
Vertical and horizontal joints are treated with a primer 3 hours before puttying. The seams are sealed with high-strength gypsum putty in 2 stages. First, the joints are covered with putty. Immediately apply a paper reinforcing tape over the fresh solution, lightly pressing it in with a spatula. The corner joints of the partition with the wall are reinforced with perforated corner profiles. The covering layer is applied to the seams only after the first layer has completely dried. In the case of two-layer sheathing, the joints of the first layer are puttied without reinforcing tape.
It is not recommended to use sickle tape to reinforce seams, as it stretches and does not hold the joint.