Hello, friends! Recently I set myself the task of creating the most comfortable climate in my apartment. You can’t be too zealous with wall insulation: a multi-story building cannot be sheathed on the outside, and when finishing the interior, for example, with mineral wool, there is a risk of creating a breeding ground for fungi due to humidity. As a result, I paid attention to the thermal conductivity of drywall, because it is close to the indicator given by wood or pine. At the same time, there are no problems with the dew point shifting, and this is the main reason for the appearance of fungus after wall coverings. Let's figure out together what drywall does when insulating a house and how to use it correctly.
How to reduce the thermal conductivity of a house with plasterboard
As you know, very often insulation is carried out outside houses. But there are situations when this is not easy to implement. Therefore, an excellent alternative would be to use certain materials to insulate the room from the inside. And the best assistant here will be sheets of drywall.
But why this particular material, since interior finishing can be done in several ways? It's all about the properties of drywall, thanks to which it outperforms all its competitors in this matter.
Properties of drywall: thermal conductivity
Drywall has become almost indispensable in modern renovations, especially when it comes to insulating a room from the inside. This popularity exists due to the following properties of the material:
- environmental cleanliness. Drywall sheets do not contain harmful substances, and also do not emit an unpleasant or harmful odor;
- low thermal conductivity, which allows you to determine the material as warm even by touch;
- the presence of excellent thermal insulation properties;
- Provides support for optimal humidity in the room, absorbing excess moisture from the air. If there is a lack of moisture in the air, drywall gives it away;
- In terms of acidity, drywall has a pH very close to human skin.
To accurately purchase high-quality material with the required thermal conductivity, buy Knauf products. This manufacturer has already proven itself to be the best in the construction market.
Thanks to these properties, gypsum plasterboard not only creates excellent conditions for retaining heat in the house, but also helps normalize the microclimate. In a room lined with plasterboard, you can even breathe easier!
Classification by area of application
Depending on the area of application and properties, there are:
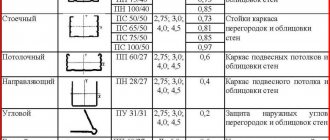
Drywall for walls
The size of the plasterboard sheet has a length of 2.3 or 2.5 m. Width - 1.2 m. Plasterboard thickness - 12.5 mm, gray cladding. Blue markings.
Plasterboard for ceiling
It is used for covering ceilings, creating arches, niches, and two-level ceilings. The size of the plasterboard sheet differs from the previous one only in the thickness of the plasterboard - it is 9.5 mm (which is why it is cheaper than the previous type).
Don't try to use drywall on walls on ceilings. It will sag under its own weight and everything will have to be redone.
Moisture-resistant drywall
Used for finishing rooms with high humidity. It has standard dimensions of a plasterboard sheet, the thickness of the plasterboard is standard, the marking is blue, but the color of the sheet is different - it is green. If you cover it with waterproofing material, the service life of the drywall will increase. The dimensions of the drywall guides depend on the area of application.
Fireproof plasterboard
This gypsum fiber material is used with high fire safety requirements and increased flammability. The size of drywall is almost standard, only it differs in length - up to 2, 3, 2.5 m. The color is gray, the markings are red. The property of non-flammability, as with all products like gypsum board, is present due to the gypsum fiber composition of additional additives. This effect is achieved by adding gypsum fiber material, which is difficult for fire to reach.
By the way, cardboard of any gypsum board and drywall, regardless of size, does not burn, but only chars. But only this type of core remains in the same shape after a fire.
Flexible arched plasterboard
The size of the plasterboard is 3 m long, standard width, the highlight is the thickness - only 6.5 mm. Gray sheets. This type of gypsum board is used to create flexible forms; it has the smallest thickness among all types of gypsum plasterboard, so it can bend to smaller radii. The greatest bending is achieved by piercing the surface with a needle roller and further wetting the surface. With this treatment, water penetrates into the sheet, the wetted gypsum becomes soaked and bends perfectly.
Thermal conductivity of drywall: an important indicator
One of the most important parameters that are determined for drywall is thermal conductivity and its coefficient. To understand this issue in detail, it is necessary to clearly define what the thermal conductivity of a building material is.
Thermal conductivity is an indicator that reflects the ability to transmit heat. In addition, this parameter also reflects the ability of the product to transfer heat from the warmest areas to the coldest ones. Thus, the lower the thermal conductivity coefficient, the better the thermal insulation properties of a particular building material.
Note! A low thermal conductivity means that the material retains more heat.
Therefore, to insulate rooms from the inside, you should choose products that have a low thermal conductivity coefficient.
Products from Knauf, as well as domestic plasterboard manufacturers, have a low thermal conductivity coefficient, which speaks in favor of high thermal insulation properties.
Thermal conductivity of Knauf plasterboard
The Knauf company's production coefficient is 0.15 units. If compared with other materials, it will be significantly lower. For example, reinforced concrete has a thermal conductivity of 1.5 units, and wood (the same for plywood and other wood finishing materials), it is also 0.15 units. At the same time, for dry plaster this coefficient is defined as 0.21-0.9 units (depending on the type of plaster). All approximate indicators (for plywood, plaster and other materials) are given in the summary table.
Based on this table, you can determine that drywall, unlike plywood, plaster and other finishing materials, has the lowest thermal conductivity. Therefore, finishing the walls with plasterboard from Knauf or a domestic manufacturer, even without the use of additional insulation materials, will give excellent results in thermal insulation of the room. But the use of plywood and other finishes will prove worse in this situation.
Note! Any insulation (for example, mineral wool or polystyrene foam) that is used to retain heat in a room has a thermal conductivity coefficient that is approximately five times lower than that of drywall.
To achieve excellent thermal insulation of a room, experts advise combining drywall with various insulation materials. In this case, it will be much easier to do this, since installing drywall involves assembling a metal frame into which insulation can be placed very conveniently and quickly.
Which is better: heated floors or radiators?
Warm floorBatteries
Properties of Knauf plasterboard and its comparison with standard plasterboard
The thermal conductivity of Knauf gypsum boards is already known to you. It's time to learn about the density of the sheets. It is equal to 10.1 kg/m2, which is 30.3 kg per sheet. If we compare it with a regular gypsum board, then the one described in this section also has a green cardboard shell. This material has a standard thickness of 12.5 mm and is usually used for interior decoration of premises that are operated at high relative humidity. It can be:
- showers;
- bathrooms;
- swimming pools;
- laundries.
This sets this drywall apart from its thermal conductivity, which is much lower than that of standard sheets. The latter are usually not used at high humidity. An additional difference is the presence of water-repellent modifiers and antiseptic impregnation in moisture-resistant sheets. The last layer is covered with cardboard. This allows you to protect the sheet from damage by mold and mildew.
Another difference is that the Knauf plasterboard core does not lose its geometric shape and does not swell at high humidity. Ordinary breathable drywall, if the air humidity exceeds 70%, begins to lose its shape, and when it dries, it cracks and crumbles. Moisture-resistant sheets do not have this property, so they can be used for finishing walls indoors, where the relative air humidity can reach 90%.
A little about drywall
The thermal conductivity coefficient for drywall varies in a small range from 0.15 to 0.35 W/ (m×K). The variability of this criterion depends on manufacturers and product quality.
When purchasing a product for internal insulation, you should pay special attention to the product certificate. It must indicate the main characteristics of the material. This way you can choose the highest quality product with the lowest thermal conductivity.
To compare the thermal conductivity of drywall at 0.15 - 0.35 W/mK, we present several other materials. This indicator for the following materials has the following values:
- for foam plastic – 0.038 – 0.043 W/mK;
- for spruce and pine – 0.18 W/mK;
- for foam concrete – 0.37 W/mK.
As you can see, this indicator is low enough to guarantee normal thermal insulation properties. It should be noted that this method of insulation will cost you much less, as well as faster and more efficiently than using other options.
In this case, the installation of the frame base comes into play here. With its help, you can not only perfectly align the walls and ceiling in your home, but also provide an air gap. As a result, the room will be organized like a thermos. Here the air gap will play the role of a heat-saving layer.
Thermal conductivity of drywall by type
In addition, it should be separately noted that plasterboard sheets, depending on their properties, may have slightly different thermal conductivity coefficients. Today there are the following types:
- standard or ordinary;
- moisture resistant;
- refractory;
- moisture- and fire-resistant.
For each type of slab, slight variations of this parameter are possible, but within the boundaries established by GOST.
There are also specially insulated slabs of products. This board has a layer of polystyrene foam. It is this that influences the thermal conductivity index, reducing it, thereby increasing the overall thermal insulation properties of the material.
A special feature of this board is the complete absence of a cardboard layer. As a result, it becomes completely resistant to external influences of fire and high humidity.
Special purpose gypsum boards
If you compare an insulated sheet with a standard one, the first one will have a layer of polystyrene foam on one side, which will reduce thermal conductivity. This material does not have a cardboard coating, which makes it resistant to open fire and moisture. Such sheets resist fire well thanks to fiberglass reinforcing inclusions. As for moisture-resistant sheets, they contain special additives against mold and silicone. The sheets are made in a different color scheme and can be green or pink.
How to reduce the thermal conductivity of drywall
Despite the fact that drywall has fairly good thermal conductivity and thermal insulation, many people use various insulation materials to achieve even better results. The most popular today are mineral wool and polystyrene foam.
The larger the gap between the starting wall and the plasterboard sheets, the thicker the layer of insulation that can be placed in the available space. This will make the room much warmer.
Thus, the use of plasterboard sheets in conjunction with any thermal insulation materials (foam plastic, mineral wool, extruded polystyrene foam) will allow you to significantly reduce the heat loss of the room.
Drywall for room insulation
Using drywall to insulate a room has the following advantages:
- The thermal conductivity coefficient of gypsum board is quite close to that of wood. This circumstance allows you to create a feeling of warmth and comfort in a room lined with plasterboard;
- the ability to place various insulation options under the sheets to create greater thermal insulation;
- the ability to mask all the irregularities and curvatures present on concrete floors;
- the ability to do without liquid leveling of walls using plaster.
However, if you use a frameless method of installing sheets on walls, you will not be able to achieve most of the above points. This is due to the fact that although the thermal conductivity of the material itself will remain unchanged, in this case the absence of an air gap will affect it. As a result, heat loss will be slightly increased.
In general, thanks to the correct installation technology, as well as the unique properties of plasterboard, it can be used for little money and a short period of time to achieve excellent thermal insulation. The excellent thermal conductivity of drywall in combination with insulation will give excellent results.
When purchasing gypsum boards, you need to be very careful and familiarize yourself with the technical characteristics, since for each individual situation not only a certain type of slab is suitable, but also certain properties (thermal conductivity, composition, etc.).
One of the advantages is the low thermal conductivity of drywall. GKL slabs “breathe”, that is, they absorb and release moisture. GKL boards meet environmental standards and consist mainly of dry gypsum, starch and paper. They provide fairly good thermal insulation and a comfortable room temperature.
How to reduce thermal conductivity using drywall
The properties of materials to transmit heat and transfer it to cold areas are called thermal conductivity. This ability is determined by the thermal conductivity coefficient of drywall. On average, it ranges from 0.21 to 0.34 W/ (m×K). The best performance is for the Knauf gypsum plasterboard - 0.15 W/ (m×K). According to these parameters, it is equated to one of the warmest environmentally friendly materials - wood. And compared to plywood or gypsum plaster, the thermal conductivity of gypsum is lower.
It is clear that due to its limited thickness, a 12.5 mm wall sheet cannot provide complete thermal insulation of the walls. But, in combination with insulation, it retains heat perfectly. Another advantage of structures mounted on a profile is that a layer of air is formed inside, which becomes an additional heat insulator. The larger the air layer, the lower the thermal conductivity. In addition, this provides additional ventilation to the wall and prevents the accumulation of moisture and the formation of condensation. At the junction of cold and warm temperatures, condensation forms (“dew point”). The air gap provides additional ventilation to the wall, which prevents the accumulation of condensation.
Additional properties: disadvantages and advantages
Among the positive properties of plasterboard, one should highlight high bending strength, poor flammability, the ability to withstand low temperatures, high thermal conductivity, environmental friendliness, low weight, and ease of installation. This material also has its drawbacks, namely poor moisture resistance, fragility during transportation and installation, as well as insufficient strength. In addition, without a frame, the sheets are quite difficult to install.
As for bending strength, we can say about this property that a square meter of canvas can withstand up to 15 kg of load with a thickness of 1 cm. A rather important characteristic is also poor flammability. It is provided with a gypsum base. The material is poorly flammable and belongs to group G1 for flammability and B2 for flammability.
The material withstands low temperatures well. In the cold it does not crack or burst, but if the temperature rises, its physical properties are restored. It is impossible not to mention the thermal conductivity coefficient. The canvas regulates the level of humidity, which is especially true for gypsum boards.
How else can you reduce thermal conductivity: supplement the properties of drywall
It should be noted right away that it is more correct to insulate walls from the outside, especially with polystyrene foam and polystyrene. These are not “breathable” materials, so if they are used to insulate external walls indoors, the effect of a thermos is created. There is a risk of condensation forming.
Such premises require regular forced ventilation. They can be used for wall partitions made from gypsum plasterboard sheets indoors, since there are no sharp temperature fluctuations, and gypsum sheets act as a breathable membrane.
Any insulation in combination with gypsum plasterboard sheets, in addition to thermal insulation properties, simultaneously performs the function of sound insulation.
What insulation materials are used in combination with drywall
- In order for the structure to “eat up” a minimum of area, isolon is best suited. This is a relatively new material, it is foamed polyethylene foam, inside of which there are closed air bubbles. There are quite a few types of this material in terms of thickness and characteristics. It can be foiled on one or both sides. It differs from volumetric insulation in that, with low thermal conductivity, isolon has a minimum thickness. For this reason, you can make the minimum width of the plasterboard layer. But you should pay attention to the need for an air gap; it also does not allow moisture to pass through.
- Various types of glass wool in mats and slabs are quite often used for thermal insulation in combination with gypsum plasterboard sheets mounted on a profile. It is made from thin strands of glass formed at high temperatures. The main disadvantage is that microparticles of the material during installation can cause irritation of the skin. Therefore, it is better to work in overalls and wear gloves.
- Basalt insulation has a manufacturing technology similar to fiberglass. Only in this case, various rocks are brought to the melting temperature, after which they form thin threads. The advantage of basalt insulation is that it is harmless to human health. Like fiberglass, these insulation materials have micropores in their structure, due to which they can absorb and evaporate moisture.
In terms of heat transfer, all insulation materials have a several times lower thermal conductivity coefficient (on average 0.03-0.04 W/(m×K)). In combination with drywall, they form an insurmountable barrier to cold.
Types, their comparison and properties
Drywall is a multi-layer board of paper and gypsum. This design allows the material to be used as finishing, as well as to create interior partitions from it. If you follow certain rules during installation, you can hang shelves on the walls and glue wallpaper.
But the thermal conductivity of drywall is not the only indicator that should be used as a guide when choosing canvases. It is important to pay attention to the types of material. He can be:
- standard;
- fire resistant;
- moisture resistant;
- fire and moisture resistant.
When you visit the store, you will see Knauf plasterboard, the thermal conductivity coefficient of which is the lowest among other varieties. In addition, this material is offered for sale in the “super sheet” variety. It has a fibrous structure, which improves the properties of sheets, facilitates the cutting process and increases strength. Supersheet is convenient for installing interior partitions.
In general, the thermal conductivity of drywall is not the only characteristic that you should pay attention to. You must choose from a variety of canvas options, including:
- acoustic
- arched;
- vinyl.
For example, arched cardboard has less thickness and weight, which allows you to create curved, complex structures. When using vinyl, you will feel that the material is easy to work with, because its surface is ready for decorative finishing and does not require putty.
The thermal conductivity of drywall was mentioned above, but you should also know about other properties of plasterboard, including:
- safety;
- smoothness;
- ease of processing;
- high noise insulation characteristics;
- low cost;
- relatively light weight;
- mechanical strength;
- environmental friendliness.
Rules for installing gypsum board sheets with insulation: reducing thermal conductivity
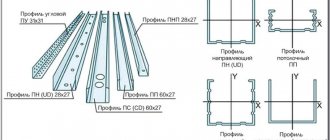
When installing plasterboard structures on a profile, between the wall, floor and ceiling, a sealing tape made of foam materials is glued to the metal frame. It performs two main functions: it serves as insulation between concrete structures and the profile, and prevents the occurrence of rattling when the metal vibrates.
Before installing the frame, you need to decide what type of insulation will be used. The thickness of the structure depends on this. The distance between the sheets must correspond to the width of the insulation.
On external walls, it is necessary to attach a vapor barrier (finely perforated film) after the insulation layer. It will create a moisture-proof barrier that prevents condensation from penetrating into the drywall, and moisture from the room will be absorbed into the gypsum board sheets and removed through them.
We advise you to watch: how to insulate a wall with mineral wool.
Drywall with minimal thermal conductivity
Recently, a new material has appeared on the market - “warm drywall” . It is available in several types. The insulation is glued to one sheet of gypsum board or fixed between two. Used for both external and internal work. The thickness of slabs with one layer reaches 60 mm, double-layer up to 100 mm, size 1200 x 2500 mm. Main scope of application: prefabricated structures, summer country houses, utility rooms. Inside buildings it is glued to the walls. Polystyrene is often used as insulation; the thickness of the layer varies depending on its width. The main advantage of the material is low thermal conductivity and high installation speed.
The low thermal conductivity of gypsum board sheets is another additional advantage of the material, which makes it in demand in the construction market.
How to treat the surface → Room decoration → How to choose the right paint → Surface treatment technologies → Leveling and finishing the walls → Selecting and applying a primer → Removal from the surface → Stretch ceilings and technologies → Reviews and testimonials
Device
Inside there is plaster with additives, outside there is a cardboard lining attached with a special glue. Depending on the properties of the drywall, dimensions may differ from standard ones.
Drywall weight and weight . Have you ever wondered, “how much does a sheet of drywall weigh?” The weight of drywall is no more than 1 s (kilograms per square meter). Fire-resistant plasterboard sheets – not < 0.8 and not < 1.06 s.
Thickness _ The size of the plasterboard sheet is not so important; in the end, it can be cut the way you want, the main thing is the thickness. It comes in different profiles - 6, 9, 12 mm, it does not depend on the place where we buy gypsum boards - on the market or in a specialized store. GKL 6 mm is used for bending sheets using the “wet method” - creating products with curves (designer fantasies, niches, arches). GKL 9 mm is usually used for ceilings, and is also used for bending sheets using the “dry method”. They make beautiful ceilings to reduce the weight of the structure. The thickest ones are used by builders to create partitions and wall cladding. They also create racks and columns, the height of which will indicate the status of the owner. There is little demand for other sizes; non-standard gypsum boards are rarely of interest to buyers.