Currently, plasterboard boards are often used during repair and finishing work. The widespread use of this building material is explained by the fact that when used, the process becomes less labor-intensive and time-consuming. Using drywall, you can quickly level walls, make unusual ceilings, create an original false fireplace, and much more. The building material has a wide range of applications and reasonable prices.
Gypsum plasterboard is a finishing building material consisting of three layers: a gypsum core and two layers of construction paper. Cardboard is needed to provide the required rigidity to the building product, reduce the stress of the gypsum during installation and during further operation, as well as to protect the gypsum from the effects of transportation.
A large number of buyers believe that drywall sheets are presented in one size. In fact, the sizes of gypsum boards are different - their weight, thickness, length and width are determined in accordance with the intended purpose of the product. Optimal selection of material contributes to more economical consumption of sheets and also leads to the best result.
Wall decoration with gypsum board sheets
Structure and features of plasterboard sheet
If renovations are underway somewhere, then we can say with confidence that plasterboard will certainly be one of the building materials. It is very popular and in demand, as it is great for finishing apartments and houses. This material is inexpensive, completely harmless and non-flammable, and has good soundproofing properties. It can take away excess moisture from the air, and then easily give it away if the air dries out. Working with drywall is pleasant and easy - it is not capricious and is easy to process.
Builders especially like the lightness of plasterboard sheets - this is a big plus both during installation and during transportation. When working with drywall, little waste is generated, and removing debris is much faster. The use of plasterboard in construction is the so-called “dry construction”.
Ease of use of the material
It is very convenient that for drywall you do not need a special tool at all - the minimum that is available in every home is enough. Complex structures can be created from this material due to its special properties. Just wet the plasterboard sheet and you can do whatever you want with it. For example, bend it in the form of an arch, build a niche, or bring to life an intricate design project. After drying, the structure will retain its shape. By the way, smooth surfaces also turn out excellent.
Thanks to the use of plasterboard, you can significantly reduce the time spent on finishing work. Let's take, for example, the manufacture of a partition. If you make it from traditional building materials (say, brick), you will have to spend three times as much time. And drywall does not cause allergic reactions, which is also a positive quality.
What are the disadvantages of drywall?
Unfortunately, there are properties and characteristics of drywall that do not add to its advantages. So, this material cannot boast of strength and water resistance. In addition, it is difficult to attach anything to it. It is useless to make holes in a plasterboard wall with nails - only dowels and screws can hold a shelf or a picture on it. But still, you shouldn’t hang anything particularly heavy, as this can lead to complete destruction of the wall.
Insufficient water resistance
Insufficient strength
Difficult to mount on the wall
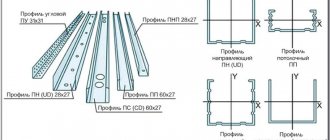
Installation of plasterboard sheet
Nothing complicated - the design corresponds to the name. The core is made of gypsum with additives, and the outside is lined with cardboard. It is held tightly with special glue. Depending on the application, types of plasterboard with different properties are produced.
What does the abbreviation SML mean?
So, SML is a glass-magnesite sheet. It is a finishing material in the form of a sheet, positioned as a substitute for gypsum plasterboard and gypsum fiber board and other sheet materials for finishing premises. So which is better: LSU or GVL? In fact, everyone answers this question in their own way. Some people prefer plasterboard, while others prefer glass-magnesite sheet.
Let's look at it in more detail.
Glass-magnesite sheet is a universal construction and finishing material with a unique set of different characteristics. There are simply no analogues to this material today. There is also economical consumption, which is important today.
SML has a unique combination of operational and structural properties.
Its main components are:
- Magnesium oxide. First, magnesite is taken, a natural material mined by open-pit mining from quarries, then it is purified from various impurities and ground into powder.
- Magnesium chloride. Bishifit is a natural material that includes a chloride-magnesium-sodium complex.
- Wood shavings.
- Perlite is a rock of volcanic origin, mined by the mine method. Used as a heat and sound insulator.
- Fiberglass. It is used as a reinforcing material in the production of SML. It has excellent thermal insulation properties, has increased resistance to acid and alkaline influences, and to the influence of various organic solvents. Material consumption depends on the characteristics of the insulation of the premises.
As can be seen from the above, glass-magnesite sheet is a natural building material that will not cause harm to health.
It is worth noting that glass-magnesite sheet, unlike many other building materials intended for interior decoration, is very convenient for installation, has incomparable flexibility and strength, and, in addition, it is also moisture-resistant and non-flammable.
Thanks to this, the scope of application of LSU is quite extensive. It (SML) can be used for both internal and external cladding of buildings, for building structures. It is also suitable for installing ceilings, creating interior partitions, etc. The consumption of material, as in the case of drywall, will not be very large.
Related article: Do-it-yourself lifting curtains: master class from professionals
In addition, magnet sheet is used for the production of:
- Construction forms.
- Billboards for advertising.
- Door panels.
- Facing and reinforcement of foam concrete blocks.
- Permanent formwork in the walls of buildings under foam concrete.
If we take into account its entirely natural and environmentally friendly composition, then we can begin to talk about its widest use without danger to life, despite the material consumption and the difference in relation to other types.
This material has the property of asepticity, i.e. it does not create optimal conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms and therefore remains hygienic throughout its operational life.
Types of drywall and their areas of application
Wall plasterboard (GKL)
The sheets can have a length of 2.3 or 2.5 m. The width of any of them is 1.2 m. The thickness of this material is 12.5 mm, its color is gray. There are markings on the cardboard in blue. There are no special additives in the core; the properties of the material are standard.
Plasterboard ceiling
The length of the sheets can be 2 or 2.5 m, and the width - 1.2 m. The thickness is less than that of wall material - it is equal to 9.5 mm. The light gray cardboard facing is similarly marked in blue. This type of gypsum board is used for cladding ceilings, as well as for the manufacture of niches, arches and multi-level ceiling structures. The properties are similar to the previous type, differing from it only in thickness. Thanks to this, by the way, it costs the least.
Moisture-resistant drywall (GKLV)
Sheets 2.3 and 2.5 m long have a standard width of 1.2 m. The thickness is the same as that of wall material (12.5 mm). The facing cardboard is green and has blue markings. These gypsum plasterboards are used in rooms with excess humidity, which they can easily tolerate. You can improve this characteristic of moisture-resistant drywall if you additionally cover the walls with waterproofing material.
Paint, primer or a layer of tile can also serve in this capacity. Both the core and the cardboard of this material have a special composition, so they are not afraid of moisture. For this, antifungal impregnation and special additives are used.
Fire-resistant drywall (GKLO)
The length of its sheets can be 2, 3 and 2.5 m, and the usual width and thickness are 1.2 m and 12.5 mm. The facing cardboard is light gray in color and all markings on it are red. GCR data is used where fire safety requirements are high. For example, this could be the lining of a chimney or fireplace. This type of drywall has a large amount of fibers and additives in its core intended for reinforcement. This structure, reinforced with an external cardboard lining, is difficult for fire to overcome. After all, it turns out to be a double frame.
Note that durable cardboard used in any gypsum boards does not burn and does not contribute to combustion. Maximum - it gets charred. But the core can only resist fire in a fire-resistant type of drywall. In case of fire, it does not collapse and retains its shape.
Moisture-resistant plasterboard (GKLVO)
Combines the properties of moisture-resistant and fire-resistant plasterboard sheets.
Arched plasterboard (flexible)
Its light gray sheets have only one length - 3 m. The width, as usual, is 1.2 m. But the thickness of the material is small - only 6.5 mm, so it is mainly installed in two layers. Arched plasterboard is used to make various curved products with different bending radii. They can be bent so easily thanks to the fiberglass threads that strengthen the core. However, due to this, the price of the sheets is quite high. And the fact that they have to be laid in a double layer further increases costs.
Marking
To find out the characteristics and groups of thin drywall that interest us, you need to know and be able to decipher the conditions indicated on the sheet.
- Designation by letter of sheet type (A or B);
- information about the group to which the plasterboard sheet belongs;
- longitudinal edge information;
- dimensions of drywall sheets in millimeters;
- manufacturing standard - GOST 6266-97.
Here, for example, is the size of KNAUF drywall “A”. Its length is 2500 mm, the width is standard, the edge is semicircular, the thickness of the plasterboard is 9 mm. These are the dimensions of Knauf gypsum boards. As you can see, the plasterboard standard sheet size applies to KNAUF.
What the marking looks like:
Types of gypsum board edges
The standard width of the sheets is 1.2 m. They are manufactured in accordance with GOST 6266-97: inside two layers of durable cardboard there is a hardened mass of gypsum with special additives for reinforcement. The lateral and longitudinal sides of the sheet are wrapped in cardboard.
There are several types of edges used in the production of drywall. This is made for more convenient processing of joints between sheets. It is worth remembering that all ends of gypsum boards are always only rectangular. If there is a need to join exactly these sides (the short ones), then they need to be chamfered by about a third.
| PC (straight edge) is used when joints do not need to be sealed. |
| UK (edge with thinning) is needed if reinforcing tape and putty are used for sealing. |
| PLC (face semicircular edge) is used when working with putty and without reinforcing tape. |
| PLUK (front semicircular edge with thinning) can be used when working with putty and with reinforcing tape, and without this tape. |
| ZK (rounded edge) is used if the joints are to be sealed with plaster. |
Panel weight
Examples of the weight of various drywall sheets
The weight of the panels is affected by the width, length and thickness. According to the standard, fire-resistant panels must weigh 1.6 kg per 0.8 mm. The weight of ordinary and moisture-resistant sheets should be 1 kg per 1 mm of material.
To calculate the load force of the structure being created, you need to know the weight of the sheets. It is necessary to clearly understand the maximum weight the panel used can withstand. This will eliminate possible defects and possible collapse during operation. In the process of working with material, a correct calculation of the load per square meter of material is necessary. This is very important when it is planned to install blind panels or install heavy elements.
Flammability of drywall
Drywall is not a flammable material, and it can also withstand fire for a long time. As a matter of fact, any gypsum-containing materials can boast of such qualities.
- GOST 30244 determines flammability - it is for G1 plasterboard;
- GOST 30402 determines flammability, for plasterboard it is B2;
- GOST 12.1.044 determines the ability to generate smoke; according to this indicator, plasterboard belongs to group D1;
- GOST 12.1.044 defines toxicity; drywall belongs to group T1.
In the event of a fire, the characteristics of fire-resistant plasterboard allow it to withstand fire. The gypsum itself cannot burn, and after the cardboard is destroyed, the core simply crumbles. To increase fire resistance, partitions are made from two sheets of plasterboard. Thus, cardboard located between two sheets is able to withstand fire for a longer time.
Water absorption and softening coefficient
For brands of drywall that are moisture resistant (including those that are also fire resistant), moisture absorption of no more than 10 percent is permissible. Drywall also has another important parameter - the softening coefficient Kp, which is calculated by dividing the tensile strength in a water-saturated state (Rн) by the tensile strength in a dry state (Rс).
If we talk about sheets of ordinary drywall, their strength is significantly reduced when they are heavily moistened. There are quite a lot of similar materials sold, and they all have a small softening coefficient of approximately 0.8. But gypsum board has a slightly different value for this parameter - 0.45. This means that after getting wet, the strength of this material will greatly decrease.
Thermal conductivity of drywall
To begin with, it should be noted that drywall retains heat quite well. The thermal conductivity coefficient of plasterboard ranges from 0.22 to 0.35 W/ (m×K). This is not bad - after all, when carrying out repairs, you can immediately make the walls even and slightly improve their thermal insulation. It should be noted that this method of thermal insulation of walls is inexpensive, fast and effective. And if you make a gap from 3 to 10 mm, then an additional air layer will appear, which will help conserve heat even better.
To achieve a good result in terms of thermal conductivity, various insulation materials are placed in the cavity between the insulated wall and the plasterboard. This could be, for example, mineral wool or ordinary polystyrene foam. The further we move the plasterboard away from the wall, the thicker the additional thermal insulation layer can be made.
A little history
To fully understand what drywall is, you need to look at the history of its creation. The beginning of its creation is associated with the beginning of the 19th century in the USA. The base was paper, pressed and folded together. Gypsum was also used, but it was a thin layer. Later, to give a denser, stronger base, it became a core, which was laid on both sides with cardboard. Already in the 20th century, they began to not only lay gypsum between this material, but wrap it in it. Now we use exactly this type of building material, only the technology has been improved several times. That is, we can say that initially and now gypsum and cardboard are used to make drywall.
About the thickness of sheets
Drywall, which is sold in stores and on the market, most often can be 6, 9, 12 mm thick. The thinnest gypsum boards, 6 mm thick, are used for the “wet method” - they are used to make complex curved products (arches, designer structures, niches). A thickness of 9 mm is well suited for bending sheets “dry” and creating the same arches - experienced craftsmen usually do this. Ceilings are also made from nine-millimeter gypsum boards in order to reduce the weight of the structure. The thickest sheets are used for cladding walls and creating partitions. Other sizes are extremely rare on sale, and therefore, as a rule, they are not of interest to the average buyer.