When owners of private houses are faced with the task of cladding the facade, many immediately have the problem of choice. The market today offers a huge range of materials that can be used for exterior wall decoration. One of them is cement-bonded particle boards (CPB).
The approach to choice among consumers is the same. The finishing material should be inexpensive, but with high quality characteristics. So, the façade made of cement-bonded particleboard exactly fits this ratio. Hence its gradually growing popularity.
How is DSP made?
The cement-bonded particle mixture from which CBPB is made is a kind of concrete based on a mineral binder. Only instead of sand and crushed stone, the filler in it is small wood shavings. The introduction of wood into the composition of the slab reduced its density, but most importantly, the shavings played the role of not only a light filler, but also fiber - an additive that creates volumetric reinforcement that absorbs tensile loads.
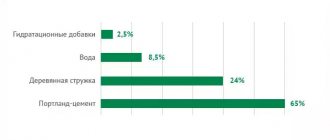
The mixture for making the slab includes:
- cement – 65%;
- chips – 24%;
- water – 8.5-9%;
- mineralizing and hydration additives, – 2-2.5%.
Preparation of the mixture begins with chopping the chips to the desired size. After this, it is divided into two fractions on sieves. Small ones are used to form the outer layers of the sheet, larger ones for the middle layer. It is then treated with calcium chloride, “liquid glass”, aluminum chloride or sulfate. This is necessary to protect the material from rotting and fungal attack.
Sifted and treated with mineral additives, shavings are mixed with water and cement. Additives that accelerate the hardening of cement dissolve in water. In addition to the above components, fuel oil and industrial oil I-20 can be added to the mixture in small quantities to reduce internal friction and facilitate pressing.
The prepared mixture is laid out in three layers on pallets, the pallets are stacked and placed in a cold press, where this “package” is compressed to a pressure of 1.8-6.6 MPa and secured in this state with locks. A special locking system maintains pressure in the mold after it is removed from the press.
The compressed bags are heated for 8 hours. During this time, accelerated hydration of cement and its hardening occurs. Wood shavings, due to their elasticity, compensate for cement shrinkage, so the specified dimensions of the slabs do not change. Unlocking molds and relieving pressure also occurs in the press. After this, the package is opened, and the slabs are removed and placed in a buffer warehouse for 1-2 weeks.
For final ripening of the material, it is blown with air at a temperature of 70-100 ° C. After this, the sheets are cut to size, sanded, sorted and transferred to the finished product warehouse.
Types of DSPs and their sizes
According to GOST 26816-2016, cement particle boards of two grades are produced – TsSP-1 and TsSP-2. They are distinguished by dimensional accuracy, strength and other quality parameters.
| Options | TsSP-1 | TsSP-2 |
| Slab size deviations (mm) | 3,0 | 5,0 |
| Deviation in thickness of unpolished slabs (mm) | 0,7-1,5 | 0,8-0,16 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 9,0-12,0 | 7,0-9,0 |
| Delamination Strength (MPa) | 0,50 | 0,35 |
| Roughness of ground slabs (µm) | 80 | 100 |
| Stains on the surface | Not allowed | More than 1 piece is not allowed. with a diameter of more than 20 mm per 1 m2. |
| Dents | More than 1 piece, with a depth of more than 1 mm, and a diameter of more than 10 mm per 1 m2, is not allowed. | More than 3 pieces are not allowed. depth more than 2 mm, diameter more than 20 mm per 1 m2. |
The tolerance limits for thickness and bending strength are set separately for different thickness ranges. The slabs are produced in thicknesses from 8 to 40 mm with gradations of 2 mm.
The dimensions of the DSP sheets of both brands are the same:
- Length – 3200 or 3600 mm;
- Width – 1200 or 1250 mm.
In addition to these two brands, there are “related” materials that have similar composition and properties.
Fibrolite
These are slabs filled with wood fibers, so-called wood wool. A filler of this shape provides better fibreing, which has a positive effect on the strength of the material and its resistance to cracking. Fiberboard is relatively soft, has a relatively low density and is often used for thermal insulation and as a sound absorber.
Arbolit
Material related to lightweight concrete. It uses wood shavings, wood chips, chopped reed stalks and rice straw as filler. Arbolite has low strength and is used in structures that do not bear loads, such as internal partitions.
Xylolite
This material is made using magnesium binder - Sorel cement. Insensitive to water. It is used for covering floors, roofs and other structures where frequent moistening of the slabs is possible.
Preparation of cement bonded particle boards for installation
DSPs are sold ready-made and do not require preliminary preparation. Before starting finishing work, you only need to cut them according to the required dimensions. A grinder or circular saw is suitable for sawing. If cutting results in uneven edges, you need to sand them with a sanding machine.
Most often, self-tapping screws are used to attach the slabs to the sheathing elements, so you will need to drill holes of the appropriate diameter on the cut slabs. To do this, use a drill with a smaller diameter than a 0.5 mm self-tapping screw.
The diameter of the screw should be from 3 to 6 mm. The optimal distance between fasteners is from 20 to 40 cm.
Characteristics of DSP
The main characteristics of the DSP are determined by the components included in its composition. For example, the heaviness of cement stone is partially compensated by the lightness of the filler - shavings.
Physico-mechanical indicators of CBPB according to GOST 26816-2016:
| Index | TsSP-1 | TsSP-2 |
| Modulus of elasticity in bending, MPa | 4500 | 4000 |
| Hardness, MPa | 45 — 65 | |
| Thermal conductivity, VT/(m 0С) | 0,26 | |
| Specific heat capacity, kJ/(kg 0С) | 1,15 | |
| Specific resistance to pulling screws out of the plate, N/m | 4 — 7 | |
| Biological resistance class | 4 | |
| Frost resistance: | ||
| — number of alternating freezing/thawing cycles without visible signs of destruction | 50 | |
| — residual strength, % | 90 | |
| Resistance to cyclic temperature and humidity changes: | ||
| — decrease in strength after 20 cycles of temperature and humidity influences, % | 30 | |
| thickness swelling, field 20 cycles of temperature and humidity influences, % | 5 | |
Density and weight of the slab
The density of CBPB is 1100-400 kg/m3 - this is less than the density of most cement-based materials. A slab with dimensions of 3200x1200x10 mm weighs from 42 to 54 kg, depending on density.
Exposure to moisture and biostability
DSP is resistant to moisture and biological factors. Biostability is ensured by special treatment of chips - mineralization. Moisture resistance is the merit of cement. Cement stone does not lose strength with any moisture. Water absorption during prolonged immersion in water does not exceed 16%, and the swelling of the slab thickness is within 1.5%.
Frost resistance
When moistened, DSP absorbs little water. This determines its good resistance to low temperatures. Frost resistance of DSP is 50 freeze-heat cycles without visible damage and with 90% residual strength. According to this parameter, the slabs are suitable for use outside heated rooms, provided they are protected from moisture accumulation.
Thermal conductivity and vapor permeability
Cement particle board is a porous material, since a significant part of its volume is occupied by wood shavings. Thanks to this structure, it has low thermal conductivity - about 0.26 W/(m∙°C). This is 1.5-2 times less than brick and approximately twice as much as plasterboard. Despite the fact that DSP cannot be fully considered a heat-insulating material, its use significantly affects the resulting thermal resistance of external enclosing structures.
The porous structure determines the permeability of the material to water vapor at a level of 0.03 mg/(m∙h∙Pa). Concrete has the same vapor permeability. This parameter must be taken into account when designing multilayer walls. When using a DSP board for interior finishing of external walls, it can serve as a vapor-limiting layer, reducing the accumulation of moisture in the wall and increasing the efficiency of thermal insulation.
Fire safety
The fire characteristics of DSP are as follows:
- flammability group: G1: low-flammability;
- flammability group: B1 – hardly flammable;
- flame spread: RP1 – non-flame spreading;
- smoke generation: D1 – small amount of smoke;
- toxicity group: T1 – combustion products are low toxic.
Based on the sum of its parameters, cement bonded particle board is considered a safe material. Its use makes it possible to increase the fire resistance of building structures and reduce the fire hazard class of premises.
Environmental friendliness
This characteristic is given a lot of attention due to the massive use of synthetic raw materials in the production of building materials. Cement particle board consists only of natural components. It does not contain formaldehyde resins, polystyrene and other substances that can serve as sources of emission of volatile toxic compounds. Thanks to mineralizing additives, the wood component is not susceptible to rotting, which also helps maintain a healthy atmosphere in the premises.
Treatment
Cement particle board is quite easy to cut and drill, which greatly simplifies working with it. Putties adhere well to its surface and can be painted well.
Application of DSP
The areas of application of cement bonded particle board are determined by its properties described above. Particularly valuable is the successful combination of valuable qualities that complement each other. Not many materials have strength, moisture resistance, environmental friendliness, fire safety and relatively low weight at the same time.
The form of the material in the form of plates provides another important advantage - ease of use and manufacturability. The use of DSP in many cases makes it possible to speed up work, eliminating the so-called “wet processes”, which require special qualifications from craftsmen, are labor-intensive and take a lot of time, especially considering the hardening time of building mixtures.
The use of cement particle boards is limited to installation work; the large sizes of the sheets allow you to immediately cover a large area and simplify the alignment of planes.
Cladding of walls and partitions
Cement particle boards are very well suited for cladding walls, both solid and framed. Environmental safety makes them a good material for interior decoration, and moisture resistance allows them to be used for wet rooms and for exterior decoration of buildings.
The slabs can be mounted on brick walls instead of conventional plaster. This method is called "dry plaster". Cladding with slabs makes it easy to obtain a flat surface. The complexity of this work, taking into account the ease of ensuring the proper quality, is much lower than with traditional plastering. For these purposes, sheets with a thickness of 8-12 mm are usually used.
Cement particle boards are very well suited for frame construction. This technology directly involves sheet cladding, which ensures high-tech work and time savings. One type of frame structures is internal partitions. DSPs serve as a soundproofing material, reducing acoustic coupling between rooms separated by a partition. For cladding frames, slabs up to 20 mm thick are used.
Curtain façade systems
A suspended ventilated façade is one of the natural applications of DSP. These sheets serve as an outer skin, protecting the inner layers from atmospheric moisture and wind. For a ventilated facade, the strength, moisture resistance and fire safety of the material are extremely important. DSP is able to withstand high mechanical loads, does not deteriorate from moisture and does not spread flame, even under conditions of strong draft in the ventilation gap. In this area, lightweight slabs up to 12 mm thick are used.
Roofing systems
DSP is used for the construction of flat roofs, including those in use. The sheets are laid on top of the thermal insulation and then covered with a waterproofing membrane. Due to the rigidity of the slabs, the insulation is not subject to concentrated loads and you can walk on the roof and even use it, for example, as a summer cafe or recreation area. Depending on the load, roofing systems use slabs up to 20 mm thick, and in special cases even more.
Floors
For flooring, the properties of DSP such as bending strength and moisture resistance are useful. This material is very well suited for subfloors - the so-called dry screed. Instead of laying a layer of cement-sand mixture on the ceiling, smoothing it and waiting for it to harden, DSP slabs are laid on the prepared “beacons” and immediately a base is smooth and ready for further finishing, which also serves as a heat insulator.
For a frame house or when installing a floor along joists, thicker slabs are used. The choice of thickness is determined by the upcoming load and the distance between the lags.
Another frequently used design is a floating floor. DSP is also perfect for it, as well as for flat insulated roofing. The choice of slab thickness is influenced by design loads and insulation density. For the subfloor, slabs with a thickness of at least 14 mm are used.
Formwork
Typically, in monolithic construction, the formwork is a temporary structure that is removed after the initial hardening of the concrete. The use of DSP allows you to combine the preparation of formwork with finishing work. Permanent formwork is made from these slabs, which remains as part of the wall, immediately forming a flat surface that does not require plastering.
Garden paths
This is one of the possible uses of the CBPB board. This is where its strength and moisture resistance come in handy. Laying the slabs on a prepared sand “cushion” creates a flat surface that will not chip, crack, or cause dips or swelling. Of course, to compensate for frost heaving, you need to take care of installing a high-quality drainage layer.
If you notice an error, a non-working video or link, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter .
0
Installation technology
External finishing of walls and foundations using DSP is similar to the construction of a ventilated facade. First, prepare the base. External walls are freed from unnecessary items: cables, drainpipes, lamps. Scaffolding is being installed. The scope of work at this stage depends on the material of the load-bearing walls, as well as their condition.
A wooden house needs special attention. The peeling surface is removed, deep cracks are eliminated using sealant or putty. Clean walls are treated with antiseptic impregnations.
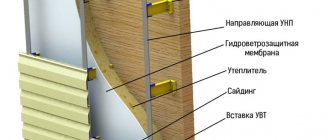
Next, install the sheathing. Often the external finishing of the facade is combined with insulation. To do this, any heat-insulating material is placed between the frame elements. It is most convenient to work on the facade with slabs, so stone wool or polystyrene foam is often used as insulation under the DSP. The insulation is securely fixed to the wall using umbrella dowels.
Then a windproof membrane is laid. It is slightly stretched and fixed to a wooden frame with a stapler.
Installation of DSP begins from any corner of the house. The slabs are installed level and securely fixed to the sheathing elements using self-tapping screws or self-tapping screws. To prevent the formation of cracks and chips, fasteners are made no closer than 2 cm from the edge of the material. When using self-tapping screws, preliminary holes are drilled in the wooden sheathing elements using a thin drill, and only after that the self-tapping screw is screwed in. The head of the self-tapping screw is heated into the slab by 2-3 mm.
To prevent air stagnation, a small gap of up to 10 mm wide is left between the thermal insulation and cladding material. A gap of 3-5 mm is left between the individual plates.
To obtain a perfectly beautiful surface, the heads of the screws are covered with gypsum putty with the addition of a small amount of PVA. After the mixture has dried, the surface is sanded with fine-grained sandpaper.
Seams require special attention during the cladding process. They are eliminated using sealant, because its elasticity makes it easy to tolerate thermal fluctuations. Metal or wooden strips can be used to mask seams.