Siding is a popular finishing material that can be used for any outdoor work. It is highly durable and low cost. Siding is easy to install. It will not require much maintenance, but the façade of the house will look great for a long period of time. If a person has already chosen a facing material, then he needs to further perform all the necessary calculations. You can, of course, resort to the services of an estimator. In this case, you will have to additionally allocate a considerable amount of funds from the family budget for payment. Today, there are several calculators online that can help you get accurate results. A person can also make the calculations himself. However, you should first study the specification of this process in detail.
Required data for calculation
To obtain accurate final data on the required material, when calculating it, it is recommended to use the dimensions from the facade sketch.
They must be entered into the appropriate fields of the calculator. To calculate, there is no need to resort to complex formulas and reference books. It is enough to know exactly the lengths and heights of all walls.
Before starting calculations, you should obtain the following data:
The height and width must be fixed for each wall separately.
This data is obtained by measuring the distance from one corner to another. The data will be obtained correctly if the bay window is taken to be several narrow walls, which are additionally separated by corners. Windows, doors and other openings that will not be covered with siding should also be taken into account. However, their functional purpose does not make sense. External and internal angles must also be measured.
At the same time, their heights and quantity are recorded. The length and width of the cornice are measured at its base. In the future, it will be used in calculating the area required for the spotlights. In the calculation process, you will also need to use the height of the ridge and its width. This data will be useful for obtaining accurate data on the gable area.
As a result of the calculations, the quantity of all elements that will be required for repair work will be obtained.
Calculation of the number of additional siding elements
Soffits for filing eaves overhangs
One way to hem overhangs is to use siding panels
Since eaves overhangs, as a rule, have the shape of rectangular strips, calculating their area is not difficult at all: you just need to multiply the planned width of the overhang by its length, total or separately on each side, followed by summation. The resulting area value, divided by the area of the siding panel, rounded up to the nearest whole number, will be the required amount of material.
For free air circulation in the under-roof space, it is necessary to use soffits with partial or complete perforation. To calculate them, it is better to use the formula: first you need to determine how many pieces for filing you will get from one strip of soffit
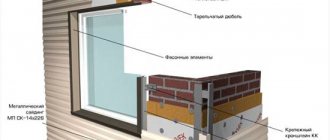
Wind bar (J-profile with chamfer) and J-profile
The wind strip (J-profile with chamfer) and J-profile serve as a frame for the soffits (1). The diagram shows their fastening
Along the wall line, soffit strips are inserted into a fixed J-profile (2) (in some cases, an internal corner is used). Thus, the total length will be equal to the sum of the lengths of the eaves overhangs along the line of abutment to the wall or pediment.
From the outside, the soffit fits into a J-profile with a chamfer (3). Its length is measured along the outer perimeter of the roof overhangs.
It is most convenient to fix the wind strip from above with a finishing profile (4). Naturally, their length is identical.
Starting bar
This strip is mandatory for installing the first strip of siding - it will set the correct direction and will fix the lower edge of the cladding, entering into a locking connection with the lower row of panels.
To calculate it, you will need the perimeter of the house.
Corner profiles
Their purpose is clear, calculation is also not difficult - based on the number and height of the corners. Here, when making calculations, the main thing is not to confuse the external and internal angles.
H-profile (connecting strip)
This strip is installed in places where the joint of adjacent panels is formed, if their length is not enough to cover the entire wall completely. To calculate them, it is necessary to calculate the number of joints and multiply them by the height, so we get the total length of the joining strip.
Window trims and trims
The use of one or another profile will depend on the location of the window relative to the plane of the wall. Several options are possible:
Option A. The window is located in the same plane as the wall. In this case, it is quite enough to make a frame around the perimeter using a platband profile or a wide J-profile (item 1)
Option B. The window is recessed into the plane of the wall, but to a small depth (up to 180÷200 mm). In this case, a near-window strip (item 2) is usually used, which on the outside has a groove for siding panels, and its inner shelf, cut to the required size, is fixed into the finishing strip (item 3) fixed around the perimeter of the window.
Option B. The window is deeply recessed into the wall, by 200 mm or more. In such a situation, the following option seems rational: the outer contour of the window opening is framed by an angular profile (item 4), the area of the slopes is assembled from short fragments of siding panels (the scraps that inevitably remain during cutting are quite suitable), which, in turn, are inserted into the groove J- profile (item 1) mounted around the perimeter of the window.
Depending on the specific conditions, the required profiles are calculated. Again, remember the rule: the window frame will only look neat if it is assembled from entire sections of profiles.
Finish bar
The finishing strip is used to complete the wall plane along the upper horizontal line - the profile configuration is designed to securely hold the thin cut edge of the siding panel. It is also used in conjunction with a window profile and a J-profile with a chamfer. Then, to calculate this strip, it is necessary to calculate the length of the horizontal end of the siding, the length of the near-window strips and the length of the wind ones.
So, the required length and, accordingly, the quantity of each of the additional profiles is calculated individually, slowly, carefully thinking through all sections of the wall cladding, summing up the obtained values, if certain planks are used for different purposes and in different places. This may seem like a tedious task, but there is nowhere to go - believe me, probably no one will do such a job better than the owner anyway.
In addition, you can approach such a task “smartly” and systematize it. For example, it will be convenient and clear if you create a table for the types of profiles and sections of cladding and, gradually carrying out calculations, fill it in parallel with the obtained values. This way it is quite possible to quickly and very accurately obtain the required result, which will be as close as possible to the “ideal” and will produce a minimum amount of waste even during installation operations.
Calculation algorithm
After receiving all the necessary data, you can safely proceed to calculating the surface area. For this it will be quite enough to know the usual mathematical formula:
Finish = Wall Length * Wall Height
Such calculations will need to be carried out for each wall separately.
After this, all received data are summarized. The final number indicates the amount of finishing required for all repair work. In order to save material, the area of windows, doors and other protruding objects is subtracted from it.
At the next stage of calculations, the owner will need to calculate the total area of one specific panel of the selected type of siding. To do this, all the necessary measurements are made, and then this formula is applied:
Panel area = Panel height * Panel length
At the last stage, you can already obtain the exact amount of material that will subsequently be mounted on the walls:
Number of panels = Finish\Panel area
What needs to be calculated?
Siding is one of the easiest ways to improve the appearance of your home. However, in order for siding to be mounted on walls, it must first be purchased. But no one wants to spend extra money on material that may end up lying around in the shed, or vice versa - buying too few siding panels. That’s why it’s so important to calculate the required number of panels before going to the store.
To cover walls with siding, it is not enough to just buy the material itself. Other elements are also needed, which are discussed in the table below.
Components for cladding a house with siding
Table. Accessories for cladding a house with siding.
| Profile type | Description |
| Wall panel | The same ordinary siding that will create the beautiful appearance of the building. It can have different sizes and colors. Usually mounted horizontally. |
| Start profile | It is attached to the lower level of the cladding and will serve as a guide for the first row of siding. Connects to the first line with a special locking connector. |
| Starting bar | Performs the same functions as the starting profile, but in the rear shelf it is lower than the profile and less durable. |
| Connector strip (H-profile) | It is used to join two pieces of siding into a single system to increase the length of the panel. Placed vertically and can be used as a divider. |
| Finishing profile | Installed on the last row of facing panels. |
| Drain plate | It is located above the projections on the wall, above the protruding part of the base. Plays the role of ebb or performs a decorative function. |
| Profile for internal corners | Designed to hide the joints of panels between two walls in the internal corners of the building. It is not always used, as it can be replaced by a J-profile. |
| Profile for decorating external corners | Designed to hide the joints of panels between two walls at the outer corners of the building. Often a different color is used than the house cladding itself (for contrast). |
| J-profile wide | It is installed at the junction and is often only a decorative element. Can be turned into window casing. |
| Wind board | Using it, the end part of the cornices is finished. It also helps secure the soffit. |
| Sloping or near-window profile | It is used to frame window openings and doors recessed into the wall of a house, and to form slopes. |
| J-profile | Used for framing cladding, fastening soffits, finishing internal corners. In general, a universal profile. |
| Soffit | A profile that looks very similar to the siding itself. It is hemmed onto the lower part of the roof eaves. |
Sheathing the cornice with siding
It is precisely these parts that you need to purchase in order to successfully install the cladding of your house. Siding panels alone are not enough here. However, some elements may not be needed - it all depends on the architectural features of the building.
Calculation of siding on the gable
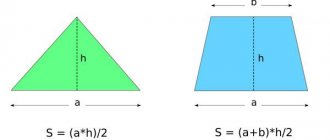
Additionally, you will need to calculate the amount of siding on the gable. Today, triangular and trapezoidal roofs are most often used. Depending on the form, the further calculation option is selected:
Gable area = (Center height * Base width) \ 2
As a rule, the gable is the same on both sides of the house, so the result should be multiplied by two.
Visually or in the drawing, the pediment must be divided into two parts by a horizontal line so that you get a rectangle on the bottom and a triangle on top. The result will be obtained for the area that will need to be added together.
Area of the rectangle = Height * WidthArea of the triangle = (Height at the center * Width of the base) \ 2
Pediment area = 2 (Area of rectangle + Area of triangle)
During the installation process, it is impossible to completely insure yourself against defects or damage to part of the material. The situation can only be avoided if you immediately buy a little more siding. It comes from unforeseen expenses. Experienced builders advise buying 15% more of any building material.
Polymer siding: types and parameters
Vinyl siding (photo No. 5)
Polymer siding is the market leader. It accounts for 50% of sales volumes of facing materials. The popularity of such siding is associated with its versatility, affordable cost, lightness and ease of installation. The panels do not rot, do not rust and do not support combustion.
!
Polymer siding is the market leader. It accounts for 50% of sales volumes of facing materials.
When temperature fluctuations occur, the panels seem to breathe - they expand and contract. This does not affect their quality. Properly installed polymer siding does not deform even with sudden temperature changes above 0 degrees.
There are several types of polymer panels on the market:
- Vinyl siding is frost-resistant and is perfect for most regions of Russia, especially the northern ones.
- Acrylic siding is UV resistant, does not fade and is suitable for southern, sunny regions.
- Foam siding - with increased thickness. Improves the thermal insulation properties of wall structures. It looks exactly like wooden panels - in texture, color and thickness.
- Blockhouse is vinyl or acrylic siding that imitates rounded timber. In terms of performance characteristics, it corresponds to panels made of vinyl and acrylic, but differs in shape and size.
How to calculate siding for cladding a house. Calculation examples
Most often, builders use a formula for calculating the surface area and front parts of a building. After this, the results obtained are summarized. In the future, they will be required to subtract the area of windows, doors and openings used for the balcony.
You need to calculate the area of the walls of a house 6 by 7 meters. The total height of each wall is 4 meters.
Applying the formula described above, we obtain the total surface area of the walls: 2*6*4+2*7*4=104 square meters. At the next stage, we measure the size of the windows. For example, we have 4 standard windows 1.47 by 1.46 and one round one, which is 0.6 m in diameter. Calculation of the area of square windows: (1.47 * 1.46) * 4 = 8.6 square meters.
The area of a square window is calculated by the formula: S = π r2(r – radius, π = 3.14). π (0.6)2= 0.36 * 3.14 = 1.1 square meters. Let's calculate the area of the front door 0.83 * 2.04 = 1.69 square meters. The pediment is located on both sides of the building and has a standard triangular form. Its height is 2 and its width is 6 meters.
2 (6*2)\ 2 = 12 square meters. Next, you should subtract the area of the windows and doors from the total: 104 – (8.6 + 1.1 + 1.69) = 92.61 square meters. To the obtained result we add the area of the pediment: 92.61 + 12 = 104.62 square meters. Further calculations will be made taking into account that a siding panel of 3.66 by 0.232 meters was previously selected. Its area is correspondingly equal to 3.66 * 0.232 = 0.85 square meters. To obtain the number of lamellas in pieces, the total area should be divided by the value for one board: 104.62\0.85 = 124 pieces. 15% should be added to the resulting value for scrap: 111+111*0.15=186 pieces.
Fiber cement siding
Fiber cement siding (photo No. 2)
This is a durable finishing material with a beautiful relief pattern. It does not change its physical characteristics either in heat, cold, or during heavy rains. But it is used infrequently in private housing construction: it is expensive, heavy and more demanding in operation than its competitors.
If complexity and price do not scare you, the material parameters will be useful to you. Dimensions of fiber cement siding panel:
- ➠ Thickness: ranges from 6 to 35 mm
- ➠ Width: from 305 to 1500 mm
- ➠ Usable width: similar, from 305 to 1500 mm
- ➠ Length: 0.45 – 3.6 m
- ➠ Area: on average from 1.2 to 2.5 square meters. m
If you need panels shorter/longer, wider or narrower, explore the range of different manufacturers. The quality in most cases will be decent, but you can choose the appropriate siding parameters to reduce the number of trims and unnecessary costs.
Subtleties of calculations
In order for the calculations to be as accurate as possible, you should use a sketch of the building and gables.
We should also not forget that siding can be up to 6 meters in length. Walls can be long. For example, 6 by 9 meters.
In this case, you can place the entire panel on one wall. For the second wall, you will have to make a special siding connection using a profile. This factor must be taken into account at the stage of carrying out all necessary calculations.
For example, when calculating the amount of material required for a house 8 by 8 meters, you should take into account the need to make a joint on each wall. The same situation will be typical for a house 10 by 10 meters.
You will also have to think about the scraps that will certainly arise from each batch. To cover a wall 8 by 8 meters, you will need to take a siding lamella of 6 and 2 meters. In this case, you are guaranteed to have 4 meters of trim left, which can be used for other walls.
In this case, builders advise making the seam in the middle. To do this, cut the siding into 4-meter sections. The remaining trimmings will be useful for tiling work for the pediment. Thanks to the drawings, it will be possible to visually evaluate all use cases. Only after this will you be able to easily choose the optimal one in terms of design and economy. Also, this layout will allow you to save a lot and not purchase extra material.
The drawings should be kept for the entire period of siding installation. You may need to consult them at any time.
In the process of repair work, the quality characteristics of the material used are of great importance.
Metal siding for the house: sizes and types
Metal siding to look like wood (photo No. 4)
Siding is made from aluminum or steel and zinc. The first option is lighter, the second is stronger. Metal siding imitates a wooden facade, but does not burn or rot. Plus - you can choose panels according to length - up to 6 m. Thanks to this, you can often do without a connecting strip.
Average parameters of metal siding:
- ➠ Thickness: 5 – 13 mm
- ➠ Width: 190 – 210 mm
- ➠ Usable width: 170 – 190 mm
- ➠ Length: from 0.5 to 6 m
- ➠ Area: from 0.25 to 3 square meters. m
Metal siding does not have a heat-insulating effect. It is most often used not in private housing construction, but for cladding industrial and commercial buildings.
Advice from professionals
Installing siding is a simple process. However, before you start, you should carefully read the instructions. Additionally, it is recommended to listen to the opinions of experts in this field:
If there is such a possibility, then when purchasing siding it is necessary to stipulate the conditions and the possibility of returning it in case of non-use.
For additional insurance, the terms should also be determined in advance. The process is beneficial for both parties, so the seller is guaranteed to meet the buyer. Correct calculation of the material is of no small importance. If it was produced by two companies and there are discrepancies, then most likely the rules and regulations were not followed.
Correctly calculating the need for material when installing siding is already half the battle. All calculations can be done independently. In order to ultimately get the correct number, you must strictly adhere to all the rules and regulations of the procedure.
Did you like the article? Share!
One of the most popular materials for exterior finishing is siding.
Those who choose this option are always faced with the question of how to calculate the amount of siding, additional elements and funds for everything.
There is a simple scheme that helps you purchase the amount you really need.
Wooden siding for exterior decoration: dimensions and application features
Wooden siding for exterior decoration (photo No. 3)
Wood is a beautiful, environmentally friendly cladding.
To decorate the facade, different wooden panels are used: planken, blockhouse, American, etc. But traditional lining is not suitable for interior decoration - it is not designed for use in cold weather, rain and sun.
Wooden products will withstand harsh natural conditions only if strict requirements for their dimensions are met:
- ➠ Thickness: 18 – 23 mm
- ➠ Width: 200 – 220 mm
- ➠ Usable width: 180 – 220 mm
- ➠ Length: 3 – 4 m
- ➠ Area: 0.55 – 0.88 sq. m
If these parameters are not met, the board may warp (twist) during operation.
Wood siding is the most whimsical. It must be regularly treated with protective agents against moisture, pests and fire. That's why it is rarely used. As a rule, for cladding houses in eco-style.
House size 9*8 meters
Calculating the amount of siding for a house begins with calculating the square meters that will be finished with siding on the outside.
Having a standard house, without recesses and extensions, measuring 9x8 meters, you just need to find the area of its walls.
Formula: (2* for width + 2*for length)* for height.
The height of a standard house, excluding the basement, is usually 2.7 meters.
In total, the wall area for siding is 91.8 square meters.
To calculate the amount of siding per house, you need to take into account the size of the windows. Let them be of standard size 1.2 meters by 1.4 meters. And there are only 5 of them in the house.
From the area of all walls, you need to subtract the area of all windows, because they will not be covered with panels. The calculation is simple: you need to multiply the length and width of each window, and then multiply everything by the number of windows.
It turns out everything is simple: 1.2X1.4X5 = 8.4 square meters. Then we subtract the resulting area from the area of the entire house: 91.8-8.4 = 83.4 square meters. meters.
In addition to windows, the house has at least one door.
Its standard size is 2.1m by 0.9m. The door area in this case will be 1.89 square meters. From the area of all the walls (already without windows), we also subtract the door.
As a result, the area covered by the panels is 81.51 square meters. This is the first floor of the house, without a roof. Roof gables are also usually covered with siding; there are often no windows in this area.
Having roof dimensions of 6m by 6m and 8m, you just need to find the area. This is from a geometry course at school: one pediment is an isosceles triangle. Its area is found by the formula: height per base.
Roof height: 4.5 meters, base 8 m. The area of one gable is 18 square meters. There are always two of them in the roof, that is, 36 squares.
You need to add them to the area of the entire house: 81.51+36=117.51.
This is the entire area that will be covered with siding. It can be rounded up, because the panels will have to be cut. So, the total area is 118 square meters.
But that's not all with the roof. In addition to the pediment, siding is also sheathed (chamfer). Its standard width is usually 45 cm.
There are four chamfers in total, each 6 meters long. A total of 10.8 squares of panels per hem is obtained. Rounding, we get 129 square meters per panel.
To calculate the number of panels for cladding a house, you need to know the dimensions of the siding. Standard size of vinyl siding: 3 meters - length, 205 mm width.
Area of one panel: 3X0.205=0.615 square meters. That is, the calculation of vinyl siding panels per house will be as follows: 129:0.615=209.756 pieces.
Rounding up, we get about 210 pieces for the whole house. But don’t rush and run to the store for siding. Panel panels are different.
Knowing the total number of panels, you need to calculate the number of starting panels, the number of external and internal corners, trims for windows and doors.
We count the starting panels in meters: we add up all the sides of the house (width and length). That is: 8+8+9+9=34 meters. The starting panels will need exactly this amount.
The size of the starting profile depends on the type of siding. So, for panels 3 meters long, you can choose the same starting profile to which the first panel will be attached.
Profile size: 3 meters long.
That is, you will need about 12 such profiles for the whole house. It’s easy to calculate: divide the total number of meters by the length of the panel. The same number of finishing panels will be required.
An ordinary rectangular house will need only four external corners. By the number of ribs near the house.
The height of the house is 2.7 m. The standard length of the outer corner is 3.05 m. That is, only 4 outer corners are required.
If there are no internal corners, then there is no need for panels for it. Since the siding will have to be joined, connecting panels (H-profile) will also be required.
The length of this panel is 3.05 m. It is mounted exclusively vertically. That is, for a house with dimensions 9 * 8, panels 3 meters long, you will need only 8 connecting panels.
Three H-profiles are needed on the sides of a house with a length of 9 meters, and one profile on sides with a length of 8 meters.
The J-profile is ideal for finishing windows and doors. Its standard length is 3.66 meters.
For five windows measuring 1.2*1.4 you will need about 9 pieces of profile. There are 3 more J-profiles under the door. With a reserve it turns out to be about 12 pieces.
Hemmed ones can be finished either with panels or with a special soffit for siding. In this case, they often choose panels that will be mounted vertically.
Since the width is only about 45 cm, they are usually made from trimmed panels, without spending money on soffit.
In total, for the whole house you will need:
- horizontal siding panels – 210 pieces;
- connecting panels – 8 pieces;
- window and door trim – 12 pieces;
- external corners - 4 pieces;
- starting panels – 12 pieces.
Only after this can you begin to calculate the average cost of covering a house without taking into account work.
How to make an independent calculation?
Calculation of the number of siding panels
It is clear that the “lion’s share” of the entire purchase will be cladding panels – in fact, the siding itself. This is where we will begin our calculations. And you can determine the number of panels in two ways - mathematical and graphical.
Mathematical approach
The mathematical calculation consists of using the formula: the approximate number of panels ( Nп ) should be equal to the ratio of the façade area to be covered ( Sф ) to the usable area of the panel itself ( Sp ).
Nп = Sф / Sp
Naturally, it is necessary to create a certain reserve - for cutting and for possible defects in the work. Typically, a margin of 7% is accepted for siding - practice shows that this is sufficient for rectangular walls.
Nп = (Sф / Sp) × 1.07
How to determine the finishing area will be discussed below, but for now, a few words about the area of the siding panels.
- If you read some articles on the Internet devoted to similar calculations. then you can come across a “nice picture” - the authors shamelessly claim that the dimensions of the siding are approximately the same - the length is “about three meters” and the width is “about 20 centimeters” (by the way, I quote it verbatim, which is why I put it in quotes).
It is not clear what motivates those who write this, but if you take their recommendations for calculation, you can “go far.”
To begin with, let's figure out what the useful or working width of the panel is.
Diagram of a siding panel highlighting its total and working width
If you look at the siding “board”, you can see that part of it falls on the area with perforations - this is a mounting strip, which, after installing the next row of panels, is hidden from view and, therefore, cannot be taken into account when calculating the covered area. This means that the total width of the panel (highlighted in blue in the figure) has, rather, a reference or technological value. But to calculate the amount of material, you have to operate exclusively with the visible (otherwise useful, working) width of the panel - it is highlighted in red in the proposed diagram.
The accompanying documentation for siding may indicate either one working value or both values - you need to be careful not to get confused with this.
But the variety of working sizes among the siding collections on sale is quite large, and very often quite different from the mentioned “about 20 centimeters”. There may also be differences in the length of the panels. For example, the table below summarizes popular siding models from the most well-known manufacturers on the Russian market - with the values of the standard length, working width and usable panel area. Please note the fairly wide range of values.
| Model name | Illustration | Panel length | Working panel width | Panel area |
| "ALTA-PROFILE", Russia | ||||
| Collection "Alta-Siding" | 3660 mm | 230 mm | 0.84 m² | |
| Collection “KANADA Plus”, “Prestige” or “Premium” | 3660 mm | 230 mm | 0.84 m² | |
| Vertical siding collection “Quadrohouse” | 3100 mm | 205 mm | 0.635 m² | |
| “Blockhouse” collection, vinyl or acrylic, single-fracture - one “rounded log” | 3100 mm | 200 mm | 0.62 m² | |
| “Blockhouse” collection, vinyl or acrylic, double-fracture – two “rounded logs” | 3100 mm | 320 mm | 0.99 m² | |
| "TECOS", Belgium - Russia | ||||
| Model range “Ship timber” | 3660 mm | 230 mm | 0.84 m² | |
| Model range "Vagonka" | 3660 mm | 254 mm | 0.93 m² | |
| Model range “Round logs” | 3660 mm | 203 mm | 0.74 m² | |
| Model range “Double rounded log” | 3660 mm | 230 mm | 0.84 m² | |
| "FineBer", Russia | ||||
| Wall siding – “Standart” profile | 3660 mm | 205 mm | 0.75 m² | |
| Wall siding – “BlockHouse” profile | 3660 mm | 232 mm | 0.85 m² | |
| NordSide, Russia | ||||
| Wall siding – “Classic” series | 3050 mm | 231 mm | 0.704 m² | |
| 3850 mm | 231 mm | 0.89 m² | ||
| Wall siding – “Lapland” series | 3050 mm | 205 mm | 0.625 m² | |
| Wall siding – “Lapland – log” series | 3050 mm | 230 mm | 0.70 m² | |
| Holzplast, Germany | ||||
| Siding wall series “Premium” and “Meister”, D4 | 3660 mm | 205 mm | 0.675 m² | |
| Siding wall series “Premium” and “Meister”, D4.5 | 3660 mm | 231 mm | 0.845 m² | |
| Siding wall series "Baumann" | 3660 mm | 232 mm | 0.85 m² | |
| Wall series siding “Holzblock” – 150 mm log | 3660 mm | 298 mm | 1.09 m² | |
| Wall series siding “Holzblock” – 180 mm log | 3660 mm | 182 mm | 0.665 m² | |
| Wall series siding “Holzblock” – 250 mm log | 3660 mm | 253 mm | 0.926 m² | |
| Mitten, Canada | ||||
| Siding wall series "Oregon Pride" | 3660 mm | 230 mm | 0.84 m² | |
| Siding wall series “Sentry Mitten” | 3660 mm | 230 mm | 0.84 m² | |
| Siding wall series “Southern Beaded” | 3660 mm | 169 mm | 0.618 m² | |
| Vertical wall siding of the “Board & Batten” series | 3040 mm | 178 mm | 0.54 m² | |
| "CertainTeed", USA | ||||
| Siding line “Encore” - “Double ship timber” D4.5 | 3680 mm | 230 mm | 0.846 m² | |
| Siding line “Encore” - “Double Christmas tree” D5 | 3660 mm | 254 mm | 0.93 m² | |
| Siding line “Encore” - “Double Christmas tree” D4 | 3810 mm | 203 mm | 0.773 m² | |
| Siding line “Encore” - “Triple Christmas tree” T3 | 3680 mm | 230 mm | 0.846 m² | |
| Siding line “Monogram” - “Double ship timber” D5 | 3660 mm | 254 mm | 0.93 m² | |
| Siding line “Monogram” - “Double Christmas tree” D5 | 3660 mm | 254 mm | 0.93 m² | |
| Siding line “Monogram” - “Double Christmas tree” D4 | 3810 mm | 203 mm | 0.773 m² | |
| Siding line "Cedar Impressions" - "Beavertail" | 820 mm | 320 mm | 0.262 m² | |
| Siding line “Cedar Impressions” - “Straight shingles” T5 | 1520 mm | 380 mm | 0.579 m² | |
| Siding line “Cedar Impressions” - “Straight shingles” D7 | 1220 mm | 360 mm | 0.442 m² | |
| Siding line “Cedar Impressions” - “Offset shingles” D7 | 1220 mm | 360 mm | 0.442 m² | |
| Siding line “Cedar Impressions” - “Straight chips” D7 | 1450 mm | 360 mm | 0.515 m² | |
| Siding line “Cedar Impressions” - “Offset Chips” D9 | 1450 mm | 460 mm | 0.667 m² | |
| "DÖCKE", Germany - Russia | ||||
| Siding of the “D4.5 Dutchlap” model range - “Ship timber” | 3660 mm | 232 mm | 0.85 m² | |
| Siding of the “D5C Herringbone” model range | 3050 mm | 256 mm | 0.78 m² | |
| Siding of the Block House model range | 3660 mm | 240 mm | 0.88 m² | |
| Vertical siding S7 | 3050 mm | 179.6 mm | 0.55 m² | |
By the way, the table shows only vinyl siding. And if you add metal to this, then the variety of sizes can be even wider.
- At first glance, the area to be covered is not at all difficult to calculate - in the vast majority of cases, the walls are rectangular in shape, and finding the product of the length of the wall (the perimeter of several walls or the entire house - if the walls have the same height) and the height - will not be difficult.
If the walls have different heights, then it is more expedient to carry out calculations for each of them and then summarize the results.
- There are areas on the walls that are not subject to cladding - these are window and door openings, and in some cases also, for example, garage doors. Usually they are removed from the calculation by subtracting their area from the total. Naturally, it would be reasonable to do this in the case where the area of the openings is really significant. But, for example, if there is one small dormer window or a small vent for ventilation on the wall, then you shouldn’t bother - it will be easier to take into account the total area of the wall.
Should such a window be excluded from the total area?
It’s probably easier to “not notice” it at all when calculating the amount of siding. The reader is offered a calculator that will help to quickly and accurately calculate the required number of siding panels for cladding the facade. Some explanations of the calculation will be given below.
Calculation of the cost of siding for a house
The cost of siding depends both on the area and on the type and company of panels.
However, the average price for the panel stubbornly remains in the region of 150-180 rubles.
This means that for a house with a size of 9*8 and a number of panels of 210 pieces, you will need (210X180) about 38 thousand rubles.
In addition to siding, accessories also need to be included in the cost calculation:
- connecting panels, price for 1 piece - about 200 rubles;
- J-profile, price for 1 piece—about 130 rubles;
- External corner - about 300 rubles;
- Starting panel - about 100 rubles.
This means that the cost of each additional element must be added to the cost of the material. The connecting panels will cost another 1,600 rubles.
For J-profile – 1560 rubles, external corners – 1200 rubles, for starting panels – 1200 rubles. The final amount for covering the house is: 44 thousand rubles.
Naturally, the amount of material needs to be taken with a small margin.
It will be unpleasant if only two or three panels are missing, and the store runs out of the appropriate color. Not to mention that the panel sizes also vary.
Depending on the size of the house, you need to choose the size of the siding so that it has less to cut, join, and connect.Instructions for installing siding
Please share this article:
At the stage of finishing the facade, a fair question arises: “how to calculate the siding for a house.”
You can contact a specialist who will quickly determine the required amount of material. Another option is to save money and calculate the siding and components yourself. It's not difficult to do this.
Before you get started, you should arm yourself with a tape measure and measure the house. If there is a detailed plan of the façade of the building with the width and height of walls, door and window openings, and various façade elements indicated on it, manual measurements can be avoided.
Purpose of the calculator
To determine the required amount of siding, you first need to know the area of the walls. Siding sheets are the main cost item, but in addition to them, various additional elements will be needed for cladding. Their number will depend on the configuration of the walls, the features of the roof structure, the number of windows and doors.
Main cladding elements
Corner profile - internal and external, is produced in a standard configuration with a bend of 90 degrees; in the case of cladding, for example, bay windows, it will have to be unbent.
Platband - made in the same color as the main siding, calculated in linear meters, but it is better also in pieces to prevent unsightly joints, used for window and door openings.
Start and finish profile - used to secure the first and last row in order to hide the attachment point, measured in linear meters. J – profile – this is a profile designed for the design of sections; it is used mainly for fastening soffits, less often – in the process of cladding. H - profile - a connecting element used to form the joints of siding sheets in the case of large spans, for example, when finishing hangars and pavilions, appears in calculations only when the length of the walls exceeds 6 - 10 meters.
Elements for finishing the roof: cornice boards and soffits. The first serves as a starting profile, therefore it is calculated in linear meters. The area of the spotlights is calculated depending on the width of the overhang. Obviously, calculating all these components yourself is not difficult, but it will take an extremely long time. An online calculator for calculating siding for cladding a house will do the job in a fraction of seconds.
Calculator for calculating siding and auxiliary elements
Rules for taking measurements of the facade of a building
We measure each wall of the building, including the pediment, separately.
Even structurally identical walls have slight differences. Determine the area of the sheathed part. It will be equal to the product of width and height. From the result obtained, you should subtract the area of areas that do not need finishing (doors, windows, other facade elements)
S side = S walls – S windows/doors,
where S=a*h (a – surface width, h – surface height).
How to calculate siding for a house, taking into account windows and doors? The area of door and window openings should be subtracted from the area of walls and fronts. The area of the pediment (using the example of a triangular pediment) is determined by the formula:
S = ½ * a * h,
where a is equal to the length of the cornice, and h is the height of the pediment.
Important! When taking measurements, record the value in the form of diagrams and sketches. This will allow you to visualize the structure and schematically plot the location of the cladding.
Vinyl siding size
Wood-look vinyl siding (photo No. 6)
Average market sizes of classic vinyl siding:
- ➠ Thickness: 0.6 – 1.3 mm
- ➠ Width: 220 – 275 mm
- ➠ Usable width: 200 – 255 mm
- ➠ Length: 3 – 3.75 m
- ➠ Area: 0.65 – 0.85 sq. m
They differ from one manufacturer to another. Siding that is too thin can be brittle in the winter and not last long. Although thickness is not an indicator of quality. Panels need to be assessed comprehensively based on a number of parameters.
For orientation, here are the dimensions of Alta-Profile siding:
- ➠ Thickness: 1.1mm
- ➠ Width: 205, 230 mm
- ➠ Relief height: 12 mm
- ➠ Length: 3 or 3.66 m
Vinyl is the most common type of siding. It is suitable for any private house, cottage, bathhouse, barn, garage, and other buildings and structures.
Acrylic siding has the same dimensions as vinyl siding. Therefore, we will not dwell on it in more detail.
Technology for calculating siding for a house
First, we calculate the number of panels in square meters.
Next, we translate the resulting value into jokes. The area of the skin will correspond to the area of the panels. It is recommended to add an additional 5-20% for waste during cutting.
The sheathed area should be divided by the area of one panel and add a margin. Thus, we will calculate the siding for the house.
Calculation of the subsystem for siding. Frame components
There is a slight difference in terms of frame composition between a ventilated siding facade and conventional cladding on a bare wall.
Frame on a bare wall
The siding subsystem consists of a frame profile, U-shaped hangers, and hardware.
The frame profile is the basis for the rigidity of the structure. It is made of durable galvanized steel.
The UD profile is used for edging door and window openings.
The CD profile is used to install vertical or horizontal racks. For cladding with metal siding, the profile is always mounted vertically in increments of 500-600 mm. It varies in width, depth of shelves, and metal thickness.
The minimum metal thickness for fastening siding is 0:45 mm. The profile is produced with a length of 2500-3000 mm. If the height of the facade exceeds the dimensions of the profile, then several elements are mounted in a row.
They are connected to each other using a CD connector. A thermal gap of 5-10 mm is left between the profile.
ES-bracket is a simplified version of the mounting bracket. This is a perforated U-shaped suspension. With it you can adjust the distance from the wall to the CD profile. Thus, possible nervousness and height differences on the facade are leveled out.
Hardware. To attach the hangers to the wall, self-tapping screws, self-tapping dowels or dowel-screws are used. It all depends on the material of the base of the wall.
To connect the metal parts of the façade subsystem, 3.5x9.5mm metal screws are used
Frame for a ventilated facade
There are several types of subsystems that are used to construct a ventilated siding facade:
L-shaped suspension system
Consists of a galvanized metal profile and brackets. The L-shaped profile is secured to L-shaped brackets using a bolted connection.
The design feature is retractable brackets. With their help, you can mount the profile at a distance of up to 380 mm from the wall. This allows you to level the most “littered” facades.
The brackets are attached to the wall with anchor dowels with wrench heads or a Phillips screwdriver. A paronite gasket is installed between the wall and the fastening element. It protects the connection point from corrosion. To construct a more durable ventilated facade made of metal siding, reinforced brackets for the L-shaped profile are used. They have a wall thickness of 1.2 mm.
The L-shaped suspension system has a high cost per square meter.
U-shaped hanging system
It consists of a U-shaped profile and L-shaped brackets with two stiffening ribs.
The profile is clamped between two L-shaped brackets, which are connected in pairs on a special strip.
To fasten metal elements together, 3.5x9.5mm self-tapping screws are used. The plank is fixed to the wall using anchor dowels.
A paronite gasket is installed between the wall and the connecting strip with L-shaped brackets.
A U-shaped suspension system for a ventilated facade is much more difficult to install than an L-shaped one.
Mathematical method for calculating material
The mathematical approach is based on determining the covered area of the house and calculating the number of panels. The number of panels for flat surfaces is determined by the following formula:
04
Source m-strana.ru 04 Source m-strana.ru
where N is the number of panels taking into account the cutting procedure (7-10% for rectangular blank walls, 10-15% for trapezoid-shaped surfaces with openings), Sd is the total covered area of the building taking into account the dimensions of the frame for installation, Sp is the working area one lamella.
Material calculation Source sv.decorexpro.com
If the house has straight walls (without protrusions, decorative ledges, the same height), then the following algorithm is used to determine the covered area:
- Using a tape are measured . The thickness of the sheathing is added to them, these values are multiplied;
- The parameters of windows and doors measured separately
- The area of window and door openings is subtracted from the total area of the walls
If the building has a non-standard layout, has a large number of decorative elements, or has walls of different heights, calculate the number of panels for each wall separately. The total quantity of siding for sheathing is obtained by summing the individual results.
The amount of sheathing for gables is calculated separately, using the same principle for non-rectangular walls.
00>
Calculation of materials for buildings with non-standard layout Source tanders.ru 00 01> Calculation of materials for buildings with non-standard layout Source tanders.ru 02> Calculation of materials for buildings with non-standard layout
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in insulation and finishing of houses.
What it is
For the first time, siding panels appeared in America in the middle of the 20th century, someone decided to simplify the process of exterior decoration of a house and at the same time decorate the appearance. This is how new finishing materials, beloved by many, appeared, distinguished by their aesthetic appearance and durability.
They produce products in different colors that do not change their original color and shape even with temperature changes and exposure to external factors. No matter what happens on the street, your home will always remain under reliable protection from bad weather, snow or rain.
Caring for vinyl panels is simple and affordable: you just need to direct a stream of water, all the dirt will be washed away, and the house will sparkle clean again.
The panels are mounted with a “reserve”, and between the wall of the house and the finishing material there is a small space for heat exchange, which allows you to insulate the house without any problems. The weight of the panels is small, easy to transport by any available transport, without hiring additional equipment. Finishing a house with siding is a modern and correct solution for a zealous owner.
Using the calculator
The convenience of this approach is that calculations are carried out simultaneously on the number of wall panels, additional elements, and the price of all materials.
When using a calculator to calculate the area of the facade of a house, the measured parameters of the house are taken into account with an allowance for the thickness of the sheathing or guides.
Calculator programs have functions for calculating siding, components, and the costs of their purchase. They allow you to quickly calculate different finishing options and compare costs. Calculations are carried out for several types of walls and house options. The following data is entered into the house siding calculator program with the cost:
- basic parameters of the house (walls);
- dimensions of all openings;
- type, geometric parameters of guides , method of their installation, cost of 1 m² of material;
- area and perimeter of door openings ;
- standard sizes of siding , as well as price per 1 m², per 1 panel, quantity per package.
Calculator for calculating the area of the facade of a house Source tr.decorexpro.com
On a note! When using a calculator, you must take into account that these are far from professional tools and work on the basis of algorithms known only to their developers. That is, you will not know whether this service takes into account any tolerances, plus, calculations are usually done for the simplest shapes and forms. Therefore, any Internet counting cards should be perceived only as toys that can make an approximate calculation, which in turn can be used to roughly estimate the profitability of using a particular material.
Geometric method of calculations
Let's determine how much siding is needed for a 6x6 house using geometric constructions and calculations for one wall:
- width 230 mm, length – 3660 mm;
- height 4 meters;
- number of stripes in height – 18 pcs.;
- Since the length of the wall is 6 m, the panels will be laid in two rows . This means that one wall requires 18 * 2 = 36 stripes for a blank wall.
If there are windows, the distances from the corner to the window and between the openings are measured. These values are applied to the sketch, and the panels are cut. For example, there is one window at a distance of 2 meters from the corner and at a height of 1.38 m from the ground, and 1.15 m from the roof.
Computations:
- solid stripes;
- from the side of the measured angle to the window, 7 pieces 2 m long;
- waste 3.66 – 2 = 1.66 meters from each of the seven lamellas, can be used elsewhere.
Types of siding Source sargorstroy.ru
Professional calculation
Before starting work, you need to know the exact area of the area that you are going to cover with siding panels. To make accurate measurements, it is best to seek help from specialists. In their work they use:
- Laser measuring tapes;
- Software for calculating estimates taking into account all the construction features of the building;
- Knowledge of atmospheric and weather conditions in the area where the building is located;
- Regulatory documents.