Filling a floor screed in an apartment or industrial premises is a mandatory procedure. The finishing coating is laid on the leveled base or it is used without finishing as a working surface for industrial production. Before deciding how to calculate the amount of cement for floor screed, you need to find out the purpose of the room and the expected load on the concrete base.
One of the main criteria in preparing a solution for pouring a base is its thickness. It should be remembered that reinforcement with metal mesh is carried out with a minimum base thickness of 20 mm, a maximum pouring height of 40 mm, this is the thickness most often used for flooring in civil housing construction.
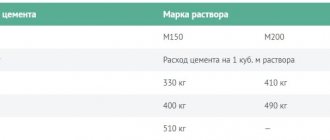
The next important point for calculations is the grade of cement. To organize the base, cement grades M300, M400, M500 are used. As a result of mixing with sand and water, a cement mortar with a value of M150 or M200 is obtained.
The brand of the mixture is determined based on the planned load on the base. Thus, M200 can be used to organize foundations in industrial buildings, for example, in garages, and the strength of the M150 grade is sufficient for pouring screed in an apartment.
To carry out calculations, it is necessary to know the rate of cement consumption to obtain a solution of a certain brand. So, to obtain one cubic meter of M150 grade mortar, you will need 330 kg of M500 cement or 400 kg of M400 cement. To obtain the same volume of brand M200 solution, you need to purchase 410 kg of M500 cement or 490 kg of M400 cement.
Let us calculate the organization of a base 40 mm thick for a room of 30 sq.m. in two versions: for mortar grade M150 and for grade M200 using cement grade M400. Calculation procedure:
- First you need to calculate the volume of fill in cubic meters. To do this, you need to multiply the area by the thickness (30x0.04). The resulting solution volume is 1.2 M3.
- Taking into account the rate of cement consumption per 1 m3 for M150 mortar and M400 cement, we obtain: 1.2 m3x400kg = 480 kg. The weight of one bag of cement is 50 kg, which means 10 bags will be required.
- Taking into account the rate of cement consumption per 1 m3 for M200 mortar and M400 cement, we obtain: 1.2 m3x490kg=588 kg, which corresponds to 12 bags.
- The amount of sand is calculated from a ratio of 1:3, which means for a solution of the M150 brand, you will need to purchase: 480x3 = 1,440 kg of sand, and for a solution of M200: 588x3 = 1,764 kg.
- The volume of water is added gradually until the required plasticity of the solution is obtained.
To carry out screeding work in an apartment, river sand is used; for industrial premises, sand from quarries is chosen.
This model for calculating cement consumption for floor screed is applicable for any area and thickness of the mixture layer. To obtain the area of the room, multiply the length and width of the room.
If the room configuration is complex, it is best to use the floor plan and calculate the area, referring to the paper. Thus, taking into account the ratio of 1:3, it will be possible to determine how much cement and sand is needed per cube of screed mortar.
For dry mixture
When using dry and semi-dry mixtures to organize screed, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics for each specific mixture, which can be found on the packaging. Usually indicate the volume of the mixture to cover one square meter of the base with a layer of 1 mm. For example, to obtain a solution of grade M100 sufficient for use indoors in residential premises, the manufacturer of semi-dry floor screed recommends the following consumption:
- mixture consumption is 2 kg per square meter with a screed thickness of 1 mm;
- water consumption is 0.22 l per 1 kg of mixture.
Taking into account the above data, you can calculate the required material for 30 square meters with a screed thickness of 40 mm.
It is necessary to multiply the area by the mixture consumption per 1 m2 and by 4 (since the planned thickness of the screed is 4 mm, and the calculation is given for a thickness of 1 mm). We get: 30x2x4 = 120 kg, while the volume of water required: 120 kg x 0.22 l = 26.4 liters.
(function(w, d, n, s, t) { w[n] = w[n] || []; w[n].push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: "RA-510923-1", renderTo: "yandex_rtb_R-A-510923-1", async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName("script")[0]; s = d.createElement(" script"); s.type = "text/javascript"; s.src = "//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js"; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t) ; })(this, this.document, "yandexContextAsyncCallbacks");
*Explanations for the calculator
- The calculator can calculate the volume for both whole numbers and fractions. Example: concrete volume 3m3, concrete volume 50l (0.05m3).
- The calculator implements calculations for a mixture with mobility P3 (9-10 cm of cone slump) for cement-lime mortars (according to SP82-101-98). Water consumption for mixtures with different mobility is based on experimental batches. The mobility you need can be viewed in the “Mobility” field, which is automatically filled in when you select “Solution purpose”.
For traditional solution
The traditional calculation of building materials for the production of ordinary cement-sand mortar is carried out in cubic meters, so for ease of calculation it is necessary to convert cubic meters into kilograms.
For example, for an area of 30 sq.m. and a screed thickness of 40 mm will require 1.2 m2 of solution. In this case, the volume of cement will be one-fourth of the total volume, and sand - three-quarters.
It turns out that 0.3 m3 of cement will be required, and 0.9 m3 of sand. The estimated number of kilograms of cement in one cube is 1300 kg, and sand - 1625 kg.
As a result, to obtain 1.2 m3 of solution, you will need 0.3 m3 x 1400 kg = 420 kg of cement and 0.9 m3 x 1625 kg = 1463 kg of sand.
The required volume of water to obtain 1.2 m3 of solution is calculated at the rate of 0.4 liters per kilogram of dry components, which is (420 + 1463) x 0.4 = 753 liters.
Typical cement consumption rates for preparing concrete
The choice of grade (strength class) of cement for preparing the mixture depends on the requirements for the technical characteristics of concrete, on the conditions under which the mixture will be used and the resulting structure will be operated.
The rate of cement consumption per 1 m3 is determined in accordance with the concrete strength class required to be obtained. The most popular classes of concrete mixture and preparation proportions per cubic meter are shown in the table:
| Concrete class | Cement, kg | Cement, kg |
| CEM 32.5 (M400) | CEM 42.5 (M500) | |
| B7.5 | 195 | 175 |
| AT 10 | 225 | 200 |
| B12.5 | 255 | 225 |
| B15 | 285 | 250 |
| IN 20 | 350 | 300 |
| B22.5 | 375 | 320 |
| B25 | 415 | 350 |
| B26.5 | 445 | 375 |
The consumption of the binder depends on the filler fraction of the concrete mixture. For example, the rate of cement consumption for fine-grained concrete (the filler is sand with a particle size modulus of 2.1 or more) can be found from the following table:
| Design grade of concrete | Cement consumption, kg/m3, grade | ||
| 300 | 400 | 500 | |
| M 100 | 345 | 305 | 265 |
| 330 | 290 | 250 | |
| 280 | 250 | 220 | |
| 250 | 225 | 200 | |
| M 150 | – | 365 | 320 |
| – | 350 | 305 | |
| – | 305 | 270 | |
| – | 270 | 230 | |
| M 200 | – | 430 | 370 |
| – | 410 | 350 | |
| – | 360 | 310 | |
| – | 315 | 270 | |
| M 250 | – | 490 | 420 |
| – | 470 | 395 | |
| – | 415 | 350 | |
| – | 360 | 305 | |
| M 300 | – | 555 | 470 |
| – | 530 | 445 | |
| – | 470 | 390 | |
| – | 410 | 340 | |
| M 350 | – | – | 520 |
| – | 590 | 485 | |
| – | 525 | 435 | |
| – | 455 | 385 | |
| M 400 | – | – | 595 |
| – | – | 540 | |
| – | – | 475 | |
| – | – | 415 | |
What does consumption depend on?
The calculation of cement mortar for pouring screed depends not only on the grade of concrete that is planned to be obtained, but also on other factors. The above were idealized calculations, but in real life various changes and amendments arise:
- Examples of how to calculate cement for screed are valid for fresh cement, but if the work is carried out using material produced more than six months ago, the strength of the concrete used will be significantly lower. Therefore, the volume of cement in the mixture is increased by 10-15%;
- If the measurements of the height of the future screed were determined incorrectly or there are significant defects in the base, the volume of the cement-sand mortar may increase to 50% of the calculated volume;
- To save on screed production, as well as to ensure the thermal insulation properties of the base, additives can be used in the mixture of large fractions, and the thickness of such a screed can reach 10 mm. Typically, expanded clay, shungizite or crushed stone are used as additives, but such materials significantly change the properties of concrete and can affect the durability of the screed;
- When placing communications at the base of the screed, a change in volume occurs, which affects the amount of materials for preparing the solution for pouring the screed;
- The amount of material used depends on the brand of cement used and the required strength of the resulting mortar;
- When pouring some rooms, there may be a requirement for organizing the slope of the screed; in this case, there is also a change in the volume of the solution and the materials for its manufacture.
Types of cement
Portland cement is the most popular in construction. To make it, natural raw materials are fired, and then the resulting cement clinker is finely ground.
Adding a small amount of gypsum (about 5%), slag and rocks (up to 10-15%) makes it possible to reduce the cost of Portland cement without significantly affecting its technical characteristics. But if the cement is intended for the construction of road surfaces with a high degree of frost resistance, only gypsum is added.
Portland cement is used to create critical structures and foundations subject to high loads. In addition, a number of cements with specific characteristics made on its basis are used in construction. This is Portland cement:
- with hydraulic additives;
- hydrophobic;
- plasticized;
- slag
There is also alumina cement, which quickly hardens in water and is resistant to aggressive environments - used for emergency work. For mortars and concrete of low strength grades, the use of mixed cements is allowed - in addition to cement clinker, their composition includes various mineral additives and binders (slag, lime) in large quantities.
Depending on the pressure indicator (kg/cm3) during compression of the concrete sample, the cement strength grade was determined - from 100 to 600. Today, a strength class is assigned from 22.5 to 52.5 (in accordance with the sustained pressure, measured in MPa).
Brick
You can even use brick to create a garden path. Moreover, you can also lay second-hand bricks. But such paths will not be beautiful. If you lay ordinary silicate white or red brick, the path will turn out both beautiful and very durable.
But brick paths have their own characteristics. They also need a foundation. For it you can use a mixture of sand and cement. It is not necessary to prepare a solution and mix this mixture with water. It is enough to prepare a trench and make a backfill of small crushed stone.
The mixture must be placed on top of the specified bedding. This mixture is prepared in a ratio of one to two. That is, one part of cement of a grade not lower than M500 is mixed with sand. It is best to mix the materials with a regular construction shovel until the finished fill is obtained.
Cost of laying paving slabs
| Name of works | Unit change | Price |
| Laying paving slabs on a finished concrete base | m2 | 730 rub. |
| Laying paving slabs with preparing the base from crushed stone and sand | m2 | 1030 rub. |
| Laying paving slabs with preparation of the concrete base | m2 | 1450 rub. |
| Installing a garden border | mp | 470 rub. |
| Installing a road curb | mp | 620 rub. |
| Earthworks (excavation) | m3 | 1020 rub. |
| Installation of drainage trays | mp | 680 rub. |
| Installation of rainwater inlets | PC | 680 rub. |
| Drainage system | mp | 680 rub. |
Calculation of materials for concrete
Before starting construction, every developer always asks the question: how many raw materials will be required for the final product and how to determine this?
It's easy to calculate consumption. For example, if to prepare one cube of the finished binder product, 325 kg is required, and the CV is 0.63, then 325 * 0.63 = 205 liters of water are needed. And there is no need to “reinvent the wheel” here. Such calculations are summarized very well in the following table:
Using such data, you can easily and quickly determine the need for raw materials to prepare, say, three cubes of the finished product M200 for the foundation:
cement M400 – 302 kg * 3 = 906 kg; it comes to the retail chain packaged in 50-kilogram bags, so you need to find out how many such bags are needed - 906 kg/50 kg = 18.12 pieces; since the resulting value is fractional, it is rounded up, that is, you need to purchase 19 bags of M400 cement; crushed stone of medium fraction 20 mm – 1208 kg * 3 = 3624 kg; you should pay attention to the fact that when using a different fraction of crushed stone, the consumption of all materials to obtain a cube of concrete will change and the entire composition must be recalculated; sand – 1208 kg * 3 = 3624 kg: water – 205 l * 3 = 615 liters.
Plasticizing additives can significantly improve the quality of concrete
Thus, knowing the initial characteristics of the raw materials, you can accurately make a calculation and determine exactly how many materials will be needed for the needs of building a foundation or any other structures.
It must be remembered that when using plasticizing additives or using a quick-hardening binder, the calculation is subject to adjustment. It is not necessary to calculate the coefficients yourself; reference books have ready-made data on consumption.
General recommendations
- First of all, try preparing a test portion of the solution. Only through experimentation can you achieve the ideal consistency.
- A good quality cement mortar will only stick slightly to the paddle. If the mixture does not stick, then the solution is thin. In this case, it is necessary to add cement to it. If the mixture sticks too much, it is a greasy solution. Sand should be added to it.
- If the product has been stored for a long enough time before use (5–6 months), it has already lost some of its astringent properties. In this case, its share in the solution should be increased.
- The strength of the solution is also affected by the quality of the sand. Sand of medium fraction is best suited. When using fine sand, cement consumption increases.
- Before mixing the solution, all bulk elements must be carefully sifted through a sieve.
- To check the accuracy of the calculations, you can weigh a cubic meter of concrete. Its weight should be 2.4 kg.
- It’s better not to take materials back to back, since it’s completely inconvenient to run out in the middle of work to buy materials that have suddenly run out.
- When making any calculations, data should be rounded up.
How to properly prepare a mortar for floor screed?
To prepare the mixture, sand, cement and water are used, sometimes plasticizers and fillers are added. Fiber or a special reinforced synthetic mesh is used as a reinforced material. The filler can be marble chips, crushed stone or expanded clay; they are used to increase the volume of the concrete mass. In addition, the additional strength and thickness of the base increases, in many cases this factor is of primary importance.
To mix the components you need a dry container, shovels and preferably several people - pouring the floor is a physically difficult process. The main fillers, fiber, and plasticizer are poured into the container. The entire mass is thoroughly mixed until a homogeneous composition and color is obtained. Then, water is carefully added, while continuing to mix the composition. Ideally, the consistency should be plastic and mobile to make it easier to work with. The moving cement mass is evenly distributed over the surface, making it easier to level to create a horizontal surface. An excessively liquid solution will take a long time to harden, a thick solution will not harden evenly, and there will definitely be unevenness.
Before making a screed, a primer is applied to the entire working surface, on which the concrete screed will subsequently be laid. Such a primer can be ordinary cement laitance; alternatively, you can buy a special primer for this. But, before doing this, thoroughly clean the surface of debris; if there are cracks in the old base, fill them with putty. The primer promotes better adhesion of the cement mass and increases the waterproofing of the base.
An important criterion in preparing a cement mixture for pouring is its actual thickness. The maximum can be about 40 mm, this is the most common example; with a minimum of 20 mm, it is advisable to use surface reinforcement - either fiber or reinforced mesh. Extra expenses at this stage will later turn into income - the surface will last for many years without cracks or repairs.
There are two types of screed - wet, semi-dry and dry.
Wet is a classic look and has its undeniable advantages. But it will take 25-30 days to mature, and if you lay flooring on it, it will begin to crumble.
Semi-dry is ideal for quick work or repairs when drying time is limited. The mixture of sand, cement and water is semi-moist, therefore, drying time is required much less than in the wet version. After maturation, the surface is polished.
A dry screed does not require drying and the base is ready for use the very next day. Here, dry components are poured onto the base and leveled horizontally, along the beacons, followed by compaction with a tamper. But the cost of this type is significantly more expensive and the main disadvantage is the fear of moisture. If moisture gets under the flooring, mold will grow there with all the ensuing consequences - a complete replacement of the floor.
If you plan to make a concrete floor, you need to compact the soil, then pour a layer of sand and crushed stone, make a cushion for the screed, and compact it thoroughly. The sand cushion is made 10 cm thick of any pure type and medium fraction of crushed stone.
The rough screed of the concrete base is made 8 cm thick on a plastic film or on a prepared sand cushion.
Calculation of components for one batch in a concrete mixer
1. Determine the yield coefficient of the concrete mixture:
2. Determine the consumption of concrete mixture components for one batch
- Cement for one batch = (Vb*β/1000)*C
- Water for one batch = (Vb*β/1000)*V
- Sand for one batch = (Vb*β/1000)*P
- Crushed stone for one batch = (Vb*β/1000)*Sh
where C, V, P, Shch is the consumption of materials per 1 m3 of concrete.
This calculation can be used to calculate the components of a concrete mixture for any vertical loading container (trough, mason's box) into which you will mix the mixture.
For the actual calculation in the concrete mixer, the mixture yield coefficient from the concrete mixer was taken equal to 0.44. To calculate the coefficient, a sample was compiled based on the responses of people from different construction forums who made batches with their own concrete mixers with different working volumes. © www.gvozdem.ru
If your mixture is too stiff, you can go in two ways to make it more flexible:
- adding a plasticizer;
- adding water and cement in the calculated W/C ratio.
Concrete hardening speed. Dependence on time and temperature - table
GOSTs, books, programs and calculators for calculating the composition of concrete
Characteristics required for each component of the concrete solution
Each component has its own requirements for different grades of concrete:
- size of gravel or sand particles;
- what brand of cement sand is used;
- how many foreign impurities such as clay or organic matter are present in the solution.
The consistency of the finished concrete mixture depends on the proportions in which all the components were added:
- the solution is so liquid that it flows off a shovel or trowel;
- so thick that it stands up like a lump on the instrument, such a solution is practically non-plastic.
When pouring a standard foundation, an average consistency of concrete solution is used, provided that the structure contains a sufficient amount of reinforcement.
Pouring the foundation
Sand is also one of the main elements of concrete mortar. And it also has certain requirements. When making concrete, it is necessary to use fine-grained sand with a grain size of 1.1-3.5 mm.
A dusty sand mass or, conversely, too large, will prevent all components of the solution from adhering well. If the sand contains other components—clay, roots, silty components, etc.—then such sand cannot be used for concrete mortar.
Gravel is one of the main components. Thanks to the presence of this material, ready-made concrete has mobility.
Depending on the amount of crushed stone in the solution, the finished structure will be:
- highly mobile - if a small amount of gravel is used;
- medium-mobile - if there is a uniform amount of crushed stone;
- sedentary - if a lot of gravel was used.
Crushed stone comes in different qualities and weights:
- crushed granite - a heavy material used for buildings that are subject to serious pressure. This material increases strength;
Crushed granite
- lighter filler for concrete mixture - expanded clay, tuff or slag. It is used in the production of lightweight concrete mixtures.
Expanded clay
The dimensions of the crushed stone depend on the planned structure and should not exceed the permissible limit of 14 times the thickness of the thinnest section of the concrete structure. For example, the concrete thickness is 10 cm, which means you can use gravel no larger than 25 mm in size.
Cement is indeed the main component in the repair and construction of most buildings and structures. Here you will learn how to properly dilute cement.
Sand is rightfully considered the No. 1 building material; without it, it is impossible to build any kind of structure. Here is the volume of sand in a ton.
Cladding the facade of your home is the final stage of construction. By clicking on the link, you will become familiar with the different types of facade plaster.
Now cement, it is also divided into various markings. Higher scores have stronger binding ability.
In order for the finished concrete mixture to be of a certain grade, you need to use a cement grade that is 2.5 times higher than the required concrete indicators.
As an example, concrete with an M200 index will need to use M400 cement. The amount of cement per 1 cubic meter of concrete varies, depending on the marking of the concrete mixture you need.
M-400
It should be remembered that the properties of cement are short-lived, so it is better to purchase it immediately before use. If you are going to use stale cement, then its dose must be doubled, but there is no guarantee that such a structure will last a long time.
Drawing up proportions
To calculate the amount of cement spent on a cube of concrete, you need to know the brand of the mixture; in addition, the brand of the binder used is also taken into account. The proportional ratio of the components is indicated in special tables. In construction, M400-M500 are more often used, and the proportion is calculated in mass parts.
For M400:
| Concrete grade | Proportion by mass C/P/Shch |
| 100 | 1/4.6/7 |
| 150 | 1/3.5/5.7 |
| 200 | 1/2.8/4.8 |
| 250 | 1/2.1/3.9 |
| 300 | 1/1.9/3.7 |
| 400 | 1/1.2/2.7 |
| 450 | 1/1.1/2.5 |
For M500:
| Concrete grade | Proportion by mass C/P/Shch |
| 100 | 1/5.8/8.1 |
| 150 | 1/4.5/6.6 |
| 200 | 1/3.5/5.6 |
| 250 | 1/2.6/4.5 |
| 300 | 1/2.4/4.3 |
| 400 | 1/1.6/3.2 |
| 450 | 1/1.4/2.9 |
This means that to prepare M300 concrete from M400 cement you will need to take 10 kg of cement, 19 kg of sand, 37 kg of crushed stone. The result will be 66 kg of finished material. The average density of the mixture is 2200 kg/m³, so the mass of the binder component consumed is 2200/66*10≈330 kg. Such calculations have already been compiled into special tables to facilitate the work of designers and builders.
When calculating the amount of solution, take into account that the volume yield is less than the total volume of all components due to compaction during mixing. The most popular fraction of crushed stone is 20 mm, it provides the required strength and is affordable. The amount of added water required to prepare 1 cube of the mixture is determined during the manufacturing process, since it depends on the moisture content of the sand used and the technical parameters of the mixture.
Types and brands of mixtures
The introduction of the concept of “cement grade” helps to calculate the cement consumption per cube of mortar if the input parameters are known. To prepare a mortar with the same construction characteristics from different brands of cement mixture, different proportions of fillers will be required. Cement is produced in production, starting from grade M100, but due to the low structural strength, the material is practically not used.
The most popular cements are M400 and M500, but some other types have also become widespread. The choice of mixture depends on the scope of application of the material.
The main areas of use of cement grade:
- M300 cement is used in installation construction, as well as during the manufacture of monolithic structures;
- M400 cement is successfully used in monolithic construction and during the preparation of reinforced concrete;
- M500 cement is actively used in the construction of buildings or slabs that must be resistant to moisture or located in water. The scope of application of this concrete mixture is quite wide: the creation of sidewalks, the construction of asbestos-cement structures, the formation of large concrete masses and all kinds of foundations;
M400 and M500 cements are the most popular
- M600 cement is used to create prefabricated structures and foundations that are subject to high loads;
- M700 is a suitable grade of cement for the construction of highly loaded and stressed structures.