Clean drinking water is protected by law in all countries because it is an invaluable natural resource. Therefore, water intake wells of any type are fenced off by several zones, which are regulated by strict sanitary and epidemiological standards. In Russia, for this purpose, SanPiN 2.14.1110-02 is used, which stipulates that there should be three such encircling territories. And each sanitary zone of the well has its own clear boundaries.
Security zone sign
Determination of standards for a drinking source
Sanitary protection zones for water supply facilities are spaces that allow the protection of aquifers and adjacent soils from polluting factors, as well as contributing to the complete safety of technical structures. Options for the parameters of such safety belts are described in detail in SanPiN 2.14.1110-02.
After an artesian well is drilled, water quality tests need to be done.
The following parameters are checked:
- Organoleptic and physical properties of drinking water: taste, color, degree of transparency, presence of various inclusions.
- Chemical composition, presence of inorganic and organic compounds, their concentration.
- Radiometric control, absence of dangerous isotopes.
- Microbiological composition, the presence of pathogenic bacteria, viruses, protozoa.
The conclusion is issued by the territorial division of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. If there are no deviations from sanitary standards in all research protocols conducted by a certified laboratory, the water is recognized as suitable for drinking and cooking. If minor inconsistencies with the requirements are identified, the operation of the well is allowed only as a source of water for technical needs.
Do I need a license
The taste and benefits of artesian water cannot be overestimated. This is the purest drinking water that can be obtained from the bowels of the earth.
Artesian is an aquifer that lies between layers of calcareous rocks at a depth of 50 to 200 meters.
According to the requirements of the law, the installation and operation of artesian water sources can only be carried out with a license.
You can operate an artesian well only with a license
Amendments to the Law “On Subsoil” indicate that a license is not needed under the following conditions of water production:
- The well is located on groundwater, at a depth of up to 5 m from the surface of the earth;
- The water is intended only for the personal needs of the owner of the site and is not used for commercial purposes;
- The volume of extracted liquid per day should not be more than 100 cubic meters;
- The source is not on the state balance and is not part of the centralized water supply.
In all other cases, a license is required, and a considerable package of documents is required, which will cost up to a million rubles and take several months. Having received a license for the legal use of subsoil, you can begin drilling. In turn, drilling a deep well on private land also requires permission, which must be obtained from the company engaged in such activities. A license for a private source is issued for a period of 25 years.
Hydrological conditions for the sanitary zone
The basis for the design of the sanitary protection zone (SPZ) of the water supply source is the hydrogeological conclusion issued for the area where the well is located. If this documentation is prepared simultaneously with drilling and construction work, its cost is significantly reduced. At the same time, important measures are envisaged for the sanitary protection of the territory itself with the hydraulic structure. All actions must be linked to the site water supply project.
Experts determine the parameters of the sanitary protection zone taking into account:
- depth of underground source;
- water intake method;
- well flow rate (volume of water produced in 1 hour).
If the soil layers are insufficient to reliably protect the aquifer, it is necessary to eliminate the factors of possible contamination of the underground source. No economic activity of any kind can be carried out here, as it can lead to industrial, chemical or bacterial contamination of drinking water.
When planning a sanitary protection zone, it is necessary to take into account:
- the presence of potential contaminants in the aquifer, the specifics of their types, changes in properties;
- time of preservation of qualities harmful to health by biological or chemical agents;
- the speed of movement of polluting agents in the aquatic environment.
To ensure the safety of an underground source, a security zone of a water intake well is required, consisting of 3 territories adjacent to the well.
Measures to eliminate pollution factors
They are carried out when designing a protected area if the soil does not provide sufficient protection to the aquifers. Such events include:
- drainage of stormwater from walking areas and other areas where animals and birds are located, with their collection in waterproofed stormwater storage tanks;
- additional waterproofing of the foundation and floors in industrial buildings located nearby;
- installation of reservoir and linear drainage systems that collect filtered water and solutions for pumping and further purification;
- the use of filtration crushed stone layers with a network of drainage pipes that remove contaminated wastewater;
- drawing the contour of contaminated aquifer fluids into a depression funnel through special drainage wells or ditches.
To accurately determine suitable protection methods, analyzes of biological and chemical indicators of water sources and soil structure are carried out.
Activities for constructing a well and creating a project must be coordinated simultaneously with the working project for water supply to the site.
The first is a high security zone
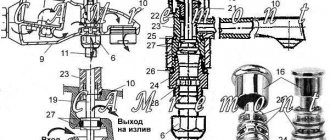
This belt is being installed to prevent contamination of the hydraulic structure. The sanitary zone of the drinking water well is located in close proximity to the water intake points and water distribution systems. It must be fenced and have a warning sign indicating the protection of the belt.
When determining the size of the first zone, the degree of reliability of protection of the underground source and the type of soil are taken into account.
If:
- the aquifer is a reliable barrier to pollution and the sanitary and technical condition of the well is excellent, the radius of the belt can be 15 m (in agreement with the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision);
- the hydraulic structure is located in the center of the zone and has strong protection - 30 m;
- the well is located below the unprotected aquifer - 50 m.
Within this strict regime sanitary protection zone it is strictly prohibited:
- place objects not intended for water supply;
- carry out any construction and restoration work;
- lay pipes not intended for the operation of a hydraulic structure;
- drain waste;
- use household chemicals, pesticides, fertilizers;
- allow the presence of pets;
- bathe;
- use water for washing and washing;
- arrange fishing;
- plant trees (low-growing shrubs are allowed).
Design Features
Domestic water supply is a specific type of work, so design should be trusted to professionals.
It consists of the following stages:
- Finding a site for a well;
- Selection of aquifer;
- Determination of potential source debit;
- Selection of a pump, water-lifting equipment and filter of a suitable type and size;
- Selection of drilling equipment and drilling method;
- Design planning and development;
- Calculations of dynamic water level and volume of water intake;
- Development of a sanitary zoning project.
Often during the construction process, deviations from the calculations planned in the plan are possible, so indicators such as the geological section, design, dynamic and static level of the aquifer are adjusted during the drilling process, and changes are made to the project.
Links[edit | edit code]
- ↑ 123
SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02 “2.1.4. DRINKING WATER AND WATER SUPPLY TO POPULAR AREAS. Zones of sanitary protection of water supply sources and drinking water pipelines.” - ↑ miscellaneous on the topic - FAQ about boilers and heating
- ↑ N.N.
Lapshin, A.E. Oradovskaya. Recommendations for hydrogeological calculations to determine the boundaries of zones 2 and 3 of sanitary protection zones of underground sources of domestic and drinking water supply. - Moscow: VNII VODGEO, 1983. - ↑ AMWELLS (undefined)
.
Program for calculating zones 2 and 3 of sanitary protection zones of underground water intakes
. Institute of Geoecology RAS. - ↑ Sindalovsky L.N.
Analytical modeling of pilot testing of aquifers and borehole water intakes. - St. Petersburg: Nauka, 2014. - 521 p.
Subtleties of sewer installation
Accidents in sewer networks are a common occurrence, and this is not only due to the natural wear and tear of pipes and systems. Sewage, like water supply, has a security zone, but it is not customary to mark it with signs and plates. The presence of sewer pipes and their location have to be judged by wells closed with massive metal covers marked “K” or “GK”.
Before starting excavation work in the security sewer zone, it is necessary to study the plans and diagrams of engineering communications, obtain appropriate recommendations and consultations from specialists.
Otherwise, it’s easy to break a sewer pipe with one careless push from an excavator bucket, and who will then count the losses and material costs of restoration? And if there is a water supply nearby, then the damage and negative consequences increase many times over.
The letters “K” or “GK” on the manhole cover indicate sewerage or city sewerage, respectively; “B” should be written on the cover of the water well.
The security zone of sewer networks is established in proportion to the cross-section of the pipe:
- up to 0.6 m in diameter - at least 5 meters in both directions;
- from 0.6 to 1.0 m and more - 10-25 meters.
It is necessary to take into account the seismological characteristics of the area, climate and average monthly temperatures, soil humidity and freezing, and soil features. The presence of unfavorable factors is a reason to increase the security zone.
The distance to sewer networks located underground from the following objects is also regulated:
- the sewer system should be 3-5 meters away from any foundations (for pressure sewer the distance is greater than for gravity);
- the distance from supporting structures, fences, overpasses is from 1.5 m to 3.0 m;
- from the railway track - 3.5-4.0 m;
- from the road curb on the roadway - 2.0 m and 1.5 m (standards for pressure and gravity sewerage);
- from ditches and ditches - 1-1.5 m from the nearest edge;
- street lighting poles, overhead contact lines - 1-1.5 m;
- supports of high-voltage power lines - 2.5-3 m.
The figures are for reference, and accurate engineering calculations allow us to obtain more substantiated data. If the intersection of water and sewer pipes cannot be avoided, the water supply must be placed above the sewer. When this is technically difficult to achieve, a casing is put on the sewer pipes.
The space between it and the working pipe is tightly compacted with soil. On loams and clays the length of the casing is 10 meters, on sand - 20 meters. It is better to cross communications for different purposes at right angles.
You can read more about calculating the slope of sewer pipes in this article.
In case of a large-scale sewerage breakthrough, it is necessary to turn off the supply of tap water in order, if not to stop, then at least to reduce the release of fecal water to the outside
When opening water and sewer pipes in connection with repairs, the use of equipment in excavation work is permitted to a certain depth. The last meter of earthen layer above the pipe is carefully removed by hand without the use of impact or vibration tools.
When laying sewers, it is strictly forbidden to touch the sanitary areas of water pipelines, but in the city the requirements are less stringent.
In urban conditions, with a forced parallel arrangement of main water and sewer pipes, the following distances must be maintained:
- 10 m for pipes up to 1.0 m in diameter;
- 20 m for pipe diameters greater than 1.0 m;
- 50 m – on wet ground with any pipe diameter.
For thinner domestic sewer pipes, the distance to other underground utilities is determined by its own standards:
- to the water supply system - from 1.5 to 5.0 m, depending on the material and diameter of the pipes;
- to rain drainage systems – 0.4 m;
- to gas mains – from 1.0 to 5 m;
- to cables laid underground – 0.5 m;
- to the heating plant – 1.0 m.
The final word on how to ensure the safe coexistence of water supply and sewerage remains with the specialists of water utility companies. All controversial issues should be resolved during the design process and not come up during the operation stage.
If you do not control household and industrial wastewater, landfills, the amount of chemical fertilizers and poisons in the fields, water supplies will become unusable
Prohibitions
There are certain restrictions for protected areas around water intake sources. There are 3 water protection zones in total, each of them has its own rules.
For zone 1 it is prohibited:
Diagram of sanitary protection zones of an artesian well.
- No unauthorized persons are allowed on the premises.
- It is forbidden to carry out construction, piling, blasting, mining and other types of work that threaten the integrity of the soil, aquifers, and may cause water contamination.
- Under no circumstances should green spaces be cut off or new ones planted without approval from the relevant authorities.
- It is prohibited to carry out work that involves excavation or deepening.
- Organize storage facilities.
- It is not allowed to arrange places for storing sewage and other waste.
For the 2nd and 3rd source protection zones, other prohibitions are observed:
In the protected zone, green spaces cannot be destroyed without permits.
- Destruction of existing green spaces, planting new ones without appropriate approval and permission.
- You cannot create an obstacle to passage, i.e., pull chains or put up barriers. Any fences fall under the same ban. The sources should not be fenced, and it is prohibited to connect any drainage networks to them unless there is a special permit.
- It is forbidden to organize warehouses and other premises, open areas in which construction and toxic materials will be stored.
- It is prohibited to organize construction, blasting, pile, mine and other works. Any action that disturbs the structure of the soil leads to its shaking.
- You cannot dig trenches and pits, or organize other earthworks that negatively affect the condition of the soil structure.
- It is prohibited to store various heavy materials, or even install temporary structures that can put pressure on the ground. This includes gazebos, decking, and outbuildings.
- Persons who are engaged in causing damage to the security zone are not allowed to be on the territory.
- Mining and any related work, including drilling, is not permitted.
- You cannot use chemicals or other substances that pollute the soil, organize landfills, engage in grazing, or install septic tanks.