In various articles on our website, two types of sheet material are constantly mentioned: plasterboard (gypsum board) and gypsum fiber sheets (GVL). Feedback from portal visitors showed that not all home craftsmen know the difference between them, and, therefore, do not always choose the right building material for a specific situation.
Therefore, let’s pay closer attention to the topic and consider which is better - gypsum fiber board or drywall when finishing walls, lining the ceiling and leveling the floor. To do this, we will consider the characteristics of the materials, their advantages and disadvantages, which will allow us to understand the difference between gypsum boards and gypsum fiber boards and determine whose set of qualities is best suited under the current operating conditions.
What is drywall (gypsum plasterboard)
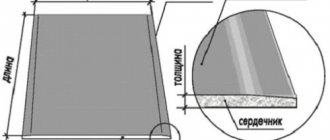
Drywall (the word is derived from the term plasterboard sheet) is a building material of varying sizes and thicknesses made from a hardened layer of gypsum dough (core), covered on both sides with cardboard (construction paper). The second name is dry gypsum plaster (in English-speaking countries - drywall).
The material was first obtained in the USA in the second half of the 19th century. It acquired its modern appearance in the 20th century. And again the author of the invention was the American Utsman.
Compound
GKL contains only natural ingredients:
- gypsum (core) - 93%;
- paper (cardboard lining) - 6%;
- water, starch (in gypsum) and sheet coating - 1%.
Attention: the amount of water indicated is in a dry state. During operation, the indicator can change significantly due to the hygroscopicity of gypsum plasterboard.
Kinds
According to established habit, gypsum board is divided into 3 types:
- classic (standard). Denoted by the abbreviation GKL. Cardboard color is gray. The marking is blue. Used for finishing work in rooms with normal operating conditions;
- moisture resistant (GKLV). Resistance to moisture is acquired after impregnation of the gypsum mixture (before molding) with a special waterproofing compound, as a result of which the gypsum absorbs water 10 times less, while quickly releasing it. Recently, antifungal additives have been added to the impregnation. The leaves are green with blue markings. Used in damp areas;
- fireproof (GKLO). The addition of fire retardants, and from leading manufacturers of crystallized water, gives the material high heat resistance - such sheets can resist open fire for up to an hour. The color is pink, the inscription is bright red.
There is another type that is not talked about much: moisture-resistant drywall with increased fire resistance (GKLVO) . It is a combination of moisture-resistant and fire-resistant material. It turns green. The marking is red.
For information: since 2015, the name of plasterboard in construction documentation has been changed to “gypsum building boards” (GSP).
Shapes and sizes
On sale you can find sheets of the following sizes:
- thickness - 8.0; 9.5; 12.5; 14.0; 16.0 mm. The most popular are 9.5 and 12.5 mm;
- width - 120 and 60 cm (rarely 90 cm);
- length - 2.0; 2.5; 3.0; 3.5 and 4.0 m. Sheets with a length of 2.5 and 3 m are in greatest demand, which is mainly due to the height of the ceilings in the house (apartment).
The shape is rectangular sheets. Differences on the side edge. She may be:
- straight - indicated in the marking by a combination of letters PC;
- thinned (UK);
- semicircular (PLC);
- semicircular thinned (PLUK);
- rounded (ZK).
Types of edges.
Purpose
Drywall is used to level walls and ceilings and construct various partitions. You can stick wallpaper and tiles on it, apply decorative plaster, liquid wallpaper. In addition, the surface can be painted with almost all types of paint.
Manufacturers
The best quality gypsum board of the following brands:
- "KNAUF";
- “Saint-Gobain” is a trademark of the Gyproc concern;
- "Lafarge";
- "Volma";
- "BelGips".
Volma plasterboard is a domestic high-quality material
Volma plasterboard has been produced in Russia since 1999 after the reconstruction and modernization of the Stalingrad gypsum plant. Due to the presence of our own gypsum mining enterprises, it was possible to establish inexpensive production of the material at modern facilities using unique technologies. In terms of cost and quality, Volma plasterboard is the best among all manufacturers present on the market.
The modern production base has made it possible to establish the production of specialized types of plasterboard and virtually completely cover the needs of the domestic market. In terms of its technical and operational characteristics, Volma gypsum boards are in no way inferior to their foreign analogues, thanks to which these products have become the most popular in the domestic market.
Main advantages
The advantages of Volma plasterboard sheets include the following:
- high accuracy of sheet geometry, which makes it possible to simplify installation work and obtain hermetically sealed joints;
- optimal ratio of strength and ductility of sheets, providing the ability to cover surfaces of complex shapes;
- ease of cutting drywall with high quality edges that are not subject to crumbling;
- the ability of the sheet to absorb the load and distribute it evenly along the entire surface due to the use of gypsum sintering technology at a temperature of +200°C;
- low price of material and excellent technical characteristics;
- almost ideal durable surface with excellent adhesion thanks to the use of multi-layer cardboard.
Disadvantages of gypsum board Volma
Drywall produced by Volma has the following disadvantages:
- lack of marking lines, which complicates the process of aligning sheets during installation;
- slight surface waviness due to the characteristics of the production technologies used.
What is GVL (gypsum fiber sheets)
Gypsum fiber sheets (GVL) are a mixture of building gypsum, fluffed waste paper (cellulose fibers firmly bind the set gypsum in all directions, giving the material high strength and viscosity) and technological additives. The mass is filled with water, stirred, pressed into sheets, and dried.
GVL with an unusual edge.
Compound
The gypsum fiber sheet has a uniform structure, without a cardboard shell. Consists of:
- from gypsum - 80-85%;
- cellulose - 10-15% (most materials indicate 20%, but this is not so);
- special additives (they are also called technological additives) - 5%.
Kinds
Like drywall, gypsum board has 4 types:
- simple (GVL). Used in rooms with moderate humidity and slight temperature changes;
- moisture resistant (GVLV) - thanks to hydrophobic additives, it practically does not absorb water. Recommended by manufacturers for use in wet areas (bathroom, shower, kitchen);
- fire-resistant (GVLO). The material itself does not burn. But in some cases, increased fire-resistant qualities are needed, for example, for lining air ducts, communication shafts, wooden walls when working in a room with an open fire, etc.;
- moisture- and fire-resistant (GVLVO) types are produced for saunas, baths, i.e. for those rooms where there are extreme operating conditions.
It is impossible to determine the type by color - all the sheets are gray. Markings on the back of the plate will help.
GVL marking.
In addition, GVL can be:
- polished (in the marking it is indicated by the letter “Ш”) - the operation is performed for painting;
- unsanded (NS) - for wallpaper, tiles, dry floor screed, etc.
Shapes and sizes
According to GOST, gypsum fiber sheets can be of the following sizes:
- thickness - 10.0; 12.5; 15.0; 18.0; 20.0 mm;
- width - 50.0; 100.0; 120.0 cm;
- length - 1.5; 2.0; 2.7; 3.0 m.
For the population, a sheet of 10 x 1500 x 1200 mm is considered standard.
Please note: products are available in other sizes. For example, floor slabs 120 x 120 x 2 cm. Before purchasing, you need to look at the markings or ask the seller. The edge can be straight (PC) and folded (FC). If necessary (for reinforcing tape), you can thin the edge of the sheet yourself using a carpenter's plane.
Types of edges.
Purpose
Gypsum fiber sheets have a wider range of applications compared to gypsum boards, both in terms of types of buildings and structural elements. GVL is used in residential and non-residential premises, balconies and loggias, baths and saunas for leveling (cladding) walls, installing partitions, lining the ceiling, as a base floor for tiles, linoleum, laminate, parquet and parquet boards.
In addition, the material is widely used in industrial construction.
You can finish gypsum fiber board on the walls using:
- wallpaper - paper, vinyl and textile hold up well. Glue only based on methylcellulose. Problems arise with non-woven trellises;
- paints. Here, firstly, you need polished slabs (putty is expensive and labor-intensive due to several layers), secondly, you cannot paint with silicate-based paints;
- decorative plaster - gypsum solutions with additives from artificial resins are allowed;
- ceramic tiles.
Important: the surface needs to be primed before finishing.
Manufacturers
Main brands of GVL manufacturers:
- “Knauf” - about 70% of the market in Russia and the CIS countries belongs to this product, “Nida Gips”, “Rigips” - another 10% for three;
- "Volma";
- "BelGips";
- "GIFAS" and others.
Material qualities to keep in mind
Of course, this brand of drywall has its advantages and disadvantages.
- Despite the fact that Giprok has high performance characteristics and almost does not break during transportation, it is nevertheless not strong enough. This is due to the properties of the material from which the gypsum board is made. Therefore, if after repair work it is planned to hang heavy objects on the wall, then it must be strengthened even during the installation of the frame.
- In addition, this drywall does not have outstanding soundproofing qualities. Therefore, when installing a suspended ceiling made of “Giprok” plasterboard, you need to put soundproofing material into the frame structure, and then fasten the sheets of finishing material.
Advantages and disadvantages
The choice is always easier if you know the strengths and weaknesses of competing materials. This allows you to avoid unpleasant surprises, both during operation and during operation.
GKL
Many years of experience in using gypsum board have formed a complete list of the advantages of the material, where nothing is superfluous, nothing is missing:
- affordable price for mass buyers. This plus is one of the most important for families on a limited budget. At the same time, the quality of work and durability do not suffer;
- low thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.30-0.34 W/ (m×K). According to this indicator, the material is comparable to wood. In combination with insulation, an excellent thermal insulation layer is obtained;
- Easy to install: no experience required. The main thing is to know the principles of working with the material, which can be easily found on the World Wide Web;
- flexibility. Many will be surprised. After all, the material easily crumbles upon impacts or strong bends. On the one hand, this is true. On the other hand, with the help of gypsum plasterboard you can make any semicircular arches and complex installations (as evidenced by the photo below);
Methods for bending gypsum boards.
- fire resistance. The gypsum itself does not burn, but only melts at +1450°C. Only cardboard can burn. But after it is treated with fire retardants, it becomes difficult to burn (painted pink);
- moisture resistance. In fact, gypsum absorbs moisture very well. However, processing sheets with special compounds makes it possible to use the material in rooms with high humidity (kitchen, bathroom);
- high level of maintainability - dents, cracks, and through holes can be easily repaired. As a last resort, the damaged area is replaced;
- versatility. Can be mounted in any room (residential, non-residential) under any finish (wallpaper, paint, ceramic tiles);
- environmental cleanliness. The material contains no additives harmful to health;
- the ability to easily and simply hide communications. But the main thing here is not to overdo it and arrange inspection hatches at the points of connections or adjustments.
The list of advantages of drywall is impressive, but the disadvantages :
- fragility is the main problem of gypsum boards. Sheets may crack during handling (carry only vertically), transportation, or installation. Therefore, special care is needed when working with slabs;
- low strength under weight loads - you can’t hang anything heavy on gypsum plasterboard partitions. It is necessary to provide embedded OSB or plywood boards at the fastening points in advance. You can also use molly dowels. But their weight is limited - for a slab with a thickness of 12.5 mm, such a mount can withstand from 16 to 25 kg of load. This way you can hang a cornice and a TV, but there are no kitchen cabinets or shelves;
- low level of sound insulation, which is important for partitions - even a whisper is perfectly audible. Exit in mineral wool insulation (not polystyrene foam) between sheets of plasterboard.
Another drawback, although common to the materials being compared, is the reduction in space. This is especially noticeable in small rooms or apartments (houses) with low ceilings.
Important: some experts consider the impossibility of covering walls in dachas with gypsum sheets to be a disadvantage—in winter, due to the lack of heating, it will tear. It's hard to agree with this. Firstly, gypsum board is afraid not of frost, but of high humidity (frost tears away sheets that have accumulated moisture). Secondly, you can use moisture-resistant modifications of drywall (GKLV). Thirdly, indoor humidity is lower in winter than in summer. Therefore, after a wet autumn, you can dry the room well and close it for the winter.
GVL
GVL also has its advantages
- high strength allows you to hang heavy objects on vertical structures (a simple self-tapping screw holds up to 30 kg of load), and on the floor to use it as a base under linoleum, parquet, laminate or tiles;
- the presence of viscosity, firstly, allows you to cut the material without dust - it does not crumble, and secondly, you can tighten the fasteners without dowels - it will hold like in wood;
- low heat transfer coefficient, which allows the material to be used as insulation;
- good level of sound insulation - perfectly absorbs air and shock sound waves. This is confirmed by measurements: the noise level drops by 35-40 dB;
- fire resistance - does not burn, but only chars. Therefore it is used as protection for wooden structures;
- the moisture resistance of sheets treated with special compounds (GVLV) is the same as that of cement-sand mortar;
- high frost resistance makes it possible to use it in the country and in unheated rooms;
- hygroscopicity allows, like wood, to regulate the humidity in the room. When the amount of vaporous moisture increases, it is absorbed by the GVL, and when it decreases, it is easily released;
- can be used in a “warm floor” system, but only from below;
- the material is safe in all respects - when heated, it does not emit harmful substances and does not contain allergens;
- there are no restrictions on use: private houses, apartments, cottages, unheated rooms, horizontal and vertical surfaces;
- easy to install - the work can be performed by a home craftsman without the help of specialists;
- not subject to deformation (change in linear dimensions) under the influence of temperature and humidity fluctuations.
There are also disadvantages that you need to pay attention to:
- the price is prohibitive for some segments of the population;
- high specific gravity, as a result of which an assistant is needed during installation. Even though they are smaller in size than drywall, the sheets are much heavier;
- moisture-resistant gypsum fiber sheets can be affected by rot in places with constant high humidity;
- does not bend - can only be used on flat surfaces.
Where is it better to use drywall and gypsum fiber?
The differences in the characteristics of gypsum plasterboard and gypsum fiber board make you think about which material is best to use for repairs. The choice will depend on the type of finishing work and the characteristics of a particular room.
Wall cladding
When deciding what to choose - plasterboard or gypsum fiber board for walls - you should focus on the degree of load on the wall, the complexity of the design and the microclimate in the room. It is quite acceptable to use ordinary plasterboard in apartments and residential buildings, and moisture-resistant plasterboard in bathrooms. It is much easier to use and is quite capable of withstanding such intensive use.
Gypsum fiber sheets are suitable for wall cladding in industrial facilities, in places with high humidity, as well as in rooms where high mechanical loads are provided - for example, fastening heavy equipment.
Ceiling lining
Using plasterboard to line the ceiling allows you to create complex structures and curved elements. When using gypsum fiber sheets, the entire structure will have significantly more weight. In this case, it is not possible to make curved elements, and the process of finishing the ceiling itself is more complicated. But if you use GVL for lining the ceiling, you can get much better sound insulation and protection against steam penetration.
Floor covering
To level the floor under the floor covering, only gypsum fiber boards can be used - the rigidity of the material and its high bending and compressive strength ensures its resistance to serious loads. The performance of gypsum boards according to these parameters is much lower, they are more fragile, and therefore are not used for finishing floors.
Wet areas
For small, well-heated bathrooms, drywall can be used. However, if a durable and reliable finish is required, which is not affected by high humidity, the advantage will be on the side of gypsum fiber sheets. The expansion coefficient of GVL does not exceed 1.5%, so the joining seams remain smooth and sealed even with prolonged exposure to moisture.
Drywall and gypsum fiber have a lot in common - both materials are environmentally friendly, affordable and quite easy to install. However, when planning repairs, it is worth taking into account the plasticity and lightness of gypsum plasterboard and the high mechanical strength, density and fire resistance of gypsum board - and when choosing, focus on the characteristics of the room and the ultimate goal of finishing work.
If you notice an error, a non-working video or link, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter .
0
Technical and operational characteristics
Based on gypsum, but produced using different technologies, gypsum boards and gypsum boards also have different characteristics. For convenience, all important indicators are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Main technical and operational characteristics of materials.
| Indicators / Materials | Drywall | Gypsum fiber sheets |
| Density, kg/m3 | 735-900 | no more than 1250 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/m*C | 0,30-0,36 | up to 0.36 |
| Swelling in thickness over 24 hours, % | 3 | 1.8 |
| Hardness, MPa | 5 | at least 20 |
| Impact strength, kJ/cm2 | 0,5-0,8 | 5 |
| Ability of 12.5 mm thick material to hold a load on one screw (vertical surface), kg | 7 | 40.8 |
| Dry bending strength, MPA | 2 | 5 |
| Flexural strength in wet condition, MPa | 0.01 | 0.3 |
| Compressive strength, MPa | to 10 | at least 10 |
| Flammability class | G1 (low-flammability) | NG (non-flammable) |
Note that during the work it was not possible to find data on the molly dowels screwed into the gypsum plasterboard. In drywall they hold weight up to 25 kg. Naturally, in a gypsum fiber sheet this figure is several times higher (where a simple self-tapping screw can withstand up to 40.8 kg).
Technical properties of the material
Swedish plasterboard is durable sheets consisting of a gypsum core, to which special components have been added that increase the performance characteristics of the material. A layer of cardboard is applied on top of the plaster, covering it on both sides. To achieve the necessary parameters required from the product, the manufacturer uses a variety of additives that help improve the desired characteristics.
- The cardboard is treated with a compound that prevents the formation of mold.
- Gypsum filler contains additives that prevent moisture from entering the sheet and causing it to deteriorate.
In accordance with the technical properties, gypsum board "Giprok" is divided into 4 varieties:
- standard plasterboard sheet;
- moisture resistant;
- fire resistant;
- moisture and fire resistant.
Since the company producing this material cares about product quality, all production processes are under strict control. The resulting drywall has undeniable positive qualities:
- The material is highly resistant to external factors.
- It does not harm the environment and is made from environmentally friendly materials.
- Makes it possible to carry out repair and construction work at the lowest cost.
- Its operation in places of high fire danger does not cause problems.
- It has a low price compared to other materials.
The tolerance for deviation from the standard size can be no more than 5 mm in both length and width, which allows you to accurately calculate the amount of material required for repairs.
What is the main difference
Despite the gypsum base, the materials have many differences:
- drywall is a three-layer sandwich made of paper and gypsum, GVL is a single piece of hardened gypsum mortar;
- The strength of gypsum fiber is many times higher. You can hang kitchen cabinets on it, which is excluded with gypsum board;
- GVL is less natural - it contains magnesium oxide and magnesium chloride. But these components of the composition are harmless;
- drywall has a much smaller scope of application;
- When cut with a knife, gypsum plasterboard crumbles and becomes dusty when working with a grinder; gypsum board is cut without residue;
- breaks differently when cut: drywall down, gypsum fiber upward. A small thing, but important. If you don’t follow the technology, you won’t get smooth edges;
- It is difficult to work alone with GVL due to its heavy weight. Need an assistant;
- The drywall is puttied before wallpapering. For GVL, such an operation is unnecessary. Here only the joints and heads of hardware are sealed;
- gypsum fiber sheets are more difficult to bend. Therefore, they are difficult to use for curved surfaces;
- Heavy gypsum fiber boards must be mounted on a more durable sheathing. Therefore, it is necessary to use a metal profile with a thickness of at least 0.5 mm.
How to choose drywall: little tricks
- Buy goods at large retail outlets. Material purchased at the market or in a dubious stall is most often not of the first freshness.
- The reputation of the company from which you purchase drywall is no less important. Large companies will not risk their track record for easy money. It is much more important for them to replenish their base of regular customers.
- But even an old woman can have trouble. When delivering the material, check the quality personally. The paper should not move away from the sheet or bulge on the back side. The sheet must have an edge marking. Externally, the drywall should not have any damage - any defect can lead to a break after installing the gypsum board.
- Close attention to the work of the loaders - the presence of defects greatly depends on their accuracy. Check the labeling personally: if the batch is mixed up, there will be no problems.
- Price. If you decide to save money, don’t forget to regret it when the Chinese cardboard starts coming in waves. Do I need to overpay for a brand? Definitely yes - just count how much money it will cost to redo the sheathing or the structure itself. Now tell me, which drywall is better : cheap, but Chinese, or a well-known company, but a little more expensive?
Comparison of characteristics
Having only the strengths and weaknesses of materials at hand, it is impossible to make a clear choice. We need a comparative analysis of the main indicators. Experts include the following selection criteria:
- price;
- density;
- strength;
- ease of installation;
- thermal insulation properties;
- sound insulation level;
- flexibility;
- environmental friendliness;
- sheet weight.
Price. The most important factor when choosing any building material is its cost. Here, drywall has an undoubted advantage. Its sheets are approximately 2-5 times cheaper than its competitor. So, 1 m2 of gypsum board (standard options are compared) can be bought from 70 rubles. and higher. And for a sheet of gypsum fiber of the same area you will have to pay from 180 to 360 rubles. per m2 (depending on the type of edge and surface of the material: polished or not).
The truth needs to be clarified: moisture- and fire-resistant options are close in cost to the standard gypsum plasterboard version, and in some cases gypsum plasterboard is even more expensive. But we emphasize this again when compared with simple, without additives, gypsum fiber boards. For improved gypsum fiber board options you will have to pay around 750-910 rubles/m2.
Conclusion: GVL is purchased either with unlimited funds for repair work, or if necessary, for example, for lifting or leveling the base of the floor, where gypsum board is not used.
Density. The density indicator affects the weight of the sheet and the ability to hold fasteners: nails, screws, self-tapping dowels. It is difficult to give unambiguous assessments based on this criterion. After all, the greater specific gravity of gypsum plasterboard (see Table 1) is an undeniable plus when leveling walls in the kitchen: you can hang kitchen cabinet drawers on self-tapping screws without any problems. In other rooms there is a minus: it is difficult to work. It is difficult to cut and lift - you need a helper.
Conclusion: using the given criterion, it is impossible to unambiguously determine what is better for walls - gypsum plasterboard or gypsum fiber board. It is necessary to evaluate the material in specific relation to the place where the work is performed. The same situation occurs on the ceiling. But for the floor, the high density of gypsum fiber boards is an undeniable advantage.
Strength. A layer of gypsum of the same thickness in gypsum plasterboard is fragile, breaks easily, does not withstand dynamic (shock) loads - holes appear. It is reinforced only by a cardboard shell.
GVL penetrated with cellulose fibers can withstand high static and dynamic loads. The difference is clearly manifested in the sealing of corners: gypsum board requires plaster corners, but gypsum board does not, and when leveling the floor - gypsum board is one of the best options, and gypsum board is not considered at all for such work.
The ability of gypsum fiber to withstand heavy loads has found application in industrial construction, where the walls of workshops are finished with this material.
Conclusion: according to the criterion: which is stronger, gypsum boards reinforced with cellulose fibers have absolute superiority.
Ease of installation. Practice has shown that when choosing a type of dry plaster, the consumer first of all evaluates the cost of the material and, oddly enough, its manufacturability. According to this indicator, at first glance, drywall is beyond competition. His:
- easier to cut;
- easier to carry;
- It’s more convenient to attach to the sheathing: firstly, special screws are not needed, and secondly, the hardware is screwed in without much effort.
However, there is another side to the problem. When using gypsum fiber:
- the surface does not need to be puttied before wallpapering;
- when passing internal and external corners, painting corners are not required;
- before painting, unsanded sheets are puttied - sanded sheets are only primed;
- When sealing joints, reinforcing tape is not needed, therefore, sheets with straight edges can be used. Falset edges are needed when leveling the floor.
Conclusion: in terms of manufacturability, the materials are approximately equal.
Thermal insulation properties. Both materials consist of gypsum. Therefore, the heat conductivity indicators are approximately the same: the coefficient value is slightly higher for GVL due to its higher density, but in practice this is not noticeable.
Conclusion: both materials are good insulators. That is why experienced specialists do not recommend laying gypsum fiber boards on top of a “warm floor”.
Soundproofing. Due to different densities and compositions of components, the compared materials have different noise insulation performance. So, when installing partitions from gypsum plasterboard, it is imperative to lay mineral wool between the walls. Otherwise, almost any noise from the adjacent room will be heard. And gypsum fiber board will perfectly dampen sound waves even without a soundproofing layer.
Conclusion: GVL has an advantage in terms of noise insulation characteristics.
Flexibility. A wet plasterboard sheet becomes flexible. Using a certain technology, it can be used to form semicircular arches, curved two-tier ceilings, and other shaped structures for finishing walls and ceilings.
Gypsum fiber board has a high level of rigidity. It is impossible to bend it without breaking it, and it is impossible to get it wet - the structure of the material does not allow obtaining a plastic mass in a wet state. Therefore, GVL is used for flat surfaces.
Conclusion: gypsum board has flexibility, but gypsum board completely lacks it.
Ecological cleanliness. The materials are absolutely equal in terms of environmental friendliness: both do not contain harmful substances or allergens.
Weight. The heavier weight of GVL makes the work of home craftsmen more difficult - an assistant is needed. If it is not there, then there is a high risk of breaking the sheet during installation. Some experts find a solution by cutting the gypsum fiber board in half, which, in the opinion of the site’s editors, is not a rational solution - the technological process becomes much more complicated.
Conclusion: when finishing the premises, it is necessary to take into account the forces with which the repairs will be carried out. If alone, then many difficulties are expected with GVL.
General conclusion: if we consider the results of the comparison based on the overall assessment, then gypsum fiber boards have an advantage. However, two main criteria: price and complexity of the technology, despite the fact that drywall requires many additional operations: sealing seams, puttying, priming, gypsum board wins. Therefore, from a practical point of view, GVL can be used if there are high incomes. It makes no sense for people with average incomes to overpay where a simple gypsum board will perfectly perform its functions.
So, let's move on to the parameters for choosing drywall.
Firstly, the filler must be white.
Secondly, the cardboard should have a dense structure and not resemble wrapping paper.
Thirdly, the sheet must be light and hard at the same time. A good leaf does not have a hollow sound when tapped.
Fourthly, the surface of the sheet has an absolutely flat surface without “hills and valleys”.
Fifth, all edges must be smooth, and the edge of the cardboard is tightly glued over the entire surface of the sheet.
It is pleasant to work with a good sheet, it will not crack under putty and the surface assembled from such a sheet will delight you for many years!
How to properly make thermal insulation on the facade of a house. Seven components.
Dear friends!
Subscribe to the channel “What does it cost you to build a house!”
You will learn a lot of new and useful things about the construction, decoration and operation of your home! Don't forget to rate my work!
The most interesting way to fight aphids. Darwin Award!
Old and new screws or how they make fools of us!
The only solution for real sewer cleaning.
How to keep pool water clean for a very long time and a useful life hack.
Russian polycarbonate, or a story about how to turn a good product into complete crap!
What and in what case is it better to choose
Based on the comparative analysis, specific recommendations can be made for different building elements in each room.
Floor. GVL is used to level or raise the floor level. Usually these are sheets 10 mm thick, laid in two layers or 20 mm slabs from Knauf. Drywall has nothing to do with the floor.
Walls. There is no clear advice: GVL or plasterboard for walls. It all depends on the operating conditions. So, in the kitchen, where wall cabinets are usually attached, it is advisable to use gypsum fiber sheets - they will withstand the weight of the attachments. At the same time, you can also use gypsum boards by first securing an OSB strip to the wall for fasteners. Based on a combination of factors, GVL in the kitchen is preferable.
For a bathroom, with its high humidity, you need either moisture-resistant gypsum board or gypsum fiber. Here the owners have a choice: if they have money, they buy GVL. Budget is limited - drywall. Arches in walls can only be made from plasterboard sheets.
Ceiling. Both types of materials are also suitable for the ceiling. But for a designer ceiling with many curves, you need gypsum board. As an option, gypsum plasterboard can be attached to linear surfaces; curved inserts can be made from plasterboard. With noisy neighbors above, gypsum fiber will help reduce the noise level, but you need to take into account the high cost of work and the complexity of installing gypsum fiber boards. The sheet cannot be secured without clamps.
Bath, sauna. For rooms with sudden changes in temperature and humidity, such as are observed in baths and saunas, there is no alternative to GVL.
Country house. Many experts do not recommend using drywall in unheated rooms. In such situations, gypsum fiber sheets will help.
Balcony, loggia. On a glazed but unheated balcony (loggia), it is still better to mount GVL on the walls and ceiling, although moisture-resistant cardboard will do the job well.
A little about sad things.
In Russia, in recent years, many factories have opened for the production of dry building mixtures and drywall.
It would seem like a good trend, if not for one thing!
The quality of the products, to put it mildly, leaves much to be desired.
For example, at one time, Volgograd plasterboard appeared on sale. Its cost is approximately 20-30% lower than Knauf or Giprok products.
But the quality is simply disgusting.
Gray filler. It looks like they added cement along with the plaster.
The leaf is very heavy, wobbly and uneven. The cardboard is of very low quality. The filler is loose.
The sheet is cut very poorly and breaks crookedly.
The self-tapping screw is very difficult to screw into such drywall. It is very difficult to drown the head of a self-tapping screw. Workers had to tighten it manually.
Ceilings mounted from such plasterboard were covered with cracks; not a single serpyanka could contain them.
I don’t know if the manufacturer has improved the quality of the products, but since then we have sworn off buying products from unknown factories.