The article was prepared with the participation of specialists from the Association of Expanded Polystyrene Manufacturers and Suppliers
The market for thermal insulation materials is represented by various categories, which greatly simplifies the selection of suitable insulation for specific tasks. One of the most popular insulators in the private sector is polystyrene foam; its popularity is explained by both its high technical characteristics and availability. Nevertheless, battles between supporters and opponents do not subside around it; it is quite difficult for a person far from construction to figure out which of the properties of insulation are real and which are from the category of “horror stories”. We will try to make the task easier for beginners, and it will be useful for more experienced craftsmen of our portal to refresh the information. And specialists from the Association of Expanded Polystyrene Manufacturers and Suppliers will help you separate the “wheat from the chaff.”
Consider:
- What is polystyrene foam?
- Main characteristics of expanded polystyrene.
- Scope of application of expanded polystyrene.
Internal and external insulation
Before you start insulating the walls, you need to decide on the insulation method. Laying insulation outside or inside is an individual preference. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages . The features of each insulation method must be studied at the time of building design.
Insulation from the inside
Internal wall insulation is characterized by the following features:
- the cost of insulation from the inside is less than that of external insulation;
- season and weather do not affect the choice of time for work;
- there is no need to build additional scaffolding for insulation work.
Negative factors for internal insulation are:
- significant reduction in living space;
- the outer wall is insulated from heating from the room;
- the likelihood of fungus forming inside the wall increases, since the dew point is formed precisely in the inner part of the structure;
- when the heating is turned off, the walls quickly cool down due to the low inertia of the insulation;
- the junction of the ceiling with the external wall cannot be equipped with insulation, which leads to the formation of cold bridges.
The method of insulating walls from the outside is more popular despite the fact that the cost of labor and materials for performing the work is significantly higher than the method of internal insulation.
Dew point
Insulation from outside
The advantage of insulating walls from the outside is:
- in winter and in cold weather, heat is retained in the wall for a long time;
- the design area of the room is preserved;
- external thermal insulation protects internal walls from dampness.
In addition, the external walls are additionally protected from weather conditions, which significantly increases the service life of the structure.
The main disadvantages of external thermal insulation of a structure are:
- restriction of work in accordance with weather conditions;
- increase in costs for materials used.
Which side of the wall to insulate with polystyrene foam?
It is advisable to insulate walls with expanded polystyrene from the outside, since the material does not allow air to pass through, which can lead to the formation of condensation inside the wall during internal insulation, and also inside the room the material can emit a specific odor.
Characteristics and properties
Expanded polystyrene is designed to retain heat. This happens due to compressed small balls containing air. They form a solid air cushion, similar to foam, which is why the material has a similar name.
The density of the material ranges from 0.028 to 0.034 watt meter per Kelvin. The indicator depends on weather conditions. Scientists proved in 2014 that mold fungi are not able to live on this insulation.
Each type has its own vapor conductivity. For example, extruded does not allow steam to pass through at all, but foamed - from 0.019 to 0.015 kg per m/h/Pascal. The difference appears due to the fact that the second type is obtained by cutting from a whole block into slabs of the required thickness. Therefore, air penetrates through the broken structure of the balls.
Moisture absorption works on the same principle as vapor barrier. Solid polystyrene foam will absorb a maximum of 0.4 percent of water, thinner ones can absorb ten times more - 4%. Due to its dense structure, extruded is considered strong, approximately 0.4 to 1 kg per square cm.
Due to the presence of antiperspirants in the composition, polystyrene foam will last for many years without losing its advantages. Based on all of the listed properties, solid polystyrene foam is significantly better than foamed polystyrene. He almost ousted his competitor from the market and became the most popular.
Advantages and disadvantages of expanded polystyrene
The polystyrene foam material is a porous, air-containing raw material , used in most cases as a heat-insulating material.
In industry, the material can also be used as electrical insulating and packaging material.
The material has become widely used due to its quality indicators:
- low level of water absorption;
- low thermal conductivity;
- ease;
- biological stability;
- durability;
- compressive strength;
- not affected by temperatures;
- ease of installation;
- low price of material.
Comparison of insulation materials
Despite the impressive list of positive indicators, polystyrene foam has disadvantages that must be taken into account during installation:
- low sound insulation;
- instability to solvents and many chemicals;
- afraid of fire. When burned, it releases harmful toxic substances;
- poor resistance to ultraviolet radiation;
- easily susceptible to the influence of rodents and insects, which, by making holes in the material, provoke its destruction;
- low vapor permeability;
- fragility.
IMPORTANT!
Expanded polystyrene is sometimes compared in terms of characteristics and external indicators with another similar material - polystyrene foam.
However, the production technology of these materials is different : polystyrene foam is produced by extrusion, when the granules melt when combined into a single structure, polystyrene foam is produced by gluing granules with dry steam.
Specifications
Main characteristics of teaching staff
Since EPS consists of 98% air and only 2% shells of foamed polystyrene, its main characteristic is the minimum thermal conductivity - 0.032-0.034 W/(m·C). In addition, the slabs are vapor permeable, but moisture resistant, since even when completely immersed they practically do not absorb water. That is, the material conducts steam quite well, but does not accumulate moisture, unlike some other heat insulators.
Interestingly, workers involved in insulating facades in seaside resort towns often used PPS as swimming mattresses, and fishermen cut floats from it for nets.
In addition to excellent thermal conductivity, vapor permeability and moisture resistance, it is worth adding the resistance of the slabs to biological damage.
Yuri Savkin
Expanded polystyrene is biologically neutral, which means that mold and mildew do not grow on the surface of expanded polystyrene, which has been proven by numerous studies.
Equally important is the long service life, which maintains characteristics even under harsh operating conditions.
Yuri Savkin
Expanded polystyrene was subjected to fifty freeze/thaw cycles in a four percent sodium chloride solution. The salt solution provided harsh test conditions. The test results did not reveal any impact on the integrity of the structure. Now blocks of expanded polystyrene are widely used in Norway for constructing roads, tunnels and artificial embankments. Our researchers have conducted tests with a large number of cycles and predict the durability of polystyrene foam to be at least 100 years.
But in addition to external influences, during operation the material can be exposed to other threats, one of them that worries our craftsmen is mice.
nikolaj-beFORUMHOUSE Member
I would like to touch on the topic of mice and polystyrene foam - I heard that after mice visit polystyrene foam, dust remains from it, is this true?
Yuri Savkin
As for rodents, PPS has no nutritional value for them, but they can live in it, as in any other thermal insulation material. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures to limit rodents’ access to the insulation and cover the surface with facing layers. In addition, mice and rats are not a construction issue, but rather a hygiene issue.
Regarding the environmental friendliness of polystyrene derivatives, battles have not subsided since the start of production to this day: some consider the material to be an absolutely harmless and environmentally friendly insulation, while others consider it a real time bomb. And the truth, as usual, is in the middle.
Yuri Savkin
Previously, it was believed that all polymers emit harmful substances throughout their entire life cycle, since the polymerization process cannot be completed on 100% of the molecules. This is all because when everyone in Europe was studying chemistry in the middle of the last century, we were studying “corn”. Modern technologies and world-class equipment (foreign lines) have long ago solved this problem. The SIBUR plant in Perm has the best equipment by world standards and uses today's advanced technology. During the drying process, all styrene molecules that are not chained together are removed. During operation, if it emits anything, then, of course, within the limits permitted by sanitary standards. According to our tests, the cube of a polystyrene foam product contains less than 0.002 mg of styrene (which corresponds to MPC standards).
Few people know, but styrene is found in such common foods as nuts and strawberries. All over the world, PPS packaging is in great demand - fish boxes, hot cups, meat trays, etc.
Another of the most important parameters is flammability, since no one is safe from fire, but it is advisable to do without tragic consequences. Users are concerned not only with the flammability of EPS, but also with its smoke-forming ability.
Yuri Savkin
EPS is a flammable material (G3), but it does not support combustion, as it contains fire retardants. That is, if you bring the burner up and remove it, then in a maximum of 4 seconds it will go out. This is during testing. And if there is a fire, like at the ZIL plant, where metal was burning and the temperature went beyond 1000⁰C, then absolutely everything will burn. When burning EPS, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide are released, the same as when burning wood. The point is that this amount of smoke is much less, since the density of EPP is on average 15 kg/m³, which is less than that of other materials. But the rate of smoke formation is higher than that of the same wood, so it is never used in open structures. The PPS is covered with a plaster layer. For example, a facade system with expanded polystyrene and a facade system with mineral wool have the same fire hazard class - K0.
Types of expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene is classified according to the method of production of the material and the inclusion of various additives in it:
- pressed polystyrene foam . Produced by pressing;
- pressless polystyrene foam . Produced by removing moisture by drying and then foaming at high temperatures;
- extruded polystyrene. Not much different from pressless; an extruder is additionally used in production. The best and optimal option for thermal insulation of walls.
There are other types of polystyrene foam (extruded, autoclaved), but they are not used as insulation materials because they have different characteristics.
In addition to types of expanded polystyrene, there are also various types of insulation, such as:
- mineral wool;
- penofol;
- penoizol;
- penoplex;
- polyurethane foam.
What is expanded polystyrene
Often, expanded polystyrene (EPS) is called polystyrene foam, which is quite justified, since polystyrene foam is a general concept that unites a group of foamed plastics (polymers), to which EPS belongs.
Yuri Savkindirector of the Association of Expanded Polystyrene Manufacturers and Suppliers
Expanded polystyrene is a rigid material with a cellular structure, obtained by sintering granules obtained from suspension foaming polystyrene using a non-press method. In Russia, expanded polystyrene has a number of other widely used names: polystyrene foam, PSB-S, foamed polystyrene. In other countries, the abbreviation EPS (expanded polystyrene) is used to designate it. In this case, it is necessary to distinguish between white expanded polystyrene foam and colored extruded polystyrene foam (XPS), which has a different structure, properties and, in fact, a different production method.
EPS is produced in the form of slabs of various densities and thicknesses, molded from granules of the same fraction, uniform white color without a characteristic chemical odor.
If you break a slab, the tear line should pass not only along the sintering boundary of the granules, but also directly through them.
The presence of foreign odors, friability, granules of different sizes are signs of low-quality insulation produced in violation of technology.
Wall pie when using insulation - polystyrene foam on the outside
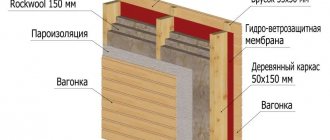
A wall pie refers to layers of materials that are laid in a certain order, each of which performs its own functions to ensure a normal microclimate in the room.
When thermally insulating brick walls with polystyrene laid outside, the wall pie looks like this:
- interior plaster;
- outer wall;
- adhesive solution for gluing polystyrene foam;
- insulation (expanded polystyrene);
- adhesive solution for gluing the next layer;
- fiberglass mesh;
- adhesive composition;
- primer;
- finishing plaster.
NOTE!
When arranging a wall using polystyrene foam, it is necessary to lay the layers in strict sequence.
Internal and finishing plaster can be replaced with other finishing materials that are provided for in design solutions.
Wall cake "wet"
Issues of vapor barrier and waterproofing
An important requirement during the construction and improvement of a house is the correct implementation of all work to ensure ventilation and waterproofing, since it is the incorrect installation of these components that significantly reduces the performance of the structure.
When insulating walls with polystyrene, waterproofing is not needed . It should be taken into account that if there is a high passage of groundwater under the building, it is necessary to waterproof the basement and foundation.
Since polystyrene foam does not allow air and water to pass through, there is no need to lay a vapor barrier layer when insulating walls from the outside.
Wall insulation cake under siding
Sealing cracks and preparing sheathing
Installing polystyrene foam on the sheathing is the most labor-intensive process among the insulation options. Most often, sheathing is done in the case of finishing siding.
Sealing cracks
If you plan to install siding on the wall of a house made of beams, you must first seal the seams properly, clean the surface of dust and debris, and seal the cracks with sealants, polyurethane foam, or a mixture of sawdust and PVA.
If the wall is concrete, brick or foam blocks, then the cracks in such houses are cleaned of sand, treated with a primer, then sealed as follows :
- if there is a small gap . Using a prepared mixture of cement and sand with the addition of PVA, seal the gap with a spatula;
- if the gap is medium in size . Make holes for dowels at a distance of 20 cm. Using screws and washers, pull the metal mesh over the gap and seal it, pressing it into the mesh with plaster. Next apply the finishing layer;
- for a large crack . Seal the gap with polyurethane foam, cut off any irregularities and seal it with two layers of plaster.
Large cracks can be repaired using anchors:
- knock down the plaster, seal the cracks with polyurethane foam;
- install a channel in the opening and attach a reinforcing mesh to it;
- you can use staples made of reinforcing mesh;
- apply plaster;
- putty.
Sealing cracks
When the wall is prepared for laying insulation, you can install the sheathing.
Preparing the sheathing
The sheathing for siding can be made from metal profiles and wooden beams . In humid climates, it is advisable to install metal slats.
Before you begin installing the sheathing, you should determine the location of the siding:
- with horizontal siding . The beam or metal profile is installed perpendicularly;
- with vertical siding . Frame boards or metal profiles are installed in a horizontal position.
The pitch of the sheathing is determined by the width of the polystyrene foam sheet: in width it should fit tightly between the sheathing slats and not form gaps.
The order of work is determined in steps:
- treat the wall with special mastic;
- frame boards are secured around the entire perimeter of the walls using galvanized screws and plastic dowels;
- if holes form between the timber and the wall, these gaps are sealed with pieces of polystyrene foam by gluing them to the wall.
When the sheathing is installed, then proceed to the installation of polystyrene foam panels.
CAREFULLY!
If the sheathing is made of wood, the boards must be pre-treated with antiseptic agents.
Lathing does not require special skills, but it should be noted that the choice of materials should be made based on climate conditions.
Lathing for siding
Wooden sheathing
Rules for working with material
Most often, extruded polystyrene foam is used to insulate foundations, floors, walls and ceilings of residential and commercial buildings. For example, for insulating the walls of a loggia/balcony or the walls of a residential apartment from the inside.
But those who decide to use this material to insulate their own building should remember a few rules.
If the wall is sufficiently smooth and rough, the EPS will adhere perfectly to the adhesive mass. But most often, due to the geometry of the walls, it is more advisable to install polystyrene foam slabs using special dowels. This method is also chosen because it is more budget-friendly.
What are EPS boards placed on?
Extruded polystyrene foam slabs are easily attached to a flat and dense vertical surface using special types of glue. It can be Penoplex FASTFIX, TechnoNIKOL or dilutable adhesive mixtures such as Ceresit CT 83.
If you don’t want to bother with glue, or the surface structure does not allow it, you can resort to fasteners such as special dowels. In general, before insulation, it is advisable to level the surface of the walls with at least rough plaster and place the slabs on both of the mentioned fasteners at once - both on glue/cement mortar and on dowels.
The Ceresit CT 83 adhesive mixture, according to the developers, can be used at temperatures from 0 degrees Celsius. It is also claimed that it is very economical and environmentally friendly
Insulation of foundations and floors
In the case of foundations, all external sides are covered with EPS slabs, after which the newly made thermal insulation layer is covered with a layer of waterproofing. Often homeowners decide to insulate even the blind area.
In this case, a layer of concrete is formed over a layer of expanded polystyrene, which, in turn, rests on a bed of sand and gravel mixture.
The concrete floor screed is also erected on top of evenly laid EPS slabs.
EPS is also used as one of the methods for insulating wooden floors. We talked about this in more detail in the next article.
A blind area insulated with polystyrene foam will help protect the upper part of the foundation from freezing. Plus, a layer of such material will also work as an additional water-repellent layer.
Cutting expanded polystyrene boards
Since the density of extruded polystyrene foam is an order of magnitude higher than that of regular polystyrene, a number of small problems arise with this. For example, this type of material can still be cut with a knife, but firstly, the blade must be extremely thin and strong, since a thick blade can cause the slab to discolor and crack.
And secondly, the creaking and grinding noise that will accompany such an “event” will be an order of magnitude higher than in the case of ordinary polystyrene foam. Therefore, before starting the procedure, it is recommended to lubricate the knife blade with machine oil.
Some people use a grinder equipped with the thinnest metal wheel to cut EPS blocks. Cutting, in this case, is efficient, but the whistle is so loud that it is better to put plugs in your ears. Among other things, this method is the most “unclean”. It will leave a huge amount of garbage behind.
If you decide to use a grinder to cut polystyrene foam, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the rules for using this equipment.
You can easily make a machine or machine for cutting polystyrene foam yourself. To do this, you just need to get some nichrome and a powerful transformer. By connecting the opposite ends of the nichrome wire to the wires coming from the power source, we get a kind of polystyrene foam knife. To make the cut as even as possible, the nichrome wire in the device should be kept taut
The most effective and simplest method is considered to be cutting with hot wire. Take two nails, between which a nichrome wire is stretched. Voltage is applied to the nails through a transformer, the wire becomes hot and the process begins. Using this method, you can cut out the most precise blocks and shapes of a high degree of complexity.
But this method is also the most harmful. As already mentioned, phenol vapors released during the cutting process can cause significant harm to the human body, and therefore, this procedure should be performed in the open air, preferably in a draft or using a special respirator, or even a gas mask.
Few people know, but polystyrene foam makes an excellent formwork for foundations. The material lends itself perfectly to cutting, drilling, etc., and therefore anyone, showing a certain amount of ingenuity and resourcefulness, is able to make a wonderful insulated foundation for their structure
Fire safety measures
When working with extruded polystyrene foam, you must adhere to strict fire safety measures, otherwise extinguishing the fire will be much more difficult than it seems.
That is why, in case work is being done nearby using an open fire, for example, there is a furnace with which bitumen is melted, etc., you should always have a water supply hose, a fire extinguisher, or, at worst, a barrel of water and a bucket at the ready .
It is recommended to do the same when carrying out welding work in close proximity to the EPS. Moreover, it is advised to either shield the material from sparks and scale flying from welding, or pre-moisten nearby polystyrene slabs with water; it is better to do both at the same time. Only in this case will you protect both yourself and your building from fire.
Most fire hazards at construction sites occur precisely because of neglect of safety precautions. If welding work is carried out near work carried out using flammable materials, always expect disaster. To prevent this disaster from happening, you should always keep at least a fire extinguisher on hand.
Technology of wall insulation with polystyrene from the outside
Before you begin insulating the wall with polystyrene foam, you should dismantle the gutters, decorative elements, clean and prime the wall. Next, insulate the sills and window slopes.
Now let's talk about the thickness of polystyrene foam.
NOTE!
When insulating walls with extruded polystyrene, sheets are used whose thickness ranges from 80 to 100 mm or more.
You can also use thinner sheets 30-40 mm thick if they are laid in two layers.
Let's start installing insulation on the walls with our own hands:
- a profile is installed at the bottom of the wall to hold polystyrene foam;
- the adhesive mixture is applied to the wall over the entire area in spots and onto the insulation sheet (amply on the center and edges of the sheet);
- tightly attach the sheet for gluing to the wall;
- Use dowels to secure the panel so that the dowel penetrates the wall at least 50 mm. The dowels are placed in the center of the panel and at the joints. It is recommended to use plastic nails;
- if gaps form (up to 2 cm), then they are sealed with polyurethane foam , if the gaps are larger, then they are first sealed with pieces of insulation, and then foamed. Excess foam is cut off;
- The heads of plastic nails are cleaned and puttied.
After installing the insulation, a reinforcing mesh is applied to the façade . You should cut strips of mesh at the corners and slopes and glue them with a spatula using an adhesive composition. An adhesive composition is applied to the mesh along the wall so that it penetrates 0.1 cm through the mesh onto the polystyrene foam. If an overlap occurs, separate strips of mesh are placed on it and additionally glued.
Sectional view of the device
Fastening slabs with dowels
Application of assembly adhesive
After the surface has completely dried, it is leveled with fine granulation sandpaper.
Next, the surface of the walls is covered with putty and a finishing decorative coating . External insulation with polystyrene foam, when installed correctly, will provide comfort and warmth in the house.
Main disadvantages
Now let's look at the problems that we encounter when using this insulation. It is easily exposed to direct sunlight , under their pressure its density weakens and becomes unstable to weather conditions.
- Many people believe that the thicker the insulation layer, the warmer the house. Cold air penetrating between the plates will cause disturbances: waves and cracks. European standard - 3.5 cm thick. With such calculations, heat is well retained, and in the event of a fire, the risk of poisoning from harmful chemicals released will be reduced .
- Another disadvantage is the complete lack of sound insulation. Insulation is completely unable to insulate a room. You can increase the number of layers, but you still won’t achieve a sufficient result. For sound insulation it is better to use another material.
- During the construction phase (more precisely, after the installation of polystyrene foam), it releases the harmful chemical styrene.
- If you heat it to 75 degrees, vapors are released: ethylbenzene, toluene, carbon monoxide and benzene, which will harm the human body. Manufacturers often try to refute this fact.
- Even the best quality insulation can catch fire sooner or later. This is confirmed by the assignment of G3 and G4 markings by GOST 30244−94 of the Russian Federation. Therefore, do not believe it when, when advertising polystyrene foam, they call it fireproof. Moreover, when melting, the smoke produced is so thick that you can’t see your hands. To summarize, calling polystyrene foam “fireproof” means its resistance to fire itself, but not combustion. However, the insulation is never used as a finishing coating for the walls; it is additionally covered with facing structures, which prevents the foam from wearing out.