Glass-magnesium sheet is a unique building material that is used for interior and exterior decoration of buildings. Thanks to its special structure, LSU is superior to plasterboard, as well as other conventional building materials, in strength and wear resistance. The glass-magnesite sheet contains magnesium oxide, perlite, fine wood shavings, and fiberglass mesh. The ratio of components depends on the LSU class: economy, standard, premium. The strongest premium boards contain the maximum amount of magnesium oxide.
Properties and technical characteristics of SML
Glass-magnesium sheet - SML, also called glass-magnesite sheet, is made from a mixture of water, magnesium oxide and magnesium chloride.
Structurally, the glass-magnesite sheet includes five layers:
- The bottom one is a layer of magnesite filler on the inside of the slab.
- Fiberglass reinforcing layer that adds durability and strength to the material.
- The middle layer is a magnesite filler, in addition to magnesium chloride and oxide, consisting of mineral additives, wood chips, perlite and cellulose fibers.
- Fiberglass mesh.
- Upper magnesite layer.
LSU sheet is characterized by a smooth front side, intended for subsequent finishing without the need to apply leveling mixtures. However, quite often the slabs are installed with the back side facing outward rather than inward.
The SML glass-magnesium sheet will not change its characteristics, at the same time, such installation will provide much better adhesion to the plaster or putty coating.
Configurationally, a magnesium sheet is a rectangle with a thickness of 0.3 to 1.2 cm, a standardized width of 122 cm and a length of 228 or 244 cm. You can also find thicker samples with a thickness of 3 cm and higher.
Scope of application of sheet construction and finishing materials based on magnesium binder
Considering that the material has very good technical characteristics, glass-magnesite sheets are widely used for interior and exterior decoration, private and multi-storey buildings. In particular:
- Internal partitions.
- Doorways and arches.
- Ventilation ducts.
- Multi-tiered ceilings.
- Chimneys.
- Finishing of bathrooms and baths.
- Permanent formwork for pouring lightweight concrete.
- Floor coverings.
It is worth noting that the sheets have minimal weight, so installation work can be done on your own.
Scope of use
The scope of application of the material is very extensive and includes:
- finishing of residential, retail, industrial, commercial and social premises;
- construction of improvised partitions, interior columns, arches, structures for zoning, etc.;
- arrangement of floors and suspended ceiling structures;
- use as mines for the further location of utilities;
- replacing plastic or wood for the construction of concrete slopes or doorways;
- application for the construction of a heat or sound insulating barrier indoors, etc.
Depending on the scope of application, the plates are divided into those intended for:
- Ceiling finishing – sheet thickness 0.3-0.5 cm;
- Wall finishing – thickness from 0.5 to 1 cm;
- Facade work – thickness 1 cm or more.
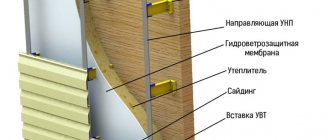
Glass-magnesium sheets have also found application in facade work, in particular, for the manufacture of permanent formwork for lightweight concrete mixtures or for direct cladding of the facade.
A magnesite sheet is installed by analogy with drywall. You just need to take into account that the slab should not be wet to ensure good flexibility and ease of cutting. In this case, installation involves leaving a gap with a width equal to half the thickness of the LSU.
Advantages of glass-magnesium sheets
The great popularity of glass-magnesium sheets is due to its undeniable qualities in relation to similar materials.
Magnetic glass sheets have the following comparative advantages:
- Low material cost. The average cost of a sheet is about 350 rubles per piece, and the material does not require additional equipment, which also saves money.
- High moisture resistance. Applies to SML Premium and Standard class, even with prolonged exposure to moisture, the sheets are not subject to deformation.
- High fire resistance. LSU sheets can withstand temperatures of more than 1000 degrees.
- Frost resistance. At low temperatures it does not lose its technical characteristics.
- Resistance to mechanical damage. In case of accidental impacts with hard objects, it does not crack and does not leave dents, tears, cracks, etc.
- A light weight. Does not create additional loads on the building foundation and floor slabs.
- Elasticity. The material has good flexibility, which allows you to design semicircular arches and doorways.
- Long service life. According to manufacturers, with proper installation, the material can last 30-50 years, depending on the operating environment.
- Environmentally friendly material. Magnetic glass sheets do not contain toxic or chemical additives.
- Strength. The material can be bent into different properties without losing its advantageous properties.
- Easy to process. LSU is easy to drill and cut with a grinder or hacksaw. Wallpaper can be glued to a smooth surface without additional finishing, and plaster fits well to the rough side.
- Resistant to development of scratches, mildew, etc.
All of the above-described advantageous features of glass-magnesium sheets can be present in high-quality material manufactured in accordance with technological standards.
Specifications
- Bending strength – 27 MPa;
- Density – 600-1300 kg/m3;
- Thermal conductivity – 0.32 W/mS;
- Thermal resistance – 1.14 m2 K/W;
- Fire resistance – 1.15 m2 k/w;
- Temperature coefficient of linear expansion – 0;
- Hardness of the front surface – 5.9-8.3 MPa;
- Surface moisture absorption ≤0.34% by weight;
- Bending resistance force in dry condition – 18 MPa;
- Bending resistance force in a wet state – 22 MPa;
- Vapor permeability – 0.11-0.14 mg/m∙h∙Pa;
- Sound insulation – 44 dB;
- Flammability group – NG (non-flammable in accordance with GOST 30244-94).
Glass-magnesium sheets, the price of which ranges from 550 to 880 rubles, are produced by both domestic and foreign factories, which is the reason for the formation of a certain pricing policy.
Installation rules
Conditions, features and standard solutions for installing LSUs are contained in the Standard Flow Chart.
Transportation and storage
Products are delivered by any means of transport. Individual sheets can be transported in dry weather without packaging or tent .
Unloading is carried out mechanically or manually. The sheets are carried in a vertical position, 2 pieces at a time , avoiding jerking, bending, and wave-like movements.
Store the material on a flat floor, in stacks up to 3.5 meters, providing protection from precipitation and direct sunlight.
Uncover
Only dry sheets are cut. Cutting order:
- The sheet is laid on a flat surface with the glossy side up. It is better to carry out cutting on a large table or a specially made stand.
- A metal ruler, corner or strip is pressed along the marking line; they will serve as guides.
- The knife is used to make several cutting movements until the reinforcing mesh is cut through.
- The sheet is shifted so that the cut line coincides with the edge of the surface.
- Break the sheet downwards.
- Cut through the second reinforcing mesh.
- Separate parts of LSU.
To cut round through holes, use a cutter or socket bit. The figured cut is performed with an electric jigsaw.
Advantages and disadvantages
The SML glass-magnesium sheet has very good characteristics, which is why it has many advantages.
One of the main advantages is its 95% water resistance, which allows it to be used for finishing any surfaces, including facades, as well as excessively wet ones, including bases located in saunas, swimming pools, underground and basement areas.
Moisture resistance was established experimentally by immersing the sheets in water for 100 days. The result of the experiments is the value of the coefficient of change in dimensions in the wet state, which is only 0.34%.
Even the most waterproof drywall, and even more so wood boards, cannot compare with LSU in this regard. The antiseptic properties of the components minimize the risk of fungal cultures.
SML glass-magnesium sheet is an excellent sound insulator. A magnesite sheet just 1 cm thick can soundproof a space at the level of 1.2 cm thick plasterboard, laid in four layers, or a brick wall up to 15 cm thick.
In addition, the magnesite sheet is endowed with an impeccable thermal resistance of 1.14 m2 K/W. This indicates the unique property of the slabs to retain heat in the room without letting in cold from outside.
The next advantage is strength, which is several times greater than the strength characteristics of gypsum plasterboard. That is, it is quite difficult to mechanically damage the LSU sheet. Even a blow with a fist will not crack the surface, as would happen with drywall.
A truly phenomenal advantage of the material is flexibility, which is confirmed by the bending radius of the slab, reaching three meters. Before the advent of magnesite slabs, only one building material could boast of such flexibility - flexible ceramic granite kerlite.
Therefore, glass-magnesite sheet can be used for finishing the most curved and non-standard bases. This characteristic greatly simplifies its transportation and transfer.
Not only the flexibility, but also the lightness of magnetite helps to increase the installation speed. Magnesium sheet is more than 35% lighter than drywall - this reduces the weight of the structure and, accordingly, the load on the wall base, and also makes the work of the master easier.
The products lend themselves well to drilling without cracking or releasing dust.
Glass-magnesium sheet, the use of which is not limited to interior work, has a frost resistance of over 50 freezing cycles, which is especially important for the construction of permanent formwork.
In terms of fire resistance, it is assigned class A, that is, the slabs are non-flammable. Even products with a thickness of only 0.6 cm are able to “hold defense” from flames for two hours and at the same time withstand temperatures up to 1250°C.
Another advantage of LSU is environmental friendliness. Only plant and mineral raw materials are used for the production of slabs. They do not contain organic chemical compounds in the form of benzene, asbestos or formaldehyde components, which makes the products absolutely safe.
Even exceeding the temperature of 1250°C, at which the material begins to burn, will not be characterized by the release of toxic chemicals.
Distinguished by its enviable environmental friendliness, magnetite does not interact with various acids and solutions in the form of hydrofluoric and chromic acid, as well as aqueous solutions of fluorine salts.
The sheets are also not affected by caustic alkalis, mineral oils or kerosene-containing liquids.
It is impossible not to note the durability of magnesite sheets. The service life declared by the manufacturers is 20 years, however, it can reach 30 or even 50 years.
Glass-magnesite sheet has only relative disadvantages, since they can be easily avoided by purchasing a quality product and the right tools for the job. It can delaminate and unnecessarily absorb water.
But this is observed only in low-grade materials - they are easy to distinguish by their rather brittle edges.
Fine dust, felt when running your hand over a sheet, is also a property of low-quality slabs. It should also be remembered that high-grade material is milky or beige-yellow. A white or light gray tint is a sign of low quality.
There may also be some difficulties when slicing. A jigsaw is perfect for these purposes. When using a regular jigsaw or hacksaw, you should expect them to become dull quickly.
Product marking
The first sheet of glass magnesite was manufactured in China, and to this day this country remains an unattainable leader in the production of this material, although products from domestic factories, which are mainly subsidiaries of Chinese enterprises, have begun to appear on the Russian market.
All material on the market can be classified into one of the following classes:
- Premium Lux or Premium with density characteristics from 1500 to 1750 kg/m3 (class A);
- Standard – from 1250 to 1500 kg/m3 (class B);
- Economy - from 1000 to 1250 kg/m3 (class C).
Also on the market there are products of lower classes D, E, F, G with a density of 500 to 1000 kg/m3.
In addition to density characteristics, different classes of products differ in strength, flexibility and adhesive surface characteristics. But you should always take into account an important pattern for this material: the higher the density, the higher the water resistance.
Therefore, for rooms with high or high humidity, only Premium or Premium Lux products should be used.
On the Russian market there are products with more understandable markings, for example “Premium 02”, which is similar to class A, and “Premium 01” is an analogue of class B. The Russian “Standard” is equal to the Chinese classes C and D and is recommended only for interior work exclusively in rooms without high humidity levels.
Products of lower classes are not produced in Russia due to low density characteristics, which do not provide the necessary strength to the constructed structural elements, as well as due to extremely low moisture resistance.
SML - material of the future, video:
Recommendations for selection
The main thing to consider when choosing LSU is the division of the material into classes. Density, strength and durability depend on the class or assortment.
- Premium class (A);
- Class standard (B);
- Economy class (C).
Premium products are endowed with the greatest strength (1200-1300 kg/m3). They contain a large proportion of magnesium oxide (40%). At the same time, magnesium chloride is added at least 35%. As the grade decreases, the percentage of magnesium also decreases.
Approximate prices
Class A “Premium” sheet, used for outdoor work. Prices for it depend on thickness. For a 6 mm sheet measuring 1220x2440 mm, sellers ask from 400 to 420 rubles. LSU with a thickness of 8 mm is sold at prices from 440 to 470 rubles. 10 mm – 580 – 620 rub., 12 mm – 670 – 730 rub./sheet.
Average prices for LSU “Standard”:
- 6 mm – 320 -340 rub./sheet;
- 8 mm – 340-360 rub./sheet;
- 10 mm – 380-430 rub./sheet;
- 12 mm - 440-460 rub./sheet.
“Economy” class sheets are sold on average 5-8% cheaper than “Standard” ones.
Structure of glass magnesium sheet
The structure of the glass-magnetic sheet consists of five layers:
The outer layer has a smooth surface and allows you to wallpaper or paint immediately after installation.
- Reinforcing layer made of fiberglass mesh.
- MSL filler is magnesium chloride, magnesium oxide and wood shavings.
- Another reinforcing layer of mesh.
- The inner layer of the sheet has a roughness, which contributes to better adhesion of the plaster during finishing.
The structure of glass-magnesium sheets is the same for all, regardless of their class.
Functions of facades made of magnesite slabs
Glass-magnesium sheets are actively used for external cladding of building walls. Such facades are in great demand during the construction of new buildings of varying complexity and renovation of existing ones.
Facades and magnesite slabs perform the following functions:
- Prevents building walls from the destructive effects of moisture and various types of atmospheric influences.
- Thermal insulation of the building is carried out.
- Concrete structures and reinforcement protect against corrosion.
- Provide the building with additional sound insulation.
- Using LSU allows you to level the walls of a building.
Fiberglass sheets are considered the most high-tech, inexpensive and universal building material.