The bluing of weapons is considered by hunters in two ways: for some it is style, beautiful execution, for others it is practicality. Blued metal is much more resistant to corrosion; the blued shade is an additional camouflage. Blueing will restore the appearance of a battered weapon, completely protect it from rust, and protect it from mechanical damage and abrasions. It is not always possible for a shooter to purchase a gun that is already blued. Many hunters blue their weapons themselves using a variety of methods.
Basic processing rules
In fact, bluing is a chemical treatment of the metal surface, so this process is considered very harmful and even life-threatening. When performing bluing, you must follow a number of rules, such as:
- Before starting work, it is recommended to study in detail the properties of all reagents used in bluing, as well as draw up a clear procedure;
- Use a special container, it can be glass, porcelain or earthenware. Containers made from other materials will simply be corroded by acid;
- All work must be carried out in a room that has excellent ventilation (preferably outdoors);
- As a material for surface treatment of metal, you can use sandpaper of varying degrees of hardness or powdered pumice. Metal brushes can leave very noticeable marks in the form of scratches on the surface of the product;
- Availability of eye, respiratory and skin protection;
- Before starting work, the surface of the product must be degreased and cleaned of debris and dirt.
Alkaline method
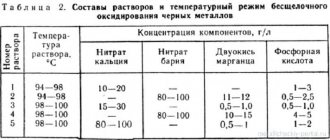
In an alkaline environment, bluing is carried out with the addition of oxidizing agents at a temperature of 130 to 150C. This method is based on the creation of an oxide film by oxidation of iron. In this case, you can use a stainless steel vessel to boil the solution. To prepare the solution, you need to add a little sodium nitrate and 100 grams of technical soda to 100 ml of ordinary water. Mix all components thoroughly, the resulting mixture must be heated to a temperature of 130-150C, and then immerse the workpiece in it for about 25-30 minutes.
Note! A boiling lye solution emits a very unpleasant odor that can cause dizziness and vomiting. It is advisable to work in a well-ventilated area or outdoors.
Acid bluing
Acid bluing is the process of imparting an oxide film to metal by immersion in an acidic environment. It is performed both chemically and electrolytically. This method allows you to make the surface even and smooth without spending a large amount of money. To prepare the solution, add 2 grams of tannic and tartaric acid to 1 liter of water and mix thoroughly. This liquid must be prepared in a porcelain or ceramic container. The workpiece is immersed in the solution for 15-20 minutes, after soaking, it is thoroughly washed with running water, wiped and dried. This method is used for steel, copper and cast iron products. But hardened and heat-resistant products should not be blackened in this way.
Application of rust varnish
Rusty varnish is a composition that causes accelerated rusting of metal, while magnetic iron oxide forms on the surface. If we talk about the financial side of the issue, then the costs in this case will be minimal. In order to prepare the solution, you need to add 100 ml of hydrochloric acid, 140 ml of nitric acid, 80 grams of iron filings (can be cast iron), 300 grams of crushed iron scale to 2 liters of water. The workpiece is completely immersed in the chemical, resulting in the formation of black or red iron oxide on its surface. Such cold bluing gives a fairly effective and long-lasting result.
Thermal bluing
Thermal bluing of metal is the oldest and at the same time the simplest technology. The essence of such processing is to heat the product (workpiece) to a temperature when the oxygen contained in the air does not begin to enter into a chemical reaction with the upper layers of the part. The more the metal heats up, the darker and richer the shade it will eventually acquire, all due to the fact that the oxidation process occurs at different depths at different degrees of heating. Literally anyone can carry out such bluing of metal at home, because this does not require any specific components or additional cash costs.
Knife bluing process
The high-carbon steel from which good knives are made can oxidize quite strongly even from quite ordinary household tasks, for example, after cutting vegetables or fruits, if they get into water, etc. The safest and most effective way to burnish a knife is a technology based on a solution of nitrate.
- Degrease the knife; to do this, simply wipe its surface thoroughly with regular alcohol (or vodka). Alternatively, you can use a 30% alkaline solution for degreasing
- Prepare a solution of nitrate. Pour 1 liter of water into a stainless steel container, add a little sodium nitrate and caustic soda, mix thoroughly and bring until completely dissolved. This mixture has a strong pungent odor, so it is advisable to work outdoors; if this is not possible, then do not forget to use protective equipment in the form of glasses and a respirator.
- Place the finished solution in a steam bath, this will prevent it from boiling since the boiling point of such a liquid is higher than that of ordinary water and is about 140C;
- Place the knife in the solution and leave the container for 80-90 minutes without removing the container from the heat;
- Upon completion of the process, remove the knife from the solution, let it cool, and then rinse thoroughly with running water.
The main advantage of this method of bluing knives is its simplicity and low cost. After the procedure, the metal surface acquires a pleasant black color, sometimes with a bluish tint.
Other bluing methods
Pencil for bluing. A pencil (marker) for bluing is often used both to restore individual damaged areas of a product, and to apply blackening to the entire surface. If the technology is followed correctly, this type of coating gives the flock a smooth and even appearance. The next step is to paint over the cleaned surface with a pencil. The chemical reagent penetrates quite deeply into the steel, achieving a fairly durable black bluing that can last quite a long time. Finally, wipe the product with a felt cloth or a special tip that is already on the pencil (marker).
This bluing gives a rather uneven color, so it is suitable not for improving the appearance, but for protecting the surface from the effects of negative external factors. It certainly won't rust!
Oil bluing. This processing method is excellent for blackening at home. To work, you will need a metal container of the required size, regular machine oil from 500 ml to 1 liter and a gas burner (any other heating element of sufficient power), paper napkins, bricks or another non-flammable surface. Also, if you are not a motorist and you don’t have car oil on hand, then gun oil, linseed oil and even olive oil will do the job well.
The oil bluing process itself looks something like this:
- Place the part on a brick;
- Heat with a gas burner until glowing (heat as hot as the heater allows);
- Place the heated workpiece completely in oil;
- Remove and place on a paper towel to absorb excess oil;
- Repeat the procedure 4-5 times until the metal is given the desired color.
Important! This method will not make the part pitch black; in addition, this coating is not resistant to mechanical damage and is more suitable not for decorative purposes, but specifically for preventing corrosion.
Blueing method
Steel blueing is a type of bluing in which the metal is given a darker color, not black, gray or brown, but a rich, beautiful blue. To prepare the solution you will need to prepare two solutions at once. No1 – add and mix 140 g of hyposulfite to 1 liter of water. No2 – dissolve 35 g of lead acetate (popularly “lead sugar”) in 1 liter of water. The solutions are mixed only before blackening begins, heated to boiling temperature, then the product is lowered into a boiling liquid and remains there until it acquires the desired color. At the end, you need to thoroughly rinse the part in cold running water, dry it, and then wipe it with a cloth moistened with machine or castor oil.
Blackening of metal must be carried out in strict accordance with the chosen technique and compliance with all necessary safety regulations.
An ancient method of bluing barrels without tin soldering
This recipe is taken from the book “Shotgun” by S.A. Buturlin, 1936. It is simple and very effective.
Burnishing in coals
To do this, birch or aspen charcoal (coke baked into a fire) is pounded into powder, then sifted through a sieve. This powder is poured into a tin or other metal box (riveted only, no soldering!) and heated on the stove until sparks begin to run across the powder when stirred. Then the well-cleaned iron or steel parts of the barrel are placed in this powder. It is best to string them on a wire to make it easier to remove. The trunks should be completely immersed in the powder and covered with it, but not touch the bottom and walls of the box.
Preparation for bluing metal at home and the process of processing the part
Home craftsmen resort to affordable methods of creating an anti-corrosion coating for metal:
- Heat treatment in an oil environment;
- Treatment with chemicals;
- Application of the finished protective composition.
Compliance with safety measures comes first, even if the home workshop does not have sufficient equipment. The cycle of metal bluing operations begins with degreasing surfaces with solvents in compliance with fire safety measures in a ventilated area.
The oxide film and rust residues are removed mechanically: with an end wire brush using an angle grinder, on a grinding or rubber wheel, or manually with sandpaper. The operation should be completed by removing the marks on the felt polishing wheel.
Mixing and heating of reagents requires eye, skin and respiratory protection:
- The lack of exhaust ventilation is compensated by active ventilation or work in the fresh air;
- Protect your respiratory system with masks when bluing with chemicals;
- Chemicals should be stored and used in non-destructive containers;
- Use safety glasses, thick gloves, and an oilcloth apron.
Blueing of metal with chemical solutions
The durable chemical coating of the metal is accompanied by maintaining a high temperature. The duration of the process extends to 1.5 hours. Evaporation of the solution due to boiling off and reduction of heating costs is facilitated by a tight lid with an internal flange for draining condensate into a stainless steel vessel.
A container for immersion for cooling purposes, plenty of running water and a tin of machine oil (even waste oil will do) are at hand.
Alkaline metal bluing
This method is most often used. We measure at the rate of 1 liter. distilled water 1.2 kg of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and 0.3 kg of sodium nitrate (NaNO3). Both ingredients dissolve well. Complete dissolution will occur with increasing solution temperature.
The operation is performed in an open space. Be sure to be on the windward side. The fumes are caustic and have an unpleasant odor.
The product is suspended on a copper wire, without touching the walls of the metal container. Heating is done with a blowtorch. The alkaline solution for bluing is poured in excess so that it does not have to be topped up.
The duration of boiling affects the depth of the coating, the thickness of the color - you can get black with blue. The duration of treatment is 0.3–1.5 hours, it stops when the desired shade is reached. The solution temperature is 130–1500C.
The removed product is washed, generously lubricated with machine oil, and wiped dry. The blackening of metal on a polished surface is uniform, without contrasting streaks.
Other component options for 1 liter of distilled water:
- KOH – 0.6 kg;
- KNO3 – 0.03 kg.
When brought to 2000C for half an hour, we obtain a matte blued surface. For brilliant bluing we use the same reagents and temperature conditions:
- Potassium hydroxide – 100 g;
- Potassium nitrate – 30 g.
The difficulty of bringing it to 2000C without an autoclave is compensated by prolonging the exposure of the reagents during active boiling under a tight lid.
Electrochemical alkaline metal bluing
Chemical dyeing or anodic oxidation does not have the disadvantages of thermal exposure in an alkali solution. A film of deep black color without streaking with improved corrosion resistance characteristics with a thickness of 5 microns is obtained under the following conditions:
- Saturation of caustic soda solution – 0.7 kg/l;
- Direct current density - 5–10 A/dm2;
- Temperature - 60–700;
- Procedure time: 40–50 minutes.
The cathode is selected to be stainless; it is important to maintain the temperature and current range with a stabilizer. The bluing surface is activated by a single dip in hydrochloric acid.
Blueing of metal in an acidic environment
Ingredients for 1 liter:
- Tannin (tannic acid) – 2 g;
- Tartaric acid – 2 g;
- Mixture temperature 1500C;
- Burnishing time – 0.4 hours.
Cold bluing method
Hot solutions are unacceptable for bluing weapon barrels. The way out is “Rusty varnish”. When preparing the solution yourself, it is necessary to take into account that liquid ingredients are taken not by weight, but in volume fractions per 2 liters of distilled water:
- Hydrochloric acid – 100 ml;
- Nitric acid – 140 ml;
- Iron scale – 25 g;
- Iron filings – 35 g.
Let's start the reaction. The end of the release of gas bubbles indicates the completion of the interaction of the reagents. Effectiveness parameters of “Rusty Varnish”:
- Salt concentration - 4.7%;
- The density of the solution is 45 g/l;
- Oxidation time – 20 min.
Retention in chemicals is repeated, if necessary, up to 5 times with intermediate washing, wiping and drying.
Rusty varnish - bluing kit
Thermal blueing of steels
Oxidation of metal under the influence of temperatures bordering the normalization process is also permissible for hardened products - tempering at 4000C does not occur. The convenience of the method is that hot bluing is superior in durability to other technologies.
Thermal blueing of steels
Selecting an oil to coat the metal is not difficult. Suitable synthetic, machine, vegetable. The part is dipped and wiped. The thickness of the layer is not important: the excess will drain and burn.
The electric furnace is heated to 350–4000C, and the products are loaded in bulk onto a pallet. The time is calculated based on the mass and configuration of the metal. The plate needs 15 minutes. Warming up of a massive part takes a long time.
Removal is carried out after the oven has cooled. If necessary, repeated bluing is carried out. When oxidizing small parts, tying with wire does not leave marks.
The simplest method of bluing metal at home
Prepare a 10% citric acid solution. A packet of food-grade citric acid dissolves in ten times the volume of boiling water without sediment. We omit the item to be oxidized. Blackening the metal takes up to an hour.
As bubbles appear on the surface of the product, shake the object or mix the composition with a glass rod. The coating is quite durable, but does not differ in mechanical resistance.
Burnishing metal with citric acid
Blueing by surface painting of metal
Oxide protection, in parallel with blackening, is provided by ready-made purchased products. Preparatory measures for cleaning, degreasing, and removing scratches by grinding are carried out without fail. Manipulations for bluing metals are carried out at room temperature and active ventilation.
"Clover". Used to restore and protect partial surface damage. The consistency of the drug is gel. Apply with a brush. Stand for 2 minutes. on the damaged area of the product, wash off with water. It is possible to coat the metal three times to give the desired shade. Safe to use, does not require special skills.
"Voron-3M". The drug is capable of coating various metals. Designed mainly for decorative blackening.
DuraCoat. A universal tool for bluing and decoration. Variations with the color of the coating are possible. It resists physical impact and aggressive chemicals well. Covers metals, plastics and wood.
Acid bluing of steel blanks
Before starting acid coating, the workpiece is cleaned and washed. You can get by with pure alcohol or a 40% strength solution (regular vodka). Some people use white spirit. Using a swab, clean the surface from greasy stains.
Recipe No. 1
Working solution for bluing:
- 2 g citric acid;
- 2 g oxalic acid;
- 1 liter of water.
Process:
- The solution is heated to a temperature of 120…125 ⁰С.
- Place the product in it for 20 minutes.
- Once completed, the part is removed and washed with a slightly alkaline solution. You can use a sponge soaked in shampoo.
- The treatment is completed by rubbing with machine oil.
The product takes on a black color with some brown tint.
Recipe No. 2
Vegetable tannins (tannins) are used. They are obtained from oak or willow branches.
Preparation of concentrate:
- willow or oak branches (about 3 kg) are boiled in a 10 liter container;
- 3 hours after cooking, a black solution forms;
- the branches are removed from the solution;
- evaporate the solution to 3 liters. The result is concentrated tannic acid. Only part of the solution is used for bluing. The remaining concentrate is poured into a glass container and covered with a tight lid (can be stored for up to 3...4 years).
Blued parts:
- Use 20...30 g of tanning concentrate per 1 liter of working solution.
- To activate the process, bluing is carried out with citric acid, which is added to the composition of the working solution (2...3 g per 1 liter of water).
- The part that needs to be blued is placed in the prepared solution.
- The duration of the process is 24..30 hours.
- After processing, the part is removed and washed.
- The finished part is wiped with machine oil.
- Remove any remaining oil from the part using a rag.
Burnishing with citric acid
This method is good for high carbon steel. Oxidation reliably protects against rust, oxide films, and corrosion.
The bluing does not have long-term durability, so it is suitable for weapons that the shooter uses extremely rarely.
For hunters living in big cities, who rarely go out to shoot, this method of bluing is more than suitable: it is budget-friendly, and the procedure can be carried out in apartment conditions. All you need is machine oil, water and a pack of citric acid.
The acid is poured into a container, poured with boiling water and stirred. The product is immersed for 1 hour, periodically moving it to knock down bubbles. Having removed the part, it is rinsed and lubricated with oil.
What benefits does bluing metal give you?
Most brands tend to rust; pockets of corrosion occur at the slightest contact with water, if the surface is not wiped with an oily rag after that. Even with high air humidity, steel can become rusty very quickly. For the most part, metal is coated with anti-corrosion paint, either by spraying or brushing. But this is not suitable for threaded connections or moving parts. Therefore, bluing is often used to protect against corrosion, which is also called blackening or blueing of steel and, if we turn to technical terms, oxidation.
In other words, conditions are created for a film of iron oxide to form on the surface of the metal, the thickness of which can vary from 1 to 10 micrometers, depending on the processing method. Based on the type of effect on the metal, bluing is divided into thermal, acid and alkaline, that is, in the last two options, the metal is immersed in the appropriate solution. When heated, the so-called tarnish colors change on the surface of the steel; approximately the same thing happens during galvanic treatment in an acid or alkaline bath. You just need to select the desired oxidation color and stop the effect on the steel surface there.
The change in tarnish colors is associated with an increase in the thickness of the layer of oxidized metal. The thinnest film is formed at the stage of yellow color; as its thickness increases, brown, cherry, violet, and then blue and gray colors will replace each other. But the latter does not mean at all that you are approaching what is called blackening. After all, bluing covers almost all tarnish colors, starting with brown.
Metal blackening
Depending on the acidity of the environment in which the workpiece is processed, the color of the resulting coating changes, from yellow to black. Therefore, bluing and blackening of metal are not the same thing. The required shade is selected by varying the intensity and duration of heat treatment and the percentage of solution components.
If you take a mixture of 7 parts copper nitrate and 3 parts alcohol denatured alcohol, apply it to the product and heat it over a fire, then as it heats up the coating begins to change its color. When the desired shade is achieved, stop heating.
It is also possible to blacken steel by coating it with oil and calcining it in an open flame. The result is a durable film of deep black color. There are other compositions for blackening.
Blueing of steel - recipes of varying degrees of complexity
With prolonged heating, after the heat of the metal passes the white stage, and then yellow, brown and violet, the surface of the steel will turn a beautiful light blue color, gradually giving way to dark. The simplest method of blueing is based on heat treatment, and it is with this that we will begin the list of existing oxidation methods. To obtain high-quality bluing at home, you will need a forge, preferably with automatic blowing; in extreme cases, you can use an ordinary metal barrel half filled with chopped brushwood.
We fill a metal box to the size of the part with small birch charcoal and place it in a well-heated forge or in a barrel with burning wood chips. When the coal heats up and begins to smolder, we place a vinegar-wiped and dried steel part into it, and then monitor the stages of its heating. At the very beginning of the appearance of blue, take out the workpiece and cool slightly in air, while cleaning it with soft charcoal. Then we put it back in the box. By repeating these manipulations several times, and finally bringing the heat to a distinct blue color, you will get a durable oxide film.
Another method is using a special solution and without heat treatment. For it you need to get only 2 reagents: 2.5 grams of potassium hexacyanoferrate, popularly called red blood salt and which is a powerful oxidizing agent, as well as iron sesquichloride. Both ingredients dissolve perfectly, so feel free to pour 0.5 liters of water into each in a separate container, then combine the resulting liquids into a single mixture. It is in this that we place the steel part that needs to be given anti-corrosion resistance. When the metal surface reaches the desired color, remove the part from the bath and dry it.
There are more complex methods of blueing, but we will turn to those that are simpler. Oxidation can be carried out not only with solutions, but also with melts of various substances. In particular, a dark blue color can be given to a steel product by immersing it in molten sulfur, into which a small amount of soot is first mixed after turning into a liquid state. The second option is a melt of saltpeter, obtained by heating it to a temperature above 320 degrees. If you keep a steel product in such a bath, it will be covered with a uniform dark blue film.
Steel bluing in the brown spectrum
In some cases, it is quite enough to achieve the formation of a brown oxide film on the surface of the steel part, the shades of which may vary depending on the substances used. The simplest recipe is based on the same ingredient that we considered earlier, namely, we need 100 grams of iron sesquichloride, as well as a kilogram of olive oil. We mix these components and get a paste, which should be evenly coated on the steel product. Then, after a few hours, the surface is sanded with a metal brush. The cycle is repeated several times.
Another option is somewhat similar to the previous one. But for the oxidation process at home, in addition to 0.5 kilograms of olive oil, you will need the same amount of antimony trichloride. The second ingredient, in fact, also refers to oils, so by mixing the ingredients, you will get a kind of ointment. We cover the steel product with it and leave it for a day. After the specified period has passed, wipe the surface of the metal with a woolen rag and apply the ointment again for a day. The final stage will again be rubbing with wool and polishing with a waxed brush.
You can further simplify the composition with which a brown anti-corrosion film is applied to steel. To do this, it is enough to make a solution to immerse a metal product in it for a certain time. You only need to stock up on iron sesquichloride, which is added in the amount of 150 grams per liter of water, or 0.2 kilograms are measured and mixed with a liter of 90 percent alcohol. It is enough to dip the steel product into such a bath several times, while immersing it, observing the change in color of the surface.
Recipes for oxidizing steel into noble gray and black colors
Steel, which acquires various shades of gray as a result of bluing, looks beautiful, and a fairly strong film of oxidized metal is obtained that protects against rust. You can obtain a color in this spectrum in a simple way, which, however, is only available for small products. You will need 70 grams of copper nitrate and 30 grams of denatured alcohol, the first reagent is a salt, the second is an alcohol.
It is better to make the solution by heating the salt until it melts with the addition of denatured alcohol after removing the container from the heat (preferably a chemical porcelain cup). We coat the steel product with the composition and heat it over the fire, placing it on a sheet of tin. The following complex recipe is suitable for oxidizing metal to a gray color. This process, over a long period of time, can lead to cold blackening of regular and stainless steel, which is easiest to do at home.
The following components are needed: 24 percent hydrochloric acid - 120 grams, 90 percent alcohol and water - 100 grams each, sublimate - 40 grams and 2 times less bismuth chloride with copper chloride. Mix acid and water, add alcohol and divide the resulting liquid into 3 equal parts. Pour the last 3 components related to salts separately into each part of the solution and then mix everything in one container. The steel product is immersed in the resulting bath for half an hour, after which it is removed and boiled in clean water. If necessary, repeat the process.
Attention, for your own safety, pour the acid into the water, but not vice versa, in order to avoid a violent reaction accompanied by splashing out of the reagent.
And finally, the recipe directly for blackening. In fact, an excellent result can be achieved only by coating the steel product with linseed oil, wax or animal fat and calcining it well in the fire. As a result of firing, a stable black film is formed on the surface of the metal. However, it is much more effective to use a preliminary immersion of steel in a bath with the following solution: per liter of water, put 100 grams of copper sulfate and add 10 grams of ammonia. By coating cleaned and degreased metal with this composition and calcining it in a fire, you will first obtain a black-brown film, and after repeated dipping and heating, a black film.
Oxidation
When using this method, the metal is treated with some kind of oxidizing agent, for example, saltpeter. The difficulty is to heat the chemical to the melting point, which is not possible for everyone. But there are several recipes for solutions that can be used without heating.
Option 1
To create a solution for 1 liter of water, you will have to mix the following components:
- disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) - 100 grams;
- sodium nitrate (NaNO3) - 50 grams;
- caustic soda (NaOH) - 2.8 grams.
Option 2
designed for 0.63 liters of water and includes a large amount of caustic soda:
- caustic soda (NaOH) - 400 grams;
- potassium nitrate (KNO3) - 10 grams;
- sodium nitrate (NaNO3) - 10 grams.
Both options are equally effective; choose the one for which you managed to find the reagents in the required quantities.
Having prepared the solution, immerse the part in it for half an hour, then dry. Please note that these methods are also suitable for bluing blades, since the resulting film is very durable.
Using "Rusty Varnish"
“Rusty varnish” is on sale. It is used for surface coating of parts:
- the part is wiped clean from residual grease;
- varnished;
- use an acetone-based solvent, for example, No. 646, to wash off excess varnish from the surface;
- This is one of the fastest bluing methods using ready-made solutions.
Video: bluing at home.
Recommendations
You yourself can choose a way to blacken metal at home, each of them can lead to a very high-quality result. A container is almost always needed. Best suited: porcelain, durable glass (if heating is not needed), galvanized stainless steel. Attach hooks to the edges of the tank: you will need them to secure the part.
Another tip: degrease not only the workpiece itself, but also the container for the procedure. This can be acetone, gasoline, kerosene or a special composition. The main thing is that they are inert towards steel, that is, they do not enter into a chemical reaction with it.
Be sure to be responsible when choosing a location; it should be a room with excellent ventilation. Otherwise, you may be exposed to dangerous, toxic fumes. Additional protection - a respirator, goggles to protect the mucous membrane of the eyes, gloves.
An important preliminary step when using any method is to remove rust and dirt before applying the metal blackening agent. It can be done using sandpaper or a grinder with a special attachment. In extreme cases, etching can be used.
We recommend carefully choosing which product can be used for a particular type of material. If you follow our tips correctly, you can get excellent results at home.
Thermal bluing of parts
In industrial conditions, they prefer to perform bluing using a thermal method. Usually this operation is combined with low tempering, which relieves internal stresses inside steel products:
- The part is heated in a muffle furnace for 20...30 minutes to a temperature of 180...220 ⁰C.
- The removed part is wiped with machine oil using a swab. It is advisable to treat all surfaces.
- If necessary, the treatments are repeated.
- Usually, a double heat treatment is sufficient to obtain a high-quality blued surface.
Information: weapons factories producing firearms and bladed weapons use thermal bluing. The coating on many products lasts more than 100 years. Example, Mosin rifles manufactured in 1891 and Nagan revolvers released at the end of 1888.
Corrosion protection
This is the most important goal. This is especially true when a metal structure is used outdoors, that is, the steel is constantly exposed to oxygen and moisture. With such actively reacting substances, an oxidative process - rusting - is possible. As a result, red rust is formed. It greatly affects the strength, reducing it, and also shortens the service life. In this regard, many car enthusiasts are actively interested in how to make the surface of the metal black, and how to blue the steel elements of the car, since corrosion spoils automobile spare parts.
Cold processing: brush or bath?
In the arsenal of craftsmen there are many solutions that cause the formation of a dark deposit on the surface of the metal. During certain chemical reactions, the substances contained in the solution form a black film on the surface of the metal. The most well-known substance for cold bluing is “Parisian oxide”. With an improved recipe, it is offered in the retail chain as Klever Schnellbmenierung (Russian analogue - “Raven 3”). The substance containing selenium is applied with a brush to the surface to be treated, after which it is thoroughly washed off. The method is quite economical and does not require special expenses. Rapid bluing can be used for parts that are not subject to high mechanical stress. Whereas high-quality steels with a chromium content of more than 3% are not recommended to be processed in this way. In addition, the blackening will be uniform only with extremely careful processing, after which polishing with a special paste is required. It is much more effective to perform rapid bluing by immersion. The effect of this procedure lasts longer. In addition, the operation can be repeated several times. A detergent is used to remove the dye. After that, the workpiece must be wiped dry with a rag moistened with alcohol. If you now apply distilled water to the product with a brush, it will not roll off in drops, but will form a uniform film, indicating the absence of fat on the surface.
Hot processing: oil and fire
The ancient artisanal method of bluing, in which the part is first oiled and then burned with a blowtorch, has a number of advantages. The process is not accompanied by the release of harmful substances, is cheap and effective. And although oil firing is also not true bluing in the full sense, the resulting coating lasts on the surface much longer than with cold processing. Those wishing to perform thermal bluing should slightly heat the surface of the product and apply a very thin layer of linseed oil to it. It is also fashionable to use olive oil or special weapons grade (for example, Ballistol). The advantage of the latter is its slightly alkaline properties, which do not have a destructive effect on the metal. Lignite and petroleum oils, as well as various paraffins, are suitable for these purposes. When slowly heated to 200-400 C, the light fractions evaporate and a dense oil film forms on the surface. Further gradual heating leads to the formation of first a brown and then a black color, which can no longer be removed. It is fundamentally important with this technology not to use too much oil to avoid stains.
The best results are achieved by using a mixture of twenty parts grease and one part sulfur. The latter contributes to the formation of a very dark layer of iron sulfide. Sulfur balm can be made from sulfur by dissolving it in a small amount of turpentine and then mixing it with linseed oil. The composition is distributed in a thin layer over the surface of the workpiece and subjected to flameless combustion, which leads to uniform bluing.
Sources
- https://accorel.ru/pokraska/voronenie-krasivo-i-prochno
- https://promtu.ru/obrabotka-metallov/sekretyi-voroneniya-metalla
- https://metmastanki.ru/voronenie-metalla-v-domashnih-usloviyah-sposoby
- https://tutmet.ru/holodnoe-chernenie-nerzhaveyushhej-stali-domashnih-usloviyah.html
- https://www.rocta.ru/info/kak-voronit-metall-v-domashnih-usloviyah/
- https://www.umeltsi.ru/slesar/1167-voronenie-v-domashnih-usloviyah.html
Hot bluing: features, advantages, disadvantages
Many people, especially older craftsmen, prefer to blue their guns exclusively using the hot method, considering this method to be the only correct one. The argument is very simple. For a product that has been hot blued, the coating lasts much longer. Another advantage of this method is the absence of harmful fumes.
Quite often this method is called oil bluing, which actually explains the technology of the process. The technology is very simple and blueing steel with your own hands using this method is quite easy.
To begin with, the part is heated, the more, the better. After this, the part is immersed in oil (this is what gave the method its name as bluing steel in oil). It can be linseed, olive, or gun oil. In principle, you can even use regular machine oil.
After the part has been kept in the oil for ten seconds, the part is taken out, and the oil must be allowed to drain on its own, otherwise stains will appear. The next step is to “bake” the butter onto the surface. To do this, it is customary to use a blowtorch. An important point in bluing steel in oil is to determine when the product is ready.
Experienced craftsmen say that you need to stop baking at the moment when the part just begins to change its color from brown to black. Burnishing steel in oil is one of the oldest and most proven methods of protecting metals from corrosion; it has not failed craftsmen for centuries, and it will not fail now.