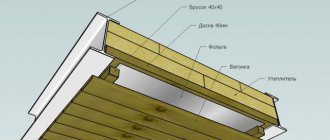
In order to make the composition yourself, you must have:
- Metal container (saucepan, ladle, etc.).
- Heating devices (for example, an electric stove).
- Resin.
- Manganese peroxide.
- Respirator or protective mask and gloves.
First, you need to pour the oil into a container yourself and put it on low heat. When it heats up to 110 degrees, water will begin to release.
Next, you need to let the water evaporate and carefully monitor the temperature of the composition; it should not exceed 150 degrees.
The solution must be boiled independently for four hours.
Note: since the mixture is a flammable substance, it is not recommended to pour it into the container to the very edge. It is enough to fill the vessel halfway.
After the water has completely evaporated and the foaming process is completed, a catalyst can be added to the container in proportions of 30/40 grams per 1 liter of oil.
The catalyst must be added in batches because it produces a very large amount of foam. After mixing the oil with the drier, you can increase the temperature to +200 degrees and leave the composition to boil for another three hours.
How to determine whether the mixture is ready or not yourself?
It is necessary to drop a small amount onto the glass. Its transparency indicates readiness.
Upon completion, leave the composition at room temperature to cool slightly.
The catalyst in this case is just an auxiliary element that determines how quickly the drying oil dries.
To make this substance, you need to mix resin and manganese peroxide together in a ratio of 20:1 (where 20 is the number of parts of resin).
Before mixing, you must melt the rosin a little yourself at a temperature of +150 degrees.
Precautions when working with drying oil
To completely protect yourself while working, you must open all windows and doors for ventilation. It is also recommended to wear a respirator and gloves; under no circumstances should the product come into contact with exposed skin. First of all, drying oil is an oil, that is, a flammable substance. Therefore, during work, you should never smoke indoors or use flammable objects.
Humidity and ultraviolet rays negatively affect the composition, as the natural solution begins to thicken. To prevent this from happening, you must tightly close the lid on the jar or any other container. If an unpleasant thing does happen and the composition thickens, there is a way out. Although, again, this is additional time and money: take any solvent that is intended for oil paints and dilute it in a ratio of 1 to 10.
Do I need to dry wood before painting?
Re: Do I need drying oil before varnish? Do not dry it under any circumstances! The varnish will roll off from the drying oil. The purpose of drying oil is to prime the surface and level out absorbency.
Interesting materials:
Is it possible to hang a flag on the balcony? Is it possible to display the flag of the USSR? Is it possible to call a function from JS itself? Is it possible to whip 20 cream with a thickener? Can you froth coconut milk? Is it possible to take a nap with contact lenses on? Is it possible to take two vacations in a row? Is it possible to take out a mortgage without proof of income? Is it possible to take leave without pay for 3 months? Can I get a duplicate check?
Advantages and disadvantages
In practice, making this component yourself has a number of advantages, but there are also some disadvantages. Let's take a closer look at the main advantages of the process:
- here you can save a lot of money, since high-quality material has a sufficient cost;
- if necessary, it will be possible to use up all the old oil that is present and unsuitable for food use;
- you can independently prepare a high-quality composition, which in terms of characteristics will not be inferior to purchased options;
- It is possible to supplement the prepared composition with auxiliary properties through special processing.
Despite some advantages, it cannot be said that such a process is considered acceptable, since there are a number of disadvantages. When cooking, a pungent, unpleasant odor is released. It is necessary to maintain a certain technology, otherwise nothing positive will come of it. Appropriate equipment is required to carry out the work.
Introduction of driers (siccativation) into drying oils
In the process of obtaining drying oil, it is necessary to introduce the optimal amount of driers. In this case, a small amount of drying agent may be ineffective to ensure the required drying rate, and an excessive amount of drying agent may not only not speed up, but even reduce the drying rate of the oil. In addition, the use of a drying agent containing 2 or 3 metals (polymetallic drying agents) increases the drying rate of drying oils.
At oil and fat industry enterprises, lead, manganese, and cobalt linoleates are most often used in the production of drying oils.
Precipitated naphthenate drying agents are most widely used in the production of drying oils, as they are more economical than fused resinates and linoleates.
Drying oil substitute
This option is for those cases when it is not possible not only to purchase factory-made drying oil, but also to make it yourself at home.
Substitute recipe:
- casein - 50%;
- slaked lime - 25%;
- turpentine - 12.5%;
- soap solution - 7.5%.
Add turpentine after thoroughly mixing the other ingredients. Next, dilute the mixture with water until the solution looks like thick drying oil. To avoid the appearance of sediment, add a little ammonia to the composition.
A surface treated with casein solution dries faster than with drying oil. The composition can be added to oil paints to improve their strength and water-repellent characteristics.
Impregnation with drying oil
Methods for impregnating a wooden product:
- Treating wood with hot solution. Soaking is carried out in a water bath. This method is good for processing small parts. Place the wooden product in a bowl with hot drying oil for 4-8 hours. Then we wait for 4-6 days for the surface to dry completely. Please note: if you mix red lead (3-4% of the total volume) with drying oil, the quality of impregnation will significantly increase, and the surface will dry in just 2-3 days.
- Treatment with a solution of oil and kerosene. We combine the components in a ratio of 1 to 1. It is acceptable to use both cold and heated ingredients. However, the temperature of the solution will affect the speed of impregnation: the surface needs to be treated with hot drying oil for only 3 hours, but if the composition is cold, it will take 1-2 days.
- Treatment with a solution of oil, paraffin and turpentine. To prepare the solution you will need 40% drying oil, 8% turpentine and 52% paraffin. First, dissolve the paraffin using turpentine in a water bath. Then add drying oil and mix the mixture thoroughly. Apply the hot solution to the wood. The drying period will be from 2 to 3 days.
- Treatment with a solution of oil and wax. The solution is prepared based on the following proportions: 85% drying oil, 15% wax. Grind the wax and immerse it in the hot mixture. The drying time for the surface will be within 2-3 days.
Drying is a responsible job that does not end after treating the surface with drying oil. Before continuing to manipulate the wood, you need to wait until the coating is completely dry. The drying rate depends on several circumstances, including: the components of the solution used, the amount of drier, the type of wood and other factors.
Drying oils with driers based on polymetals dry the fastest. But monometallic driers do not promote rapid drying. For example, a surface treated with drying oil with lead drier will dry in 20 hours. If lead is replaced with manganese, drying time will be reduced to 12 hours. An even better drying performance is achieved by combining lead and manganese into a polymetallic drier. In this case, the surface will dry in 7-8 hours.
Air humidity and temperature have a significant impact on drying speed. Drying oil with cobalt drying agent will dry 1.5 times faster when the air temperature rises to 25 degrees.
Under the same conditions, a solution with manganese drier dries 4 times faster. The optimal air humidity for drying the surface is 65-70%.
Preparation of driers
Manganese resinate - 100 wt. parts of rosin are melted at a temperature of 150° and 5 parts of manganese peroxide are added in small portions; At the same time, the mass foams strongly. Each subsequent portion of manganese peroxide must be added after the foam from the previous addition begins to subside. Then cook the mixture at a temperature of 190–200° for 3–4 hours. When the sample on the glass is transparent, the drier is considered ready.
Lead resinate is obtained using the same method, but taken at 100 weight. rosin infusion 10 parts of lead litharge.
Manufacturers
In Russia, drying oil is produced by large paint and varnish enterprises:
- "Kotovsky paint and varnish plant" (Tambov region);
- "Perm Paint and Varnish Plant" (Perm);
- "Management Company ZLKZ" (Sergiev Posad);
- Ufa Paint and Varnish Plant (Bashkortostan);
- "Azov Paint and Varnish Plant" (Rostov region);
- "Bobrovsky Experimental Plant" (Sverdlovsk region).
For many decades, drying oil has been in constant growing demand among consumers. That is why well-known and large enterprises are engaged in its production.
The most popular products are from the following brands:
- "Tex" . This company sells drying oil that is already prepared for impregnation. It is sold in containers from 0.5 to 8 kg. Distinctive features of the products of this brand are high hardening speed and a significant reduction in paint consumption during finishing. This drying oil can be purchased as a primer.
- "Coachman" . Produces an impregnating agent in strict accordance with the requirements of GOST and all Sanitary Regulations and Regulations. The product arrives in stores in packaged form, the weight of the container is 0.8-20 kg.
- Isolate . It is considered one of the highest quality materials and is packaged in containers from 0.5 to 200 liters. The disadvantage of this brand is the fact that they produce drying oil only to order and only in large wholesale quantities.
- "Vesta-Color" . Offers drying oil both wholesale and retail. The impregnation produced by this manufacturer is characterized by exceptional quality and excellent performance properties.
- "Khimtek" . Has been producing oxols for over two decades. The product of this brand has decent quality and an affordable price for the average Russian. It comes to stores in containers of various sizes, thanks to which each consumer can buy packaging that meets his scope of work.
Drying oil from the listed brands has been proving its practicality and high quality for many years, which is why when choosing impregnation you should give preference to these manufacturers.
How to make drying oil with your own hands
It is not very clear why drying oil is harmful. For now - an article about what drying oil is and how it is prepared. Now, of course, it’s easier to buy it ready-made; in the old days, you cooked it yourself.
In some ancient recipes, amber and other resins are introduced into drying oils, but according to modern classification such compositions are classified as varnishes.
Drying oils
(from Greek - ointment, oil) - film-forming substances based on vegetable oils subjected to heat treatment or alkyd resins. Drying oils wet wood and metal well. They are used as protective coatings, impregnations, bases for natural paints, oil paints, etc.
Natural drying oil almost entirely (according to GOST - 97%) consists of natural vegetable oil (linseed, less often - sunflower, soybean or other), the remaining share is occupied by drier. During the production process, oil can undergo heat treatment with or without air purging. Drying oil obtained by heat treatment without blowing is called polymerized
, with blowing -
oxidized or oxidized
.
Natural drying oil has the appearance of an opaque thick oily liquid of black-brown color with a faint odor.
Flaxseed oil
In the old days, drying oil was made by boiling linseed oil, resulting in linseed drying oil. Any metal utensil and any heating method are suitable for this - gas stove, kerosene stove
Flaxseed oil can ignite, like any oil in general, so you should be careful when working with it: fill the vessel with oil no more than half the volume and heat it slowly
First, the oil releases water (its release stops only at 110-120° C), foam forms, especially if you take fresh
linseed oil. You need to make sure that the oil does not rise above 160° C. After 3-5 hours of heating, the linseed oil is completely dehydrated, and foam will no longer form in it.
a drier to it
(from Latin siccativus - drying) - special auxiliary substances that are added to oil paints to speed up the drying process. Drying agent is added to linseed oil so that the drying oil dries faster.
Add 30-40 g of drier for each liter of heated oil.
The introduction of the additive vigorously foams the mass; the drier must be introduced very carefully!, in small portions. Heat the finished mixture for a few more minutes and then cool
Preparation of drier
To prepare a drier (manganese resinate), 100 parts by weight of rosin are melted at a temperature of 150 ° C. Then 5 parts by weight of manganese peroxide are added to the melt in small portions. This mass also foams a lot, so each subsequent portion of manganese oxide should be added only after the foam from the previous addition has subsided. When the introduction of manganese peroxide is completed, the temperature of the mass is brought to 190-200 ° C, after which it is boiled for 3-1-4 hours.
To determine whether the desiccant is ready, a drop of the mass is applied to the glass: if the drop turns out transparent, the desiccant is ready.
Metal compounds such as cobalt, lead, manganese, iron, zirconium, lithium, strontium are used as driers. The content of drying agents in drying oil is very small. Their presence accelerates the oxidation of the oil due to the fact that the drier actively absorbs oxygen from the air, which is used for oxidation. The effect of the drying agent on the drying oil does not stop after drying, therefore the coating quickly darkens and becomes brittle. The composition of the drying agent significantly affects the drying speed of drying oil; for example, polymetallic drying agents give a drying speed several times higher than monometallic ones.
Drying oil from sunflower oil
Drying oil made from sunflower oil will be worse than from linseed oil, since sunflower oil is semi-drying.
We start by gradually heating the oil to 280°C - note - much higher than for linseed oil. When thick dark flakes begin to form in it, stop heating
Then the sunflower oil is cooled and then filtered through gauze folded several times.
Drying agent is added to the filtered oil - 20 g of drying agent for each kilogram of oil.
PREPARATION OF Drying oils and varnishes
Natural drying oils are certain vegetable oils that have been properly processed.
They are used in the production of oil paints, primers, etc. When applied to the surface and dried, drying oils form a well-adhering and water-insoluble film. In addition to natural drying oils, our industry produces a number of substitutes (oxol, sulfoxol, etc.), as well as surrogate (chemical) drying oils with mineral oils. To prepare high-quality drying oil, mainly linseed, hemp, sunflower and other vegetable drying oils and siccatives (drying agents) are used - special substances that are introduced into the processed oil in order to dehydrate it and increase its drying ability. The best quality drying oils are made by blowing air through heated oil and then adding a drying agent.
Previously, only metal oxides and various salts of inorganic acids were used as driers, for example, litharge, red lead, manganese peroxide, boron-manganese salt, etc.
Wood treatment with drying oil
You can impregnate wood bases yourself using drying oil using several methods, namely:
- Using a hot solution. This means immersing the product in a vessel with heated drying oil for four to eight hours. Upon completion, you need to give the part time to dry (about four to six days). For greater effect and faster drying, you can mix drying oil with red lead in a proportion of 3-4 percent of the total mass.
- Using a mixture of oil and kerosene. To begin with, the components need to be combined in a 1:1 ratio. You can use cold or heated ingredients, this does not affect the quality. But, at the same time, the hotter the drying oil is during processing, the faster the surface will dry completely (about three hours), while after treatment with a cold composition the surface will dry within 1 - 2 days.
- Using mixed oil, paraffin and turpentine. The solution must be prepared independently in the following proportions: drying oil - 40%, turpentine - 8% and paraffin - 52%. First of all, you need to dissolve the paraffin in a water bath, then add drying oil to it and mix everything thoroughly. Next, you need to treat the wooden surface with the hot mixture and leave it to dry naturally for two to three days.
- Using a mixture of oil and wax. The mixture is made in the following proportions: drying oil - 85%, wax - 15%. First, you need to grind the wax and pour it into the heated mixture yourself. Afterwards treat the surface. The base will dry completely in about two to three days.
Treating wood surfaces is not limited to applying drying oil; this is just the beginning.
But before moving on to the next stage of work, you need to let the surfaces dry as well as possible.
How quickly this will happen depends on several factors, including the type of wood being worked with, the volume of catalyst used in the process of making the solution, the ingredients from which the mixture is made, and others.
Minimum drying time for surfaces coated with drying oil with catalysts made on the basis of polymetals.
While monometal-based driers even slow down this process to some extent.
For example, take the use of drying oil with a lead-based catalyst; the drying speed of such bases is approximately 20 hours.
If the catalyst is manganese, the drying time will be several times shorter - approximately 12 hours.
But the best result is obtained by drying oil with a polymetallic catalyst based on lead and manganese - approximately 7-8 hours.
How quickly the treated wooden surface dries is also influenced by the temperature and humidity level in the room where it actually dries. Drying oil with a cobalt catalyst dries approximately one and a half times faster, at a temperature of +25 degrees.
At this temperature, drying oil with a manganese catalyst dries completely four times faster.
The humidity level should be between 65 and 70%.
Varnishes and polishes for furniture polishing
1) Gasoline…………………………..500 g
Flaxseed oil (boiled)………….56 g
Cedar oil…………………28 g
Mix and use with a soft sponge or cloth. Rub until shiny after 30 minutes.
2) Stearin………100 g
Turpentine……….140 g
Dissolve stearin in heated turpentine and allow to cool. A small amount of this ointment is applied to a piece of wool and polished.
Drying oil oxol
The composition of semi-natural drying oil (oxol) includes natural vegetable oils and solvents that have undergone long-term heat treatment. Its composition is dominated by solvents, which is why the product has an unpleasant specific odor, which sometimes persists even after drying on the surface being treated.
The color of the drying oil of the existing composition is light brown or brown. Has the property of drying quickly. The main task of this type of drying oil is to protect wooden surfaces from parasites and moisture; after covering the products with it, a protective film is formed.
It has also become widespread in the paint and varnish industry; it is used in the production of paints and for diluting them in the process of performing interior and exterior painting work.
The surfaces of products primed with such drying oil acquire a good shine, high strength, and become water resistant. In terms of cost, drying oil oxol is very economical and much more profitable than natural options.
Technical characteristics and composition of natural drying oil
The main purpose of the composition is, of course, to protect surfaces from various types of mechanical influences. Natural drying oil is intended, first of all, to maintain environmental standards (GOST 7931 76) of the product coated with drying oil.
Today people use several types of composition: natural (all components are environmentally friendly), semi-natural (a drier is added to the base to strengthen the technical characteristics of drying oil) and synthetic (usually added to paint coatings to increase the volume of paint and its ability to adhere).
Natural drying oil can be made from different components, that is, it can be based on: olive, sunflower, hemp oil. One of these substances is boiled and brought to a certain temperature. Dryers are added in accordance with the manufacturer's requirements: 35% per 1 liter of natural oil. This is necessary to prevent a fire in the house.
IMPORTANT. When pouring natural oil into a container, pour the mixture into half the pan, since when the temperature rises, the mass foams and rises, and, accordingly, a fire may occur, or you may receive serious burns.
How can I replace drying oil?
If it is not possible to buy or prepare natural drying oil, you can replace it with a product that will protect the tree no worse.
Mix casein with soap solution and slaked lime:
- casein – 100 parts;
- soap solution – 10-15 parts;
- slaked lime – 20-50 parts.
Mix the ingredients thoroughly and gradually add turpentine (25-35 parts). Dilute with water to the consistency of regular thick drying oil. Casein lime may precipitate, but this can be avoided by adding a small amount of ammonia.
This solution is much cheaper than GOST drying oil from any store. However, he can successfully replace it in all respects. It dries much faster than drying oil. It can also be mixed with oil paint for interior and exterior decoration. Resistance to water and mechanical shock makes it an excellent alternative to natural drying oil. In addition, the composition adheres well to metal products, giving them shine and protecting them from scratches.
Water-based varnishes
Water-based varnishes are used for varnishing furniture, leather, wallpaper and other items. The preparation of water-based varnishes is carried out as follows. In an enamel pan, heat water to a boil and add alkali or alkali salts (ammonia, borax, goda). After the alkali has dissolved, shellac is added in small portions. Subsequent portions of shellac are added only after the previous portion has dissolved. The solution is cooled. Shellac wax that floats to the surface is removed by filtration. While preparing the varnish, you can add water to replace the boiling water.
How to choose?
Before purchasing drying oil, you should look at its color and consistency. Normally, the shade varies from yellow to dark brown. There should be no suspended particles, separations or lumps in the solution.
The label will certainly indicate the GOST or TU number if you are buying a composite drying oil, the name and address of the manufacturer, composition and technology of use.
As for the areas of application of different types of drying oils in repair work, follow a simple rule: for external coatings, combined compositions with an oil content of up to 45% are suitable; for internal coatings, you should give preference to an improved brand, in which the percentage of natural components is 70 or higher.
Durable, fast drying benzene varnish
Benzene………………………..1 kg
Rosin………………………400 g
Coal tar pitch……….900 g
Crushed rosin is dissolved in benzene when heated in a water bath at a temperature not exceeding 70°. Crushed pitch is added to the resulting solution. After stirring for an hour, the solution is cooled. The finished varnish is allowed to settle, after which the clear solution is drained from the settled sediment. The varnish can be used for coating metals, wood, and leather.
Making drying oil from sunflower oil at home
Few people know that drying oil can be prepared with your own hands, and in the manufacturing process you do not need to resort to complex technologies. In order to make drying oil from oil at home, you will need to do the following series of sequential actions:
- You will first need to prepare all the ingredients for manufacturing, as well as an auxiliary tool.
- Next, you have to choose the appropriate option for preparing this substance for wood processing.
- The next step is mixing the components and subsequent cooking of the substance under appropriate conditions for a specific time.
- At the end, you just have to cool this composition, then mix it thoroughly and use it for application to the surface.
In itself, the process of boiling old drying oil or a fresh composition from the appropriate components is not particularly difficult; the main thing here is to follow the technology, and in addition, adhere to a specific recipe for implementation.
Important. The cooking procedure for this substance involves the release of a strong and unpleasant odor, which will require you to open a window if the process takes place indoors, otherwise you may get poisoned.
Cementin is a cheaper product
The high cost of painting drying oil prompted us to find means to replace it with a cheaper product.
After numerous experiments based on studying the properties of oils, as well as drugs offered abroad, it was possible to prepare a composition called cementin, the merits of which have been fully determined over the past decades.
Cementin is a liquid with the consistency of ordinary painting varnish, light fawn in color, which makes it convenient for priming under different colors of oil and adhesive paints on wood, brick, cement, plaster, and also as an independent paint for inexpensive household paints. It is especially recommended for priming fresh (new) wood, such as facades, roofs, fences and other wooden structures.
When using 16 kg of cementin, add 4 liters of hot water, carefully stirring and priming with a usually bristle brush. If the cementine thickens somewhat during operation, you can add a little more water. Diluted cementin must be consumed at once, without leaving it for another day.
For cheap work, a single coat of oil paint is usually sufficient to obtain a smooth and shiny surface.
Fixatives
In order for drawings made with pencil, charcoal or chalk to become indelible and indelible, they are treated with a fixative of the following composition:
Casein powder…………….50 g
Ammonium carbonate………….75 g
Wine alcohol………………..800 cm3
Water……………………………2.5 l
Dissolve ammonium carbonate in water and add pure breech powder. Shake the mixture well and place in a warm place. Shake the liquid occasionally until the casein dissolves. The liquid takes on a yellowish-turbid color. Then pour alcohol into it little by little, shaking vigorously. You need to add alcohol carefully so that casein does not separate out in the form of flakes. During storage, the fixative usually produces a sediment; You need to drink clean liquid, trying not to stir up the sediment. The fixative is applied to the picture (drawing) using a spray gun.
Celluloid varnish from old photographic films
Celluloid……………….…40 g
Amylacetate……………….500 ml
Acetone…………………….500 g
Celluloid varnish can be made from old photographic films. The films must first be freed from the negative layer, for which they are soaked in a hot soda solution. After removing the negative layer and washing in warm water, the celluloid is dried in air. Celluloid cut into small pieces is processed in a wide-neck bottle with a mixture of acetone and amyl acetate. The bottle is carefully corked and shaken from time to time. Dissolution occurs relatively slowly. After allowing the liquid to settle after dissolving, carefully pour the clear liquid into another bottle. Instead of photographic films, you can use celluloid in any form to make this varnish.