Modern private construction is increasingly leaning towards the principles of energy efficiency; today almost no house is built without the use of thermal insulation materials. Considering the huge selection provided by insulation manufacturers, choosing an insulator that suits all parameters is not difficult. However, often the price of the issue is put at the forefront, and then the circle of searches is sharply narrowed. As an option, our craftsmen save on installation by performing available operations themselves, and some prefer to save on the insulation themselves. Of course, it is impossible to create a plant for the production of mineral wool, PSB and EPS at home, but mastering the handicraft production of ecowool is quite possible. So far these are isolated cases, but, as in everything, hard trouble begins, FORUMHOUSE craftsmen begin, the rest will join.
In this material we will consider:
- What kind of insulation is ecowool?
- Scope of application and methods of application of ecowool.
- How to make ecowool yourself.
What kind of insulation is this
Wool from cellulose fibers has been known in Europe since the 30s of the last century. In Russia, the first installations for the production of a new type of insulation appeared in 1993. However, only from 2008-2011 did the product begin to gain popularity among consumers. Therefore, even some professional builders classify ecowool as a new product in the construction industry.
Insulation is produced from recycled newspaper waste paper (glossy and coated paper does not split into fibers), resulting in a loose mass of fine-fibered material that is dirty gray, due to printing ink, or light gray, if it is absent, in color. This material retains heat perfectly, but is easily flammable and becomes a base for the growth of mold and mildew, as well as food for mice and rats.
To eliminate emerging problems, additives began to be introduced into ecowool: antiseptics and fire retardants. Now the composition of the insulation is as follows:
- cellulose (about 80%) - has good thermal insulation properties and high mechanical strength;
- boric acid (12%) - antiseptic. Protects cellulose fibers from rot, fungus and other microorganisms;
- sodium tetraborate or borax, which is the same thing, (about 8%) - antipyrine. Reduces the fire safety of wool to G2 (the material does not ignite), which is considered an ideal option when insulating building elements (walls, roofing, floors, floors). In addition, borax protects the insulating layer from the invasion of mice and the appearance of various insects.
Characteristics
Like any building material, cellulose wool has its own technical characteristics. Let's focus on those that are really important and needed by the consumer:
- thermal conductivity – 0.032-0.041 W/(m×°K). The thermal conductivity coefficient is no better and no worse than that of other insulation materials - comparable to polystyrene foam, as well as glass and basalt wool;
- density – 30-75 kg/m3. The ability to vary the specific gravity of the insulation allows you to select for each building structure the optimal weight load with good thermal protection performance. For example, when insulating a ceiling with ecowool, the most effective thermal protection is achieved at a density of 30-40 kg/m3, a sloping roof - 45-55 kg/m3, walls - 55-65 kg/m3;
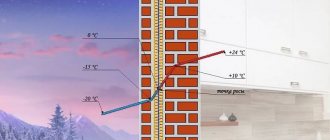
- vapor permeability – 0.3 mg/(m h Pa). The numerical expression of the value of vapor permeability is not significant. The main thing is: it exists (the walls breathe) or not (condensation forms on the surface of the wall). In European standards for building materials, this approach is expressed in only two indices: MU1 - yes, MU0 - no;
- noise insulation - absorbed up to 63 dB with a thermal insulation layer thickness of 5 cm. However, it should be remembered that this is protection against the usual type of noise, which is called airborne. The insulation is powerless against shock and structural sound waves at any layer thickness;
- flammability class - G2 (does not ignite when exposed to an open flame).
Thermal frame or how to prepare walls for insulation
Thermal frame system is an innovative technology for preparing walls for thermal insulation with dry cellulose. Includes installation of 200 grams per cubic centimeter engineering plastic retaining mesh. For better distribution of the material, it is necessary to ensure the release of excess air during blowing. The breathable membrane Izospan AM copes with this task perfectly. Installation of horizontal jumpers or slats made of wood at a distance of one to one and a half meters. Let’s say the ceiling height is three meters. Accordingly, it will take two or three cutoffs, maximum, to cover from the bottom to the top point.
The combination of a mesh and a diffusion membrane allows you to achieve the effect of pre. tension. When ecowool comes inside, the air leaves through the pores and is removed, the material remains and forms an elastic, springy pillow without seams or joints. Without these components, it is impossible to obtain an insulation density of 65 kilograms per cubic meter. You can read about the hidden capabilities and advantages of plastic mesh in a separate article on the website by left-clicking on the corresponding link. Now let’s look at the step-by-step preparation of a heating frame for insulating a frame house with ecowool.
First step
It all starts with sealing seams and joints. Craftsmen close them up manually using mineral wool or flax wool. Everything can be broken through with an ordinary chisel and hammer. The result is a tight seam under the heating frame. Some inexperienced builders use polyurethane foam, but it does not provide the necessary sealing.
Second
Upon completion of the above-mentioned manipulations, workers set cutoffs from the section board to 100 millimeters. Jumpers are placed every 1.5 meters when the ceiling height exceeds three meters. They support the cellulose in the space between the post beams of a frame house and prevent it from shrinking.
Third
At the 3rd stage of preparation, the master stretches the vapor-permeable membrane of the popular brand “Izospan” and secures it with an industrial stapler. The tension is done from bottom to top with an overlap. The bottom layer is laid first, then the top layer. The reference point is the red dotted line.
Fourth
The penultimate part of the preparatory work is stretching a plastic retaining mesh with a density of 200-250 g/cm3. It is laid on top of the membrane with an overlap of 20 centimeters and secured with the same stapler. It is imperative to leave a small splash on top of the counter bar - 3-5 centimeters.
Fifth
The final stage involves the installation of a counter block of natural humidity with a cross-section of 100-25 millimeters along the racks of the heating frame. It is advisable to mount the beams not with black, but with yellow screw-in hardware. This minimizes the risk of caps being torn off during the process of blowing ecowool into the prepared space. Want to know more? Watch the video.
Advantages
When considering the pros and cons of ecowool, it is difficult for an ordinary buyer to separate reality from the myths propagated by the marketing services of manufacturers.
Reality
Ecowool has the following advantages:
- good level of thermal protection. Not excellent, as many publications claim, but sufficient for insulating various structures of a house or apartment - approximately at the level of mineral wool and polystyrene foam;
- durability. Insulation manufacturers claim a 50-year service life. The given figure cannot be verified on the territory of Russia due to the short period of application. In Finland and Canada, many houses built more than 70 years ago have such insulation;
- the absence of connecting seams is an important advantage over other types of thermal insulation materials. Even under conditions of the most complex surface geometry, cellulose fibers fill all cavities and cracks, eliminating the appearance of cold bridges;
- good sound insulation properties. Slightly lower than basalt wool, but higher than most types of insulation;
- fire safety - does not ignite when exposed to an open flame;
- ability to retain heat when wet. For example, glass wool, which has absorbed only 1% of water, increases the thermal conductivity coefficient by 8-9%, ecowool, when wet by 25%, increases thermal conductivity by 2-5%;
- vapor permeability - walls under such insulation “breathe”;
- good adhesion to all types of building materials, especially when working wet;
- environmentally friendly, despite the presence of borax and boric acid in the composition;
- high resistance against microorganisms and rodents.
Myths
The marketing services of manufacturers and sellers are actively promoting advantages that do not exist at all or cannot be explained logically:
- low moisture permeability - in fact, insulation based on cellulose fiber perfectly absorbs water. Another thing is that it dries well without losing its properties;
- good absorption. This plus is generally difficult to comment on, since the word “absorption” refers to the ability of a substance to absorb moisture. It turns out that with mineral wool getting wet is a significant disadvantage, while with ecowool it is a plus;
- the ability of insulation to soundproof an apartment from the noise of a construction site, a plane taking off, or passing cars. This is not entirely true. The insulation protects against airborne noise at a fairly good level, but cannot damp out sound waves of the structural and shock type (these noises are well distributed by the ground and the building structure);
- ease of insulation. It is difficult to agree with such a statement, since the vertical and inclined layer of ecowool does not adhere to the base of the insulated surface. It is necessary either to attach a film to the sheathing and add insulation between it and the wall (roof), or to resort to the wet application method, which is not feasible without special equipment;
- quick implementation of thermal insulation - when working manually, it takes several days to insulate, for example, a roof. Using special equipment for applying fibers using the wet method, you have to wait 2-3 days until the thermal insulation layer dries;
- low cost of material. The budget price of insulation is the main mantra of manufacturers. But there are nuances here that are ignored: expensive installation technology (hiring a team of specialists makes the total cost of insulation work equal to that of basalt wool insulation, and in some cases even slightly higher); insulating ecowool with your own hands, instead of saving, leads to excessive consumption of material and a thicker layer of insulation, which, ultimately, again equalizes the cost of work with insulation with basalt fiber wool;
- the possibility of applying it over old insulation is a myth that is difficult to explain. For example, as the experts who proposed this insulation option see, the technology of thermal insulation work on the outside of the building (along the facade) or in the attic space.
Properties of ecowool
Naturally, all its properties are determined by its composition. In more detail, ecowool has a low heat conductivity coefficient, it is approximately 0.03 - 0.04 units. At the same time, it provides the building with the ability to “breathe”, that is, it can allow a certain amount of air to pass through, especially if it is not compacted too tightly during installation.
The technology for laying ecowool is quite simple, however, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the correct proportions, since it is its loose structure that allows it to provide the necessary properties: allow air, steam and moisture to pass through without absorbing it.
Ecowool is available for sale in several variations; it is available in densities of 40, 50 and 60 kg/m3. Accordingly, depending on the density, the value of its thermal conductivity will fluctuate; this fact must be taken into account when planning insulation work.
Ecowool is sold dry. Manufacturers package it in bags of various capacities: 5, 10 and 15 kg.
Flaws
The disadvantages of cellulose wool include:
- an increase in thermal conductivity during operation, which is caused by two reasons: a decrease in volume due to shrinkage (starts from the second year of operation); increasing the humidity of the insulating layer (when wet, it dries, but not to its previous state);
- significant shrinkage on vertical and inclined structures, and therefore manufacturers recommend increasing the layer thickness by 25% compared to the calculated one, or increasing the insulation density to 65 kg/m3. Both options lead to increased consumption of material, and, consequently, to increased costs of repair work;
- weak rigidity, which requires the installation of gratings on the walls and roof of the attic;
- complex technology for performing work not only in the wet state, but also when blowing dry fibers - without special equipment it is practically impossible;
- long drying time when applied “wet” - up to 3 days;
- strong dependence of the quality of ecowool on the feedstock, which is difficult to control even among leading manufacturers.
Manual dry application method
Laying dry ecowool
This is a very labor-intensive process that is characterized by low efficiency. If possible, it is better to rent or purchase a special unit. The manual application method is suitable if you need to make thermal insulation in some hard-to-reach places that have a small area.
To work, you will need a construction mixer and a scoop, a large container. Ecowool should be purchased in briquettes.
First, the briquette is opened and the material is placed in a container. It is fluffed up with a construction mixer for several minutes. It is necessary to take into account in advance that loosening increases the volume of cellulose by about 4 times, so you should prepare a large container.
Taking a scoop in your hands, the material is poured into the cavity, and then compacted well. When the work is completed, the hole through which the material penetrated inside is sealed. When working, you must use personal protective equipment.
Main differences from other insulation materials
The main feature of ecowool is its average performance compared to other insulation materials. It retains heat well, if it is hygroscopic, it does not lose its properties when wet, is durable, and perfectly protects the apartment from noise transmitted through the air. But due to consumers’ poor knowledge of the properties of this material and complex insulation technology, many prefer basalt wool.
To find out which is better, ecowool or basalt insulation, let’s conduct a mini comparison.
- In terms of basic technical characteristics, the insulation materials are approximately equal.
- Both materials do not support open combustion.
- The service life is comparable.
- Due to the absence of seams, cellulose wool retains heat better.
- Ecowool can be used to insulate a surface of any shape and configuration - basalt will have to be cut to fit the protrusions and depressions.
- The insulation technology is much simpler with stone fiber wool.
- The cost of thermal insulation work when insulating a private wooden house is one third more expensive than glass wool insulation, and almost the same when using basalt fiber insulation.
General conclusion: with almost identical costs for insulating a house with cellulose and basalt wool, the owner of the home is freed from work on his own when purchasing cotton wool insulation (performed by professional workers). Ecowool loses to glass wool due to the high cost of work. Otherwise, the choice is up to the consumer.
User reviews
Reviews about the insulation of walls and floors with ecowool are positive. But in this case, the insulation of outbuildings, sheds, garages and small private houses is specified. It is somewhat more difficult to manually insulate multi-storey buildings or private 2.3-storey buildings with ecowool yourself. It is necessary to use the services of professionals who work using special equipment.
The characteristics and properties of the insulation correspond to the information declared by the manufacturers. Most note the actual absence of mold, rodents and insects in the house, even if it is built from wood or OSB boards.
Application area
Ecowool can be used for insulation with the same effect:
- facades - applied to the sheathing using the wet method;
- walls - when laying using the “well” method;
- walls from the inside of the room - dry or wet on a pre-prepared lattice;
- attics and roofs - performed using the dry blowing method;
- floors - insulation is carried out using the dry method, followed by covering the heat-insulating layer with plywood or OSB sheets;
- attics - roof insulation with ecowool is carried out by dry blowing. The floor can be insulated manually.
Attention: cellulose fiber wool cannot be used under floating floors or screeds.
Popular manufacturers and prices
The high quality of ecowool is guaranteed by trusted manufacturers who do not allow the replacement of antiseptics and fire retardants with cheap analogues. Among them there are several of the best.
Isofloc. German with its products has earned numerous positive reviews from builders from all continents. The price for a 15 kg bag is about 660 rubles.
Termex. Finnish brand, known in Russia since 1988. Products are of high quality, which is facilitated by well-established process control.
Equator. Russian manufacturer of insulation made from waste paper. Production is fully automated, which allows us to obtain high quality products. Price for 1 kg - 34 rubles.
Nanovata. Another Russian enterprise with an unclear name, producing ecowool under the Alfagreen brand. Good quality is provided by equipment from Finland and the USA. A package weighing 15-17 kg can be purchased for 550 rubles.
Boric acid is an antiseptic
The third element included in ecowool is Lewis acid 8*. There was such a scientist. He brought her out. Formula "H3BO3". Tenth grade, third quarter, chemistry. Externally, it is a crystal-like mass with a characteristic scaly structure, colorless and odorless. Used as an antiseptic - it resists the popularization of harmful microorganisms. Suppresses mold growth in the bud. Fights against fungal plaques of various origins. In classic ethyl alcohol it occupies ¾, that is, the majority (75%) of the main composition. For obvious reasons, it is dangerous for humans if it enters deep into the esophagus and stomach.
8* Gilbert Newton Lewis - chemist from the USA
Use in medicine
As you probably understood from the above paragraphs of the text, not a single medical procedure can be done without boric acid. Antiseptic agents based on it are used by doctors from all over the world everywhere and without any exception. Drops of it are placed in the ears to prevent otitis media and other diseases. In general, I can talk about it for a long time. The article is not enough to describe all the benefits of the acid, which was discovered by a famous scientist from the United States of America. Want to know more? Click on the link indicating the chemical properties of boric acid.
Other applications
- research and laboratory activities of scientists;
- production of construction and finishing materials;
- food industry in Western countries 9*;
- film industry and photography;
- jewelry making and foundry production;
- fire protection and fireproof environment;
- luminescence and non-thermal glow.
9* preservative “E-284”
Nuances of insulation of various building elements
Stan
Walls can be insulated using all available methods. For example, insulation is poured into a frame house manually or blown mechanically into closed wall cavities. The brickwork “well” is also insulated in the same way. The wet method is not suitable here.
When insulating the facade, the wet-adhesive method is used. The technology for applying insulation includes:
- fastening to the wall a sheathing made of timber with an edge of 10-20 cm and a cell size of 60x100 cm;
- preparing the insulation mass for application;
- applying insulation under pressure;
- drying the applied layer;
- cutting off the excess, after which the outer layer of thermal insulation is covered with OSB boards.
Walls from the inside can be insulated manually, dry or wet.
For manual and mechanized blowing of cotton wool, a frame is made of timber or metal profiles. The pitch between vertical posts is 600-1000 mm. The thickness of the insulating layer is 20 cm (the width of the timber or metal profile is 200 mm). If the room height is more than 3 m, horizontal partitions are attached in the middle of the wall, which should take up half the weight of the insulation.
Otherwise, after a few years, under the weight of the column of cotton wool, the bottom will sag, opening a large bridge of cold at the top of the room. A vapor-permeable film or kraft paper (wrapping paper) is attached to the sheathing to create an enclosed space. A hole is made at the top of each niche to supply cotton wool. After filling each cavity, the hole is sealed, after which the operation is repeated with the next cell of the frame.
Important: in some materials you can find a recommendation to use parchment on the walls, which does not allow them to breathe. Oiled paper can only be used when insulating the roof, but, again, not in the attic.
After insulating the entire wall, the sheathing is covered with sheets of OSB, plywood or plasterboard. The disadvantage of this method is a significant reduction in the volume of the room.
Wet wool is applied using the same technology as on the facade of the building, which can be seen above.
Roofs
At the stage of preparation for insulation, the roofing material is waterproofed. The rafter system is reinforced with metal profiles or well-dried coniferous timber. The attic space is cleared of all unnecessary things.
There is no need to prepare the sheathing, since the rafters serve as a ready-made frame. All that remains is to use parchment or vapor barrier film to create a niche for blowing in the cotton fibers. Here, unlike the wall, the roof slope can be closed from the bottom up in stages, one meter in height, if the work is done manually. When using specialized equipment, it is more convenient to attach film or paper over the entire surface of the roof and fill the cavities through the hole at the top of the film.
Note that the wet method is not used for thermal insulation of roofs, although there are no obstacles to this.
Paula
Dry cotton wool is used for the floor. Insulation can be done manually or using equipment. In the first case, cotton wool is manually poured between the joists, leveled, and then covered with a finished wooden floor. If the finishing floor covering is laminate, linoleum, parquet or ceramic tiles, OSB or plywood sheets are laid over the joists.
When using the equipment, the finished floor or protective boards should already lie on the joists, creating a closed niche for the insulation.
Soundproofing
GreenWool is the best ecowool in terms of sound insulation qualities:
- A 25 mm layer of GreenWool can absorb 10 dB of sound;
- An 80 mm layer of mini-slab is capable of absorbing 10 dB of sound.
To ensure high-quality sound insulation in small apartments, there is a method of using ecowool using the technology of applying plaster to concrete, wood or brick surfaces. In this case, the material is laid using smooth spatulas in a 10-12 mm layer. One bag of insulation is enough for 6 square meters. m of surface.
The sound insulation properties of GreenWool ecowool have been confirmed by tests at the Acoustic Research Laboratory (Moscow). Evidence of this is the certificate of conformity SNiP 23-03-2003 and GOST 23499-2009. Based on the test results, ecowool is recommended for soundproofing of residential, public, and industrial buildings.