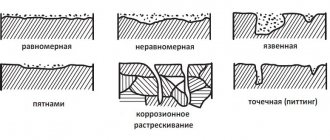
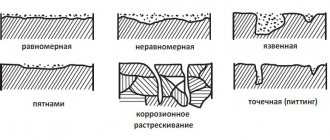
Corrosion of pipelines is the main cause of depressurization, as a result of which cracks, ruptures and cavities appear on the surface of the pipe. And therefore, protecting pipelines from corrosion is a task not only for builders or manufacturers, but also for specialists creating projects and those who will use them.
The cause of rust and corrosion on steel tanks can be the inappropriate composition of the liquid flowing through them, the wrong combination of various metals, as well as insufficient corrosion control and poorly selected protection methods. The danger of corrosion is that it can cause pipelines to leak. Repairing pipes after damage can only be done using welding.
General provisions
Corrosion processes are the oxidation of a metal, in which its atoms change from a free state, losing their electrons, to an ionic state . An underground pipeline is subject to two types of corrosion, the nature of which is worth understanding before starting to deal with them. Therefore, I will pay a little attention to their description:
Soil
Diagram showing the effects of soil corrosion on a metal pipeline
As you probably guessed from the name and the accompanying diagram, soil corrosion occurs due to contact of steel with soil. In turn, it is divided into the following subspecies:
- Chemical _ Appears as a result of exposure to iron by gases and non-electrolytes of the liquid type. It is noteworthy that with it the material is destroyed evenly, and the formation of through holes is almost impossible, which makes this type of corrosion process the least dangerous for a highway laid underground;
- Electrochemical . The metal acts as an electrode, and groundwater, of which there is an incredible amount in our climate zone, acts as an electrolyte. The ongoing process is very similar to the work of a galvanic couple and provokes the destruction of point areas on the surface of the pipes, which ultimately leads to their emergency condition;
The result of damage to the wall of a steel pipe by electromechanical corrosion
- Electric . It occurs due to the impact of stray currents on steel, which can “drain” from rails, substations and other electrified devices that fill modern cities. It is the most dangerous and destructive corrosion process.
We recommend: Wood impregnation for exterior use
Internal corrosion
Diagram showing the effects of internal corrosion on a metal pipeline
If the transported liquid has a low hydrogen index, but its content of oxygen, sulfates and chlorides, on the contrary, is high, then internal corrosion processes cannot be avoided, as a result of which:
- The level of roughness of the inner surface of the wall increases , which leads to a decrease in water permeability;
The inside of the pipeline becomes rougher due to the effects of internal corrosion
- The quality of the transported liquid deteriorates as rust gets into it;
- Over time, a through hole may appear , which can cause a pipeline rupture.
Chemistry on guard
Protection of pipelines from corrosion according to SNiP includes many different comprehensive measures, but I want to give some specific methods that great science so graciously “gives” to us, and which I was able to put into practice:
Gift #1: External insulation
We figured out above that most troubles occur due to chemical reactions that occur as a result of long-term contact of metal with the ground. Therefore, the simplest and surest step is to eliminate it completely. Moreover, in this case, it is also easy to protect pipes from freezing, that is, “killing two birds with one stone.”
I will describe to you the option that I used myself, as well as alternative methods of insulating the pipeline being laid:
- Petroleum bitumen . It was this material that I took as the basis for protecting metal from rust in underground conditions. Its price fluctuates around 18-22 rubles per kg, which is quite favorable to the family budget. The working process:
- First of all, I cleaned the surface of the pipeline until it was shiny with a steel brush;
To do this, I recommend using a grinder with an appropriate attachment. This way the task will be completed much faster and with better quality.
Grinder with a steel brush attachment
- Then I diluted part of the purchased bitumen with gasoline to obtain a bitumen primer in the following proportions:
| Substance | Component |
| Bitumen | 1 |
| Petrol | 3 |
Mixing bitumen primer
- Carefully treated the metal surface of the water main with the resulting solution;
I do not recommend neglecting this stage, since it significantly increases the level of adhesion of iron to the oil substance.
- Next, I prepared bitumen mastic over the fire with the addition of crushed asbestos to enhance the strength characteristics of future insulation. Cement and kaolin are also suitable for this purpose;
Making bitumen mastic with your own hands
- I applied the first layer of hot mixture, after which I wrapped the pipeline with waterproofing . I used a model with the following characteristics:
| Parameter | Description |
| Base | Fiberglass |
| Weight of one square meter | 2500 g |
| Daily moisture absorption | No more than 1.2% |
| Absolutely waterproof | Three days of constant exposure |
| Price | 43.5 rubles per 1 m2 |
Waterproofing rolls in stock
- Then he repeated the procedure two more times. For your region, you may need less or, conversely, more layers of bitumen with waterproofing, depending on the corrosive activity of the soil, which is affected by its moisture level, chemical composition, acidity and structure;
Protecting a gas pipe with bitumen waterproofing
- Polyethylene . It is worth noting two completely different situations:
- The first includes the personal execution of the plan. This method can be called the easiest to implement, since you just need to wrap the pipe in several layers with polyethylene cloth and secure it with mounting tape. But this material itself has low strength characteristics, so I would be careful not to use it to protect long sections of the highway;
- In the second, we are talking about the factory application of reinforced extruded polyethylene. That is, you buy metal pipes that have a special protective layer. Of course, such products will cost more, but they will provide quite effective protection against corrosion;
Factory application of extruded polyethylene to a steel pipe
- Polyurethane foam . Here you can also take two roads, but in any case it is worth immediately noting the very high thermal insulation qualities of the finished anti-corrosion protection:
- Use special polyurethane foam shells . They are two halves of a cylinder, which are put on the pipeline on both sides and are joined to each other, creating a tight connection;
Ready-made casings for water and gas pipelines
- Injection of liquid polyurethane foam between the pipe body and a pre-installed sheath of extruded polyethylene or other suitable insulating material. After the substance hardens, the seams are completely absent, which, of course, significantly improves the quality of the insulation, although the process itself is more labor-intensive to implement.
Graphic representation of a pipeline, the waterproofing of which is created by pouring liquid polyurethane foam
External insulation is not limited to the above options; here you can use many more moisture-resistant materials that can take a cylindrical shape. Therefore, in any case, also be guided by the current offers of a specialized store located near you.
Gift #2: Internal Insulation
Steel pipes with internal sand-cement insulation
As I noted above, liquid transported through pipes can also provoke the occurrence of corrosive processes, and here things are somewhat more complicated. The fact is that without special equipment at home, high-quality internal insulation is impossible. Then all that remains is to order the appropriate services from specialists or immediately buy already protected products.
The most common option today is to apply a cement-sand mixture to the inner walls of the pipeline and then crimp it using a special pulled device. The result is a smooth, non-corrosive coating.
Inside view of a protected pipe
When I ordered this type of service, I was offered the following prices:
| Pipeline cross-section, mm | Cost of internal waterproofing per linear meter, rub. |
| 159 | 401,5 |
| 219 | 460,7 |
| 273 | 519,3 |
| 325 | 591 |
It is noteworthy that the instructions allow processing of both new metal pipes and old ones.
petroleum bitumen can also be . In this case, products with a large cross-section are dipped into a liquid solution, and the joints are then processed manually. And samples with a small diameter are coated after welding, by passing a mixture with a hollow copper cylinder through them under the influence of a direct electric current. Due to the influence of electricity, bitumen particles adhere tightly to the iron, creating a thin, reliable film.
Pipe with internal bitumen insulation
Gift #3: Active Insulation
This includes electrical protection methods, which I was quite able to implement on my own. Here is their description:
- Cathodic protection:
- We apply a negative potential to the pipeline, transferring it to the cathode zone;
- Next to the pipes we bury iron pipes , pieces of rails or other ferrous metal products that will take on the role of an anode;
A steel rail is quite suitable as an anode.
- We connect a source with negative direct current to the pipeline;
- We connect a source with positive direct current to a rail or other product that you used as an anode;
- This creates a closed circuit of electric current , which flows from the positive pole to the anode grounding, spreads over the ground, hits the pipe and then to the negative pole;
Scheme for implementing cathodic protection of a water supply main
- Since current comes out of the rails in the form of positive metal ions, it is the rail itself that is gradually destroyed, and not the pipe . So much for chemistry;
- Tread protection. It is much easier to implement, since it does not require an external power source . This is the option I prefer to use:
- We place a rod of metal next to the water supply, which has a negative chemical potential , which exceeds that of steel. This may be a product made of zinc, magnesium or aluminum;
- We connect it to the protected structure using a cable;
I also recommend filling the protector with a special mixture of salts, which facilitates the process of its corrosion and thereby increases the performance of its protective functions.
The diagram shows the tread protection of pipelines
| Symbol | Element |
| 1 | Priming |
| 2 | Protected pipeline |
| 3 | Metal protector with high negative chemical potential |
| 4 | Salt mixture |
- The entire impact will fall on the anode protector, excluding pipe corrosion;
- Once the zinc or magnesium rod is completely destroyed, it must be replaced;
- Drainage. With its help, pipelines are protected from stray currents:
- We connect the pipe with a cable to the nearest electrified source , through which the currents that enter it are returned;
- Metal ions stop going into the soil, due to which corrosion processes stop.
Thus, all active methods of protection come down to preventing the loss of metal ions due to “sacrifice” or getting rid of stray currents.
I recommend using an integrated approach to waterproofing your pipeline. That is, combine external, internal and active protection. This will give the most effective result, allowing you to extend the operational life of the highway for decades.
The essence of the procedure
Protective protection is based on a substance called an inhibitor. This is a metal with increased electronegative qualities. When exposed to air, the protector dissolves. As a result, the base material is preserved even if it is severely affected by corrosion.
Various types of corrosion can be easily defeated if you use cathodic electrochemical methods, which include sacrificial protection. This procedure is an ideal solution when an enterprise does not have the financial capacity or technological potential to provide complete protection against corrosion processes.
Types and properties of anti-corrosion coatings for pipelines
What is used to protect pipes from corrosion? The main treatment of pipes against corrosion can be divided into treatment of the internal surface of pipes against corrosion and protection of pipelines from external corrosion. For each surface, approximately the same materials are used, but in different proportions.
The most commonly used substances include:
- Bitumen and bitumen-polymer materials;
- Polyethylene-based materials;
- Resins;
- Primers and putties;
- Enamels;
- Paints.
The main properties of these coatings:
- Effective protection of steel pipes from corrosion;
- Relatively long service life;
- Quick and easy application;
- Possibility of application to large products and small parts;
- Economical consumption;
- Affordable price;
- Prevalence in the construction products market.
Protecting pipelines from corrosion will extend their service life
All pipeline protection methods have a large number of advantages. They are:
- increasing the strength level of pipes,
- increasing the level of resistance to the influence of an aggressive environment,
- extending the service life of pipelines of various types,
- increasing the hardness of the pipe surface both inside and outside.
Thanks to all protection methods, it is possible to ensure a long service life of all pipelines. They give them the opportunity to serve for at least ten years.
Causes
Corrosion of steel underground pipes is a phenomenon, the main reason for which can be called the reaction of electrochemical oxidation of metals from their constant interaction with moisture. As a result of such reactions, the composition of the metal changes at the ionic level, becomes covered with rust, disintegrates and simply disappears from the surface.
We recommend: How to treat wood against mold and mildew - in the basement of a wooden house
The oxidation process may be influenced by the nature of the liquid that flows through the underground heating pipeline or the properties of the environment in which it is located. It is for this reason that when choosing suitable means to combat rust, it is necessary to take into account all the features that preceded its occurrence. Otherwise, repairs by welding are inevitable.
About the features of electrochemical protection
The main cause of pipeline destruction is the result of corrosion of metal surfaces. After the formation of rust, cracks, ruptures, and cavities form, which gradually increase in size and contribute to the rupture of the pipeline. This phenomenon occurs more often near highways laid underground or in contact with groundwater.
The principle of cathodic protection is the creation of a voltage difference and the action of the two methods described above. After carrying out measuring operations directly at the location of the pipeline, it was found that the required potential to help slow down the destruction process should be 0.85V, and for underground elements this value is 0.55V.
To slow down the corrosion rate, the cathode voltage should be reduced by 0.3V. In this situation, the corrosion rate will not exceed 10 microns/year, and this will significantly extend the service life of technical devices.
One of the significant problems is the presence of stray currents in the soil. Such currents arise from the grounding of buildings, structures, rail tracks and other devices. Moreover, it is impossible to make an accurate assessment of where they may appear.
To create a destructive effect, it is enough to charge steel pipelines with a positive potential in relation to the electrolytic environment, these include pipelines laid in the ground.
In order to provide the circuit with current, it is necessary to supply an external voltage, the parameters of which will be sufficient to break through the resistance of the soil foundation.
As a rule, such sources are power lines with power ratings from 6 to 10 kW. If electric current cannot be supplied, then diesel or gas generators can be used. The installer for the protection of underground pipelines from corrosion must be familiar with the design solutions before performing work.
We recommend: How and with what to cover wooden lining?
Principle of cathodic protection
a) using galvanic sacrificial anodes.
b) using polarization from a direct current source.
1 - pipeline buried in the ground, 2 - galvanic sacrificial anode,
3 - direct current source, 4 - slightly soluble anode
The galvanic method is based on the fact that different metals in the electrolyte have different electrode potentials. If you form a galvanic couple from two metals and place them in an electrolyte, then the metal with a more negative potential will become the anode and will be destroyed, thereby protecting the metal with a less negative potential (Fig. 1.4a).
In practice, protectors made of magnesium, aluminum and zinc alloys are used as sacrificial galvanic anodes. The use of cathodic protection using protectors is effective only in low-resistivity soils (up to 50 Ohm.m). In high-resistivity soils, this method does not provide the necessary protection. Cathodic protection by external current sources is more complex and labor-intensive, but it depends little on the soil resistivity and has an unlimited energy resource (Fig. 1.4b). As a rule, converters of various designs powered from an alternating current network are used as direct current sources. The converters allow you to regulate the protective current over a wide range, ensuring pipeline protection in any conditions. 0.4 overhead lines are used as power sources for cathodic protection installations; 6; 10 kV, as well as autonomous sources: diesel generators, thermogenerators, gas generators and others. The operating principle and circuit of cathodic protection is shown in Fig. 1.4c
Operating principle and cathodic protection scheme
1-protected pipeline, 2-connecting wires, 3-DC source, 4-anode grounding, 5-points of damage to the insulating coating
The protective current applied to the pipeline from the converter and creating a “pipe-ground” potential difference is distributed unevenly along the length of the pipeline. Therefore, the maximum absolute value of this difference is located at the point of connection of the current source (drainage point). As you move away from this point, the potential difference “pipe-ground” decreases. Excessively increasing the potential difference negatively affects the adhesion of the coating and can cause hydrogenation of the pipe metal, which can cause hydrogen cracking. Reducing the potential difference does not provide corrosion protection and, within a certain range, may promote stress corrosion cracking. The main way to combat hydrogen cracking is to control the value of polarization potentials, especially at drainage points, and maintain it at a given level. Stress corrosion cracking is observed in a narrow range of pipeline potential, from minus 0.75 V to minus 0.83 V, and appears only under simultaneous exposure to high temperature and pressure, and also depends on the condition of the metal surface, the composition of the ground electrolyte and the condition of the insulation.
Application of anti-corrosion coating
The method of applying anti-corrosion coating depends on the selected coating material and requires an individual approach. However, there are uniform rules that apply in any case:
- The surface is prepared: cleaned of scale, rust, old protective coating, paint;
- Clean the cleaned surface;
- The surface is degreased using special compounds;
- Clean using a sand or shot blasting machine with fine sand;
- Treated with detergents to clean the deep layers of the product;
- Rinse the surface;
- Dry the surface before applying the main protective coating;
- Each layer of protective coating applied is thoroughly dried.
Anti-corrosion painting of pipes is most often used, since this material is widespread, affordable in price, easy to apply (spray or roller applied) and durable.
Equipment used for anti-corrosion treatment of pipes
Depending on the type of protective coating, special equipment is used, for example, an electric arc metallization installation (allows the application of metal coatings), plasma spraying installations, cold galvanizing installations for steel products (for paint and varnish products), spraying installations (primers and paints and varnishes) ), roller.
It is mandatory to comply with safety precautions when performing work. The specialists performing the processing must wear special protective uniforms.
External insulation
The first and most important way is external insulation. In addition to anti-corrosion functions, it reduces heat loss and provides mechanical protection. Different materials can be used to create insulation; we will briefly consider the possible options. 1. Bitumen insulation.
It consists of a layer of polyethylene, which is protected by a bitumen coating.
Sometimes there may be fiberglass wrapped around the pipes. Can be used for pipelines located in clay, sandy and rocky soils. 2. Polyethylene anti-corrosion insulation.
It consists of a multi-layer coating, specially designed to protect pipelines from corrosion.
3. Polyurethane foam insulation.
There are two types. The first is the use of polyurethane foam shells, used for above-ground and underground pipelines for channel and non-channel pipe installation. The second is the creation of a polyurethane foam shell by injecting liquid polyurethane foam between the pipe and pre-created polyethylene insulation, after which the polyurethane foam hardens and turns into a complete shell.
There is also insulation with glass wool and mineral wool, however, these options are initially designed to reduce heat loss and prevent the creation of condensation, and not to protect against corrosion, which is why they are used primarily for insulating pipelines of heating networks. The thickness of the insulating layer can vary. In each specific case, the thickness is calculated depending on the functional load on the pipeline, the importance of the water line and the corrosive activity of the soil in which it is located - the higher this activity, the thicker the insulating layer should be.