From a structural point of view, the pediment is the upper part, the end of the front side of the building, while performing several functions: to be a support for the rafter system and to protect its interior from bad weather. Don’t forget about the aesthetic component - gables can well be a decoration of the house, which is facilitated by a huge range of modern facing materials.
The most common form of construction is a triangle, and it does not have to be isosceles. Pediments in the form of a trapezoid are quite common; recently oval and more complex designs have come into fashion. Note that their appearance directly depends on the shape of the roof itself, and the correct calculation of its parameters - height, area, amount of necessary materials for cladding - is of great importance.
What you need to know to carry out calculations
You can find out how many bricks you need for a new house by using an online calculator that will help you calculate the exact amount of stone for any building, be it a house, a bathhouse, a change house, etc. It is suitable for calculating both building and facing materials.
Without much difficulty, you can calculate the bricks for a house manually. But first, a few words about what kind of bricks are on sale. It can be solid, hollow and porous. Due to the existing voids in the material, its weight is reduced. And a room made of such building material will retain heat longer, since the air remaining in the voids is a poor conductor of heat. The most popular brick size is 250x120x65 mm.
To show how easy it is to calculate the amount of building material needed, let’s take for example a square house, the size of which is 10x10 m with a height of two floors.
If we know the total area of the house, then it is necessary to carry out additional calculations, namely:
- find out what the perimeter of the building is;
- calculate the area of the walls taking into account their height;
- determine the thickness of the walls (external and internal).
Each of these parameters affects how many bricks are needed to build a cottage according to the given parameters.
Although the facing brick differs in texture, its dimensions are standard Source sv.decorexpro.com
See also: Catalog of projects of brick houses presented at the exhibition “Low-Rise Country”.
Main design features of the pediment
The pediment, being a continuation of the end wall of the building, rests against the cornice in the lower part, reaching the ridge in the upper part, regardless of its shape. The shape of the slopes also determines the type of pediment, which in the simplest case is an isosceles triangle.
Two methods of its installation are used:
- before the construction of the rafter system begins. In this case, it is important to correctly calculate the height and area of the structure. The main advantage of this method is the absence of interference during the construction of a pediment; it is usually used to build an extension of the end of a brick wall;
- after installation of the rafter system or even after completion of the entire complex of roofing works. The main problem is that the roof will interfere with the construction of the pediment, but there is no need to calculate its height, since it will be determined by the height of the ridge. Typically, this method is chosen in cases where there are difficulties in performing calculations.
In any case, it is important to calculate the area of the gable, and at the design stage of the building and/or roof - this will help determine the amount of material required for its cladding.
Types of bricks included in the calculator
If the perimeter of the external walls is: 10 x 4 = 40 m, then in order to calculate the area of the walls, the sum of the perimeter should be multiplied by their height. Let it be equal to 3 m. From this it follows that the height of the two floors is 2 x 3 = 6 m. From this it turns out that the area of the external walls is: 40 x 6 = 240 m2.
To find out how many bricks are needed for a 10x10 house without a calculator, you need to take into account the thickness of the masonry and select the type and size of the stone from which it will be made. Dimensions of masonry material can be of three types:
- Single - 250x120x65 mm
- One-and-a-half - 250x120x88 mm
- Double - 250x120x138 mm.
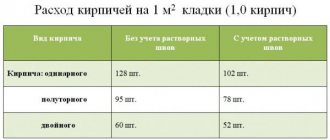
How many bricks are needed to build a house can be found out by referring to the consumption table of the required material per 1 m2 of masonry:
Number of bricks depending on the laying method Source line-home.ru
On a note! A building built from double brick looks less elegant than one built from single brick. But this can be easily corrected using any facing material (granite panels, siding, plaster or brick of standard sizes).
Important points
It is possible to calculate the amount of material for construction with maximum accuracy only by taking into account the openings for windows and doors.
Their total area should be subtracted from the area of the entire masonry. Almost every house has a certain number of partitions inside the house and non-load-bearing walls. It is worth considering the ventilation system in the room. To calculate the required volume of bricks per house, take into account the area and thickness of the internal partitions. The consumption for them is calculated in a similar way, adjusted only for the thickness of the wall, which will be much smaller. When dressing the front and interior masonry with a poke is carried out, much more material is required.
An example of calculating a house with an area of 100 square meters. m
Now let’s calculate how many bricks are needed for a house of 100 sq. m. As in the previous example, to do this, you first need to find out what the perimeter of the walls is. Let’s say each wall of the house is 10 m, and there are four of them in total: 10 x 4 = 40 m;
- To find out the area of the external walls, you need to multiply the perimeter by the height, which in our case is 3 meters: 40 x 3 = 120 m2;
- It is not difficult to calculate how many bricks are needed for such a house. For example, if the masonry is made with a thickness of 2 bricks, and a single brick is chosen as the building material, then for each square meter of masonry you will need 204 bricks (including seams).
- We subtract the total size of all openings: 120 m2 – 12 m2 = 108 m2.
- The final calculation will look like this: 108 x 204 = 22,032.
Result: to build a house with an area of 100 m2, you will need to buy 22,032 single bricks, plus about 5% reserve in case of battle.
To get a good result, any construction must be preceded by careful calculations Source superdom.ua
Geometry can help you make calculations
Calculation of the area of a pediment using the parallelogram method: to determine the area of a triangle-pediment, you need to enlarge the triangle to a parallelogram with an imaginary line and calculate its area using the formula S=ah, where S is the area of the entire parallelogram, a is the length of the base, h is the height of the parallelogram and pediment. The resulting value must be divided by 2 - this is the area of the triangular pediment.
Knowledge of geometry and a calculator can help you carry out the necessary calculations to find out the area of the system. With a triangular shape, the ridge will act as the vertex of the triangle. Its height is the side of a right triangle. The role of the second leg is played by the width of the house with a pitched roof. With a gable roof, this is the width of the house divided by 2. And with a hip roof, this is the diagonal of the house, divided by 2. The height of the ridge can be calculated by multiplying the length of the leg by the tangent of the slope angle of the roof structure. There is an excellent opportunity to find a table of tangents in a geometry textbook.
For example, a house with a width of 10 m has a gable roof with a slope of 35 degrees. Tangent of 35 degrees is 0.7. Similarly, the height of the pediment: 10/2x0.7 = 3.5 m. Knowing this value, you can determine the area of the triangle. Here again a calculator can help: the height is multiplied by the length of the base and the resulting result is divided by two. In the example given, this value will be: 3.5x10/2=17.5 square meters.
Calculation of the area of the pediment using the triangle method: you can calculate it by knowing the angles of inclination of the pediment and geometric formulas for calculating the area of triangles.
An example of calculating a house with an area of 200 square meters. m
By analogy, a brick calculator will help you calculate how many bricks you need for a house of 200 sq m:
- Perimeter: 20 x 4 = 80 m
- Area: 80 x 3 = 240 m2
- If the walls are laid with two and a half bricks, and a single stone is chosen as the material, then, in accordance with the table, it turns out that at least 255 pieces will be needed per 1 m2.
- Subtract the area of the openings: 240 m2 – 18 m2 = 222 m2.
- The final calculation is as follows: 222 x 255 = 17,316.
Bottom line: to build a house of 200 m2 you will need 56,610 pieces. bricks.
On a note! Approximate parameters were used in the calculations, including window and door openings. Each house has individual dimensions. To find out a more accurate number of bricks required for a cottage, you need to subtract the area of all existing openings inside the room from the total area of the external walls.
For the construction of houses located in areas with a temperate and cold climate, it is preferable to choose a load-bearing wall thickness of at least 2-2.5 bricks.
Typically, in every building, the interior space is divided by walls. It is also necessary to allocate a separate place for the ventilation system. For their construction, similar building materials may be needed.
You can find out how many bricks are needed for the interior decoration of a house by multiplying the total area of the internal walls by the number of bricks per 1 m2 of masonry.
Internal partitions are often made one brick thick - this must be taken into account when making calculations Source strojbum.ru
Thus, the calculator will calculate how many bricks are needed for a house of 150 sq. m (and any other size). But it is worth remembering that to the obtained result you need to add another 5-10% of building material as a spare. During transportation, storage and laying, it often breaks.
The block calculator for walls works in approximately the same way, only it takes into account the size of the blocks; they are usually larger than bricks, and accordingly fewer of them are needed for construction.
Brick Pediment - Advantages, Disadvantages, Masonry, Instructions, Masonry Tips
The gable brick superstructure for supporting the gable roof of houses, in comparison with other materials, has characteristic advantages. Among them are the following:
- structural strength,
- durability,
- the material is not subject to destructive processes, like wood - to rotting,
- mold does not form on the surface,
- material is financially accessible.
The only serious drawback is a significant increase in the mass of the structure, and as a result, the load on the supporting structures and foundation.
What are the stages of construction?
The construction of a brick pediment involves carrying out this process in several stages. Initially, even before installing the structure, you need to make all the required calculations. This is the most important stage of construction, because incorrect calculations can lead to very bad consequences, in particular such as skewed roofing.
The second stage will be the marking work. If the project involves building a structure in the form of an isosceles triangle, then you need to calculate the middle of the wall and fix a wooden strip at this point.
The length of such a batten must fully correspond to the height of the brick pediment. In the corners of the room you need to stretch the nylon cord and then secure it at the very top of the slats. Thus, the end result should be an isosceles triangle. In this case, the walls of the triangle are the base, and the top is the slats. The nylon laces will be the sides of the triangle.
If the structure is an irregular triangular figure, then the rail can be moved in any direction.
The choice of guide side depends entirely on the design idea. After all stages are completed, you can begin laying bricks.
How to calculate?
Let's move on directly to the calculations. The masonry thickness is determined not only in metric measurement, but also by the quarter elements of the building material in question. These calculations can be made using a calculator - how to calculate how much is needed for a base, knowing the parameters, but you can do the calculations yourself. They will depend on the masonry thickness and you can use two methods - find the total volume of the wall and divide it by the volume of the brick, obtaining a certain amount, or calculate the exact area and divide it by the block area, ultimately obtaining the final result.
Now we will talk about performing calculations for various types of masonry without using a masonry mesh. If we are talking about stone laying, then it can be different in individual cases and have different bindings. But its width will definitely be twenty-five centimeters - the length of the bed of material. Let's assume that we need to raise the level of the base by half a meter with a length of seven meters, and we will calculate by area. Let's see how many rows there are. Divide 500 by 65 to get a value of approximately 7.69. That is, you can raise the base either by seven or eight rows.
But you need to understand that the calculation is carried out from the material lying on the bed with the side facing inwards and the other facing outwards of the building. On this basis, you should calculate the amount of material per row in length. If the wall is seven meters long, then 7000 needs to be divided by 120. We get a value of about 58. At the same time, we also have connecting seams, we need to multiply 7 by the resulting value, that is, by 58. We get 407 pieces.
To double-check this value, you can use another method - by volume. We have the following plot parameters: 7x0.5x0.25 meters. If we multiply these values, we get 0.875 cubic meters. And one unit will have the following data - 0.25x0.12x0.065, which in total will give us 0.00195 cubic meters. Now we multiply the obtained values and get a figure of 448.7 bricks.
As you can see, there is still a difference, but it is not too significant. And the first method will be more accurate, because we based it on the number of copies in a row.
Let's consider the option of calculations in half a stone. This method of laying on a wall is usually used when carrying out finishing work using facing material. In this case, it is interesting to know the quantity needed for a certain area or pillars. In this case, we will not change the dimensions of the base and will leave the quantity nearby, since the height of the block will be the same as in the previous case - 6.5 centimeters.
Now let's find out how many units we need to create a row. To do this, you need to multiply 7 by 0.25, we get 28 pieces. Now we multiply this value by 7 and get the figure 196. As you can see, less material is needed, which means you can save money, but we should not forget that half-stone masonry can be a whole wall, and not just a facing solution.
Another masonry option that should be mentioned is called quarter stone. In this case, the brick is laid on a spoon, which will face inward, and the bed side will face outward. This method is also usually used as a facing method, but here there will be fewer rows. There will be about 4 of them with the expectation that there will be more seams. In length we will also need 28 bricks, and the total quantity will then be 112 pieces.
That is, as you can see from the example of the three main methods for calculating the material for the plinth and wall, there is nothing complicated in carrying out the calculations. In this case, a situation may arise when you have to lay thicker masonry with your own hands. But whatever it is, nothing will change much. It needs to be divided by the width of the unit (25 centimeters) and, having counted each of them separately, it is necessary to sum it up and get the total quantity.
Tools and materials
There is no need to calculate the necessary tools, but you must have them. To cover the gable of a building with siding yourself, you will need:
- metal scissors;
- electric drill;
- construction level);
- a screwdriver (it is advisable to have a cordless one - it is more convenient to work with);
- at least one plumb line;
- screws or nails (the latter must be galvanized).
* You will also need pliers, a pencil, a tape measure, and a square.
Heat transfer resistance of enclosing structures
| Wall design | Heat transfer resistance, R (m2x°C)/W |
| Single solid brick 120 mm expanded clay gravel 140 mm single solid brick 120 mm | 1,87 |
| Single hollow brick 120 mm expanded clay gravel 140 mm single solid brick 120 mm | 19,4 |
| Single hollow brick 120 mm expanded clay gravel 140 mm single hollow brick 120 mm | 2,01 |
| Single hollow brick 120 mm expanded clay gravel 140 mm single solid brick 250 mm | 2,23 |
| Single hollow brick 120 mm expanded clay gravel 140 mm single hollow brick 250 mm | 2,38 |
| Single solid brick 120 mm expanded clay gravel 270 mm single solid brick 120 mm | 2,95 |
| Single hollow brick 120 mm expanded clay gravel 270 mm single solid brick 120 mm | 3,02 |
| Single hollow brick 120 mm expanded clay gravel 270 mm single solid brick 250 mm | 3,31 |
| Single hollow brick 120 mm expanded clay gravel 270 mm single hollow brick 250 mm | 3,46 |
| At the request of SNiP 02/23/2003 thermal protection of buildings for Izhevsk | 3,39 |