If the owner of the apartment decides to thoroughly carry out repair work and level the walls, he needs to stock up on plaster. It is known that the material is distinguished by type and composition, and it is also a known fact that the mixture must be applied simultaneously.
To do this, you need to immediately knead the required amount. How to correctly calculate the amount of plaster for walls?
What factors influence the amount of plaster used?
The most obvious factor on which the consumption of building material depends is the curvature of the surface. The more uneven the walls, the more mortar will be needed to level them.
Reference! This item includes not only horizontal and vertical deviations, but also various depressions and protrusions, chips and cracks.
The consumption of plastering material is determined based on its type:
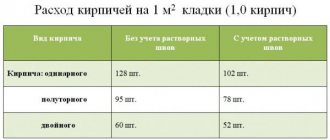
Since gypsum plaster has significantly less weight compared to cement plaster, its consumption will be significantly less;
Reference! Many people make the mistake of thinking that cement material is more profitable. Of course, its cost is much lower, but if you take into account the cost of straightening the walls, then gypsum plaster will be much cheaper.
Briefly about the main thing
In order to know exactly how much building materials are needed for the work, you need to take into account the areas of walls, floors and ceilings, as well as the consumption rates of building materials. You can find out the average consumption by asking the sellers, but you need to measure the square footage of the house yourself. To do this, you need to use knowledge from elementary geometry. When calculating the area of complex figured surfaces, they are divided into simple parts, the necessary calculations are made, and then they are summed up.
Ratings 0
What tools can you use to calculate square meters?
The consumption of plaster material directly depends on the number of square meters. How to correctly calculate the area required to be treated with plaster?
List of tools that are used to calculate square meters:
- building level;
- tape measure with limiter;
- ruler;
- pen and paper;
- calculator.
To make it easier to record measurements, builders create a drawing of the room.
Online Assistant
How much paint you need can be quickly calculated using a calculator - a computer program posted on websites about repairs and construction. The online calculator takes into account:
- Type and composition of material. Silicone, acrylic, plastic paint consumes less than latex or waterproof paint. The consumption of enamel, plastic, water and oil composition is even greater. The calculation result is given for single-layer painting;
- “dead” volume - the degree of roughness of the surface being painted;
- undissolved solid particles of paint;
- calculation of the need for pre-treatment with soil solution;
- losses.
It should be noted that some manufacturers indicate not the weight, but the volume of the material sold. Look carefully at the density indicator on the jar. It ranges from 1.2 to 1.6 kg in 1 liter. If the calculation is made in kilograms, and the paint is purchased in liters, for an accurate measurement you need to recalculate its mass into the required volume. For example, with a density of 1.3 kg/liter, according to the data specified in our calculation, 6.612 / 1.3 = 5.086 liters are needed per layer.
Manufacturers offer a huge selection of paints and varnishes for painting. Careful study of the composition features and correct calculation of consumption will ensure proper quality of coloring and save money on their purchase.
How is layer thickness calculated?
If you correctly calculate the thickness of the layer, you can more accurately determine how much plaster you will need to purchase for repairs. In order for these measurements to be more accurate, you need to clean the surface of the walls on which the plaster will be applied as much as possible.
The old finishing material is removed and the following work is carried out:
- using a plumb line, the level of the walls is checked and 3 main points with deviations are identified;
- the selected values are added;
- the resulting number is divided by the number of points taken as a basis. The final number will become the thickness of the future layer.
Reference! Before calculating the plaster consumption, you need to take into account the layer of plaster beacons, which is 6 mm.
Tips and tricks
It must be remembered that the geometric parameters of buildings can rarely be ideal. Therefore, to determine exact values, it is better to take measurements in several places and then derive the arithmetic average. For example, when calculating the area of a room based on the walls, it is better to measure the length along the ceiling, baseboard and in the middle of the vertical plane. Height - in the corners and the middle of the wall along a plumb line.
To calculate the perimeter in the presence of many protrusions and niches of different shapes, you need to lay a cord along all the elements, then measure it with a tape measure.
Having calculated the exact parameters, you can go to the store for building materials. It is better to show diagrams with dimensions to the sales consultant. A specialist will help you calculate the consumption of materials, taking into account overlaps, selection of wallpaper patterns or losses when cutting tiles.
Source
What is the consumption of plaster mixture per 1 m2?
In order to calculate the total consumption of plaster material, there are several basic calculations. How to produce them correctly and what you need to know?
Calculation of plaster consumption on rectangular walls
First you need to determine some quantities:
- height(h);
- length(a);
- width (b).
Next, the basic formulas for determining area are used: S = P × h, perimeter: P = (a + b) × 2.
The length and width of the rooms are measured along the baseboards. Height - vertical angle.
How to calculate the area of walls with a complex surface
This point can be subdivided into additional sub-points. After all, not every wall has a flat surface; the builder needs to take into account openings, windows and ventilation.
Deduction of wall area taking into account doorways
Necessarily, one of the walls in the room will have a doorway or a hole for a window. Carrying out calculations will help to correctly determine the consumption of plaster.
The arithmetic of such work is quite simple, because you need to measure the length and width of the opening along the edges of the frame - these will be the dimensions of the door.
By multiplying these values, the user will receive a number that must be subtracted from the total area of the room.
Reference! It is better to immediately take measurements of all “empty” areas: doors, windows, fireplaces, ventilation, and so on.
How is the area of a room with an irregular shape determined?
If the room is irregularly shaped with overhangs or extra corners, this will require additional measurements.
Here the action plan is also very simple:
- the irregular room is divided into several simple figures;
- calculate from area.
Thanks to this, the builder will receive an accurate consumption of plaster per room area.
Correct calculations regarding rooms with round elements
An equally common trend is to make arches or semicircular openings in rooms. The calculation here is quite interesting.
Reference! To do this, you need to multiply the diameter with the number Pi.
Calculate the squares of the room, multiply the length and width. The area of a circle is the radius multiplied by 3.14, and the area of a semicircle is the circle divided by two.
To measure the circumference of round columns, the formula S = P² / 4π is used.
Correct calculation of footage in a room with triangular elements
It is very important here to find a table for determining area. The builder must figure out which triangle the overall space of the room most resembles, and only then begin the calculations.
Calculation of area volume
To determine the exact volume, it is necessary to measure the floor area. It is this number that is multiplied by the height.
How to calculate the dimensions of walls and ceilings
To do this, you just have to remember your favorite school and geometry lessons. It is known that the area of a rectangle is its length multiplied by its width. The area of window and door openings, as well as places where plastering is not required, is taken from the result obtained.
For example, it is planned to renovate a room 3 meters wide, 4 meters long, let the ceiling height be 2.8 meters. The room has a window measuring one and a half meters by one meter and a door measuring two by one meter. Let's calculate the area (S) of the walls:
If you have an unusually shaped room, calculating the area will be a little more difficult. You may need to remember the formulas for the area of a triangle, circumference, etc. To simplify the task, special programs are used - plaster area calculators. This application can be installed on your phone, tablet or computer.
How is consumption calculated based on the type of mixture?
The total consumption of material depends not only on the area of the room, but also on many other factors.
Reference! The surest option is to refer to the manufacturer’s markings on the packaging, which shows the calculation for one square.
But the principle is identical:
- the total thickness of the layer is determined;
- consumption as noted by the manufacturer;
- wall area;
Reference! You still need to add 5-10% to the overall result.
Gypsum plaster
Do not forget about the consumption specified by the manufacturer.
Ideally, 0.9 kg of dry mixture will be needed per 1 mm. The calculations are quite simple: the area is multiplied by the total consumption per 1 square, and this value is multiplied by the thickness of the layer. Due to its plasticity and low consumption, gypsum plaster is the best option. Although, many people use cement mortars.
Cement based mixture
The standard consumption value is 1.7 kg of dry mixture. It all depends on the manufacturer, but as a rule the consumption is at least 1.4 kg. This is a significant difference compared to gypsum material.
Reference! You should not make the mixture yourself, since it is almost impossible to make such calculations correctly.
The same formula is used here as with gypsum plaster, only instead of 0.9 the value of 1.7 kg is taken.
Mixtures of decorative plaster
The type of mixture plays a big role here. The decorative base is applied to an already flat wall, and is not used to straighten it.
- textured plaster is applied in a thin layer of 3 mm, and the consumption does not exceed 1.5 kg per square;
- the Venetian mixture is much more economical. Consumption does not exceed 600 grams per square. But it is applied in several layers.
How to accurately calculate the area of walls for plaster?
To calculate the cost of plastering walls, you need to simply and accurately calculate the area. Tell me a simple method for such a calculation, preferably with a clear example. How craftsmen calculate the area, my calculation will not coincide with the master’s calculation.
Where I live, they use a very simple and, in my opinion, very convenient method for calculating the area of plastered walls:
And now a little more detail using the example of simple walls without complex elements:
Consider a wall measuring 4m*2.5m
without openings its area is 2.5 * 4 = 10 square meters ,
Now let's look at an example of a small wall measuring 2m*2.5m
If the wall is blank, its area is 2 * 2.5 = 5 square meters
if there is a door: 2.5+2.5+1=6m.p which is the same price as 6m.sq.
if window: 2.5+2.5+1.5+1.5=7m.p = 7m.sq.
And another example with a larger wall 6m*2.5m
a blank wall has an area of 6 * 2.5 = 15 square meters
if with two windows and a door 2.5*4+1.5*4+1=17m.p= 17m.sq.
The total area of the walls is calculated without subtracting from them the area of windows and doors, and window and door slopes are calculated separately.
Source
What consumption standards per square meter exist?
There is no universal value, since much depends on:
- uneven walls;
- plaster composition;
- manufacturer.
Experts can definitely say that you need to make calculations based on formulas and add 5-10% to the resulting number. This is what will ensure more accurate consumption of plaster material.
Correct calculation of the area and the required amount of plaster will greatly facilitate the repair and improve the quality of work.
Experts do not recommend starting the plaster several times. It’s best to make the correct calculations once and not torture yourself.
Finishing work.
Sales department:
Delivery, setup and consultation FREE
Licensed SN-2020, TSN-2001, Russian Railways, TSNB-2001, FER-2017
30% discount on weekly courses
A. Cladding works
Calculation of construction work for surface cladding with natural stone and reinforced concrete textured slabs and parts should be calculated based on the surface area of the cladding. When determining the cladding area, you must be guided by the following rules:
a) the dimensions of walls and columns should be taken taking into account fractures in the plan along the outer contour, i.e., along sections that include facing slabs;
b) do not take into account the relief of the profiled parts, taking the area of the vertical projection of the cladding.
When the extension size of profiled parts is greater than the height, take the extension size (larger side).
The scope of work for facing steps and laying window sill boards made of natural stone should be calculated taking into account the ends of the slabs embedded in the masonry or plaster.
The scope of work on surface cladding with artificial slabs should be calculated based on the projection area of the cladding surface without taking into account the relief.
The scope of work on facing surfaces with artificial marble should be calculated based on the unfolded surface of the facing.
B. Plastering facades
The area of plaster on facade walls should be calculated minus the area of openings along the outer contour of the frames.
With high-quality plastering of facades, the area occupied by architectural details (cornices, corbels, platbands and other drawn parts), as well as columns and pilasters adjacent to the building, is not included in the area of the walls and must be calculated separately.
With improved plastering of facades, rods and cornices should not be calculated separately, since the pulling of these parts is taken into account by the standards.
Window slopes and ebbs, door slopes, as well as the side surfaces of architectural and structural parts protruding from the plane of walls or protruding into the thickness of walls during high-quality plastering of facades should be calculated separately, subdividing by width up to 200 and more than 200 mm.
With improved plastering of facades, slopes and ebbs are not calculated separately, since their plastering is taken into account by the standards.
The scope of work on plastering columns (adjacent to the building or free-standing), as well as pilasters, should be calculated based on the area of their vertical projection.
The amount of work on pulling out cornices, rods, belts, platbands and other drawn parts for high-quality plastering of facades should be calculated by the area they occupy on the surface of the facade (as projected onto the wall).
When installing cornices with a pitch greater than the height, take the area of the horizontal projection of the cornice.
B. Internal plaster
Building codes and regulations establish three types of wet plaster for internal surfaces: simple, improved and high-quality.
As a rule, simple plaster is prescribed in warehouses, basements, attics, elevators, etc., utility rooms, and improved plaster is prescribed in apartments and all other premises of residential and civil buildings, as well as in domestic and service premises of industrial buildings. High quality plaster is installed as specified in the design in the main areas of the most significant public buildings.
With improved and high-quality plaster, the finishing area is calculated separately for the following surfaces:
a) walls, pilasters, niches, pillars on stone and concrete;
b) the same, on wood;
c) ceilings with cornices on stone and concrete;
d) the same, on wood;
e) ceilings without cornices and arches on stone and concrete;
f) the same, on wood;
g) window and door slopes;
h) lower window plugs.
In addition, you should separately calculate the areas of walls, ceilings, columns, cornices and rods, the surface of which is plastered over a metal mesh with a division: with and without a frame device.
The plastering of staircases and landings from individual elements is also calculated separately, indicating:
For simple plastering, the total (total) area of finishing of walls, ceilings, pillars and pilasters is calculated, subdivided into plastering for wood, stone and concrete. In this case, the area of window and door slopes is not taken into account.
The varieties of wet plaster listed above are used to finish the surface of brickwork or other small-sized elements.
In large-panel buildings, the area of surface finishing for painting or wallpapering is calculated separately: walls and partitions, ceilings, staircases and landings.
When calculating the area of plastered surfaces, you should be guided by the following rules:
a) the area of the walls should be calculated minus the area of the openings along the outer contour of the boxes and the area occupied by the stretched platbands. Wall heights should be measured from the finished floor to the ceiling; the area of the sides of the pilasters should be added to the total area of the walls;
b) the area of ceilings (including coffered ceilings with a horizontal projection area of the caisson up to 12 m2) should be calculated by the area between the internal edges of walls or partitions;
c) the area of ribbed floors and coffered ceilings with a horizontal projection area of the caisson of more than 12 m2 should be calculated based on the unfolded surface;
d) the area of internal platbands should be determined by their vertical projection on the wall;
e) the area of staircases and landings is calculated according to their horizontal projection (floor-by-floor);
f) the area of plastering walls, ceilings and columns using wire mesh should be determined by the area of the surface to be finished, and cornices and rods - by the total area of vertical and horizontal projections;
g) the area of the base under artificial marble is not included in the scope of plastering work.
The scope of work for installing scaffolding should be calculated:
G. Painting work
Estimated standards establish three types of painting: simple, improved and high-quality. As a rule, simple painting is prescribed in warehouses, basements, attics, elevators and other utility rooms, and improved painting is prescribed in apartments and all other rooms of residential and civil buildings. High-quality painting is used in the main areas of hospital buildings and the most significant public buildings.
The area of painting facades with lime, silicate, cement and emulsion compositions is calculated without deducting openings and without taking into account the area of painting window and door slopes, as well as the unfolded surface of cornices, rods and other architectural details.
The scope of work on painting facades with perchlorovinyl compounds should be determined based on the actual surface to be painted.
The area of painting internal surfaces (walls and ceilings) with aqueous compositions should be calculated without deducting openings and without taking into account the area of window and door slopes and the sides of niches. The area of the pillars and sides of the pilasters is included in the total area of painting the internal surfaces
The area of painting of internal walls with an opening of more than 50% is determined by the actual surface to be painted, i.e. minus the openings and adding the area of window and door slopes and the sides of the niches.
The area of walls painted with oil compositions should be calculated minus the openings. The area for painting pillars, pilasters, niches, window and door slopes is added to the area for painting walls.
The area of window and door openings to exclude it from the area of the walls is calculated by the outer contour of the frames.
The scope of work on painting ribbed ceilings should be calculated based on the area of their horizontal projection using a coefficient of 1.6.
The scope of work on painting coffered ceilings should be calculated based on the area of their horizontal projection using a coefficient of 1.75.
The scope of work on painting stucco ceilings should be calculated based on the area of their horizontal projection using the following coefficients:
when saturated with modeling
The saturation of the molding is determined based on the area of the horizontal projection of the molded parts.
The area of floor painting should be calculated excluding the areas occupied by columns, stoves, foundations and other structures protruding above the floor level.
Painting of baseboards for plank floors is provided for in the standards and is not taken into account separately.
For linoleum and parquet floors, the area of skirting boards for painting is taken to be 10% of the floor area.
The painted surface of the filling of window and door openings is determined by applying the transfer coefficients established in the technical part of the collection to the filling area calculated from the outer contour of the frames. 15.
The scope of work on painting wooden trusses with silicate paint should be calculated based on the area of the vertical projection of the trusses (on one side), without excluding the gaps between the truss elements.
The scope of work on painting metal roofs should be calculated by the area of the roof, while painting seams, gutters, caps on chimneys and coverings of dormers are not taken into account separately.
The scope of work on painting drainpipes, belts, sandriks and external window sills should be calculated based on the area of the facade without deducting openings.
The volume of work on painting surfaces made of corrugated asbestos plywood and steel should be calculated based on the area measured without taking into account the bending (wave), applying a coefficient of 1.2 to this area.
The scope of work on painting steel gratings should be calculated based on the area of their vertical projection (on one side), without excluding the gaps between the posts and belts, using the following coefficients:
The paint area for central heating and sanitary fixtures, as well as small metal parts, is determined as follows:
D. Glass works
The scope of work on glazing wooden window sashes and balcony doors in residential and public buildings is calculated by the area of the openings, measured along the outer contour of the frames.
The scope of work on glazing doors (except for balconies) and shop windows should be calculated based on the glazing area calculated based on the design dimensions of the glass.
When glazing with display glass on elastic gaskets, the weight of the gaskets must be separately indicated according to the design data.
The scope of work on glazing wooden partitions should be calculated by the area measured along the outer contour of the bindings.
E. Wallpaper works
The scope of work on wallpapering walls should be calculated based on the area of the surface to be pasted.
To exclude it from the area of the walls, the area of window and door openings should be determined by the outer contour of the frames.
The scope of work on door upholstery should be determined by the area of the upholstered surface.
The areas of the surfaces to be finished are calculated using tables in the construction of which three methods are used.
The first is that since a surface can have different types of finishes, not each individual type of finish should be counted, but only the one that occupies the least area on this surface. The area of the predominant type of finishing is obtained by subtracting the calculated area of other types of finishing from the total area of the surface to be finished.
The second technique follows from the interdependence of the structure and its decoration. For example, the area of painting ceilings is equal to the area of floors without taking into account the area of thresholds and niches, the area of painting window and door blocks is equal to the area of filling openings with the corresponding coefficients, the area of finishing partitions is equal to their area multiplied by 2, etc.
The third method uses previously obtained data to calculate finishing areas with the additional use of specially calculated corrections
For example, the area of finishing at the bottom of flights of stairs and landings is taken according to the area of their horizontal projection with a coefficient of 1.55, calculated experimentally.
About the group of companies
The group is one of the oldest suppliers of estimate programs in Russia.
The group of companies sells, implements and supports estimate programs, and supplies the necessary estimate and regulatory frameworks.
Source
Why is it worth calculating paint consumption in advance?
The amount of material required must be calculated in advance, before the start of repair work.
If you do not resort to preliminary calculations, you may encounter the following problems:
- there is excess paint left or, conversely, there is not enough material;
- The required color is not available for sale or the batch has run out (the color may differ in another batch);
- the paint from the previously purchased manufacturer is no longer available;
- the surface texture required the application of an additional layer;
- the flow rate inside and outside turned out to be different, etc.