Plasters are compositions based on a binder that are applied to walls and ceilings for various purposes.
There are antibacterial, decorative, “medicinal” and other types of plasters, but the bulk of plasters are used to level walls.
Important!
Plasters are called coatings with a thickness of 5 to 80 mm. Coatings thinner than 5 mm are called putties.
Applying plasters not only levels the surfaces and prepares them for further painting, wallpapering or tiling, but also insulates the premises and improves sound insulation.
Why is binder needed?
The binder components react with water and, as a result of chemical processes, a new substance is formed. Cement and water or lime and water separately and after reaction are completely different substances, so you cannot think that the solution simply dries out; it crystallizes, gains strength, and the final strength of the coating depends on how correctly the proportions of the binder component and water were maintained.
Sand
There are no trifles in the matter of plastering.
Plaster primarily levels surfaces, so the use of coarse or mixed-grade filler is unacceptable. Washed quarry or fine quartz sand is used in plaster mortars and must be sifted through a sieve with a mesh size of 1.5 mm, since even a small amount of small pebbles can spoil a perfectly smooth and even plastered surface.
Manual kneading
Cement grades up to M350 are suitable for manual mixing.
You can manually mix only a small amount of solution efficiently:
- Dissolve the plasticizer in warm water as indicated in the instructions, stir with a construction mixer for 15 minutes.
- Mix cement and aggregate.
- Add diluted plasticizer to water and mix.
- Mix all ingredients.
Manual kneading is possible not only in a container, but also on a wooden board or metal sheet with sides:
- Pour sand in a heap along the sheet.
- Make a depression in the center.
- Pour cement into the hole and use a shovel to gradually “wrap” the sand into the cement.
- Mix sand and cement well.
- Pour water from a watering can and mix.
- Scatter the crushed stone evenly and mix.
- Continue mixing, gradually adding water.
Determine the amount of water in advance and never add water to the prepared solution.
Use clean water and the most pure, free of impurities, fillers. Choose coarse and medium sand, and fine crushed stone.
Approximate density of fillers (in kg/cubic m):
- gravel filler – 1600,
- granite crushed stone, quartz sand – 1500,
- expanded clay – 600-800.
Do not use expired cement or residues from previous work. The cement must be fresh, then the structures will turn out without cracks.
The shelf life of cement in packaging is 3 months. When opened, cement is good for a week in low humidity conditions, and for a day in high humidity conditions.
Sometimes when preparing a solution at home, they use the proportions of the components not by weight, but by volume, for example, in buckets.
Popular formula by volume:
- cement 1 part,
- sand 4 parts,
- crushed stone 2 parts,
- water 0.5 parts.
When using M400 cement, M250 concrete is obtained; when using M500 cement, the concrete is M350.
Other options for the ratio of cement/sand/crushed stone/water by volume:
- for paths, floors – 1/ 3.5/ 5.7/ 0.5;
- for fences, garages, foundations – 1/ 2.8/ 4.8/ 0.5;
- for strip foundations and walls – 1/ 1.9/ 3.7/ 0.5;
- very durable, quickly hardening – 1/ 1.2/ 2.7/ 0.5.
Video: three ways to mix concrete by hand
Why do you need a plasticizer for plaster mortar?
To prepare cement mortar, water and cement are mixed in certain proportions, which are called water-cement ratio. The ideal water-cement ratio is 0.45–0.55. But the mixture turns out to be very thick, heavy, and inflexible. It is difficult to lay, and it sets quite quickly, making further work difficult.
Adding more water seems like the logical thing to do. The mixture will immediately become more pliable, but the price of this convenience is reduced strength of the hardened coating.
A plasticizer helps to get out of this situation beautifully.
Mechanized mixing
A concrete mixer facilitates the work of mixing the solution and allows you to prepare large volumes of the mixture.
The device is turned on empty, then the components are added:
- water,
- half cement
- large filler,
- the rest is cement,
- sand.
In winter the order changes:
Video: How to mix the right concrete
What properties does a plasticizer give to plaster?
Adding a plasticizer makes the plaster more plastic, flexible, mobile and viscous, and also allows it to not set for longer, which means you can work at a calm pace or dilute more mortar at once. Plaster with plasticizer “lives” three times longer than a solution without this useful additive, that is, you can mix a solution and it will last for a whole day of work.
Important!
Cement mortars shrink during the hardening process, and as a result, cracks and detachments of the plaster from the surface may appear. To prevent this defect, a special reinforcing mesh is used, located between two layers of plaster. Naturally, the use of mesh complicates the coating process and significantly slows it down.
A replacement for the mesh is polypropylene fiber, which is added directly to the solution. Its advantages:
- light weight;
- ease of distribution in solution;
- harmless to the skin of the hands.
Plaster mortar with polypropylene fiber fiber is durable, shrinks less and does not develop cracks.
Technological features
Wanting to save financial resources and using a self-made plasticizer, builders are faced with problematic situations:
- the appearance of salt stains on hardening concrete. This is due to the leaching of salt onto the surface of the concrete mass when soap is introduced;
- difficult to predict concrete hardening time. The ingredients in soap have different effects on the hardening of cement;
- absence of pores inside the concrete monolith. A soap-based additive complicates the migration of water in concrete, disrupts the structure of the mass, which quickly absorbs moisture, which contributes to the formation of mold;
- increased shrinkage of cement mortar. The detergent does not form microscopic pores inside the monolith, which increases the density of concrete and increases the load on the foundation;
- lack of the desired effect from the introduction of a modifying additive. The introduction of soap, which is an alkaline medium, into the finished concrete reduces the effect. It is necessary to add soap at the initial stage of kneading;
- increased foaming. When intensively mixing the solution in a concrete mixer using detergents, intensive foam formation is possible. You should pause mixing, wait until the foam settles and continue the process.
Selecting a plasticizer depending on the type of plaster
There are three main types of plaster mixtures based on the type of binder:
- cement;
- limestone;
- plaster.
Each type of plaster has its own pros and cons, so sometimes several binders are mixed to make combined plasters, for example, cement-lime, lime-gypsum. Plasticizers for different types of plaster may vary.
Cement plaster (sand-cement composition)
The composition of cement plaster includes:
- cement grades M150–M500 depending on the purpose of the coating;
- sand;
- water.
For one part by weight of cement, take from 3 to 5 parts of sand. Water is added to the required consistency.
Video: Preparation of plaster mortar
Advantages of cement plaster:
- high strength;
- moisture resistance;
- resistance to infection by fungus and mold.
Therefore, cement plaster has no restrictions on temperature and humidity conditions and is successfully used on building facades, for finishing walls in rooms with high humidity, and is used as a coating for subsequent laying of tiles.
But the cement mortar is very heavy, non-plastic and sets within 3-4 hours, after which it is no longer possible to work with it and you have to mix a new batch. It also tends to delaminate during storage.
To give the solution plasticity, mobility and increase its lifespan, add the following plasticizing additives:
- lime;
- detergent;
- PVA;
- ready-made plasticizers.
Adding lime
Lime is the cheapest plasticizer for cement plaster. Quicklime is used, which must first be slaked. It is then diluted to the consistency of milk; the resulting solution can be used for mixing cement plaster mortar.
Cement-lime mortar is more plastic, it is easier to process, and remains suitable for work longer.
Adding Detergents
At home, a common practice is to use detergents as plasticizing additives in cement mortars, including plaster.
The use of liquid soap as a plasticizer actually makes the plaster mixture more flexible, more flexible, increases its lifespan and prevents delamination. But can liquid soap be a full-fledged plasticizer?
The working components of any detergent, from dishwashing liquid to expensive shampoos, are surfactants (surfactants). They are cationic, anionic, amphoteric and nonionic. Different groups of surfactants vary significantly in properties, and their concentration in different types of detergents can vary significantly. Therefore, adding a conventional 50 ml of liquid soap to 10 liters of plaster mortar, we do not know how much and what type of surfactant we actually added, and how this additive will affect the properties of the mortar; accordingly, it is impossible to predict the behavior of the plaster.
Adding PVA
Polyvinyl acetate emulsion is used in cement mortars to increase plasticity and increase adhesion. Use PVA-MB glue or PVA dispersion at the rate of 50-100 ml per 1 liter of mixing water.
Moreover, cement-sand mortars are mixed on polyvinyl acetate emulsion without adding water; in this case, a particularly powerful solution is obtained for laying ceramic tiles.
The disadvantage of using PVA is the high consumption of this additive.
Addition of starch esters
Starch esters are added to plaster mixtures to prevent the plaster layer from slipping and for better adhesion.
Application of plasticizers
The use of detergents, while there are ready-made plasticizers and superplasticizers for cement mortars, seems unjustified.
Industrial plasticizers, for example CemStone, are designed specifically to give concrete mixtures and other mortars mobility, plasticity, prevent delamination and extend the time of working with the mortar.
Since a mixture with a plasticizer with the same mass has a larger volume than a solution without a plasticizer, it is consumed more economically and, due to its lightness, fits better and slides less under its own weight, which significantly reduces labor costs.
Plasticizers prevent shrinkage deformation and cracking of the coating and promote rapid strength gain.
Adding plasticizers does not increase the cost of the solution, because plasticizers are used in small quantities and at the same time allow saving cement without loss of strength.
Lime plaster
Lime-based plasters include hydrated lime, sand and water. The proportions of lime to sand are from 1:2 to 1:5.
Quicklime is supplied in the form of powder or dough in double bags; It must be extinguished before work.
Advantages of lime plaster mortars:
- plastic;
- high adhesion;
- ease of processing;
- cheapness;
- remains plastic for a long time;
- “breathes” and creates a favorable indoor microclimate.
The disadvantages of lime plaster include:
- long time to gain strength;
- instability to moisture;
- large shrinkage;
- low tensile strength, which means the possibility of cracking.
Lime plaster does not require the addition of plasticizers, since it is plastic and mobile.
To increase strength, cement is added to lime plaster, and gypsum is added to speed up setting and reduce shrinkage.
PVA glue is used as a strengthening additive at the rate of 50-100 ml per 1 liter of mixing water.
Lime-gypsum composition
Gypsum plasters are characterized by rapid hardening. Other advantages:
- efficiency;
- no shrinkage;
- plasticity and ease of installation.
Disadvantages of gypsum plaster:
- instability to moisture;
- low strength.
Therefore, gypsum compositions are used only for finishing dry rooms and are not recommended for laying tiles.
Lime-gypsum mortar is plastic, with good adhesion and low shrinkage. Thanks to the addition of gypsum, it sets faster and gains strength.
Adding PVA
Polyvinyl acetate emulsion is added to lime-gypsum compositions in order to increase the strength of the plaster.
Plasticizers
The use of CemStone plasticizer affects the chemical reaction of gypsum with water, increasing the strength of gypsum stone. Due to the effect of the plasticizer, gypsum is completely involved in the hydration reaction, and the increased plasticity of the mixture contributes to its self-compaction.
For further finishing work, it is important that the surface plastered with gypsum compositions with the addition of a plasticizer is more opaque, which reduces paint consumption during subsequent painting.
Why are they added?
The main advantages of introducing surfactant additives into concrete include:
- Increased fluidity and mobility of the solution, resulting in increased ease of placement, it fills the formwork better. The likelihood of voids forming, especially when filling frames of complex structures where vibration compaction is difficult, is reduced.
- Reducing the amount of water in the solution: it gains strength faster.
- Better grip on the surface (adhesion).
- Resistant to cracking and temperature changes. Frost resistance.
- Strengthening the water-repellent properties of plaster.
- Ensures uniform mixing and reduces the risk of water separation and segregation.
- Increasing the strength and service life of concrete.
According to the methods of action, all plasticizers can be divided into:
- Hydrophilic action. By increasing wettability, the formation time of colloids (particles mixed in a medium with another substance) is reduced, resulting in increased fluidity and plasticity.
- Hydrophobic. Enriched with air bubbles. Increase the plasticity of the mixture and the strength of the plaster.
According to the degree of effectiveness, plasticizers are divided into:
- Superplasticizers. Manufactured from melamine polymers.
- Hyperplasticizers. The composition contains polycarboxylates. More active than superplasticizers. Due to their high cost, they are mainly used to create thin-layer self-leveling mortars, for example, for self-leveling floors.
Proportions for adding plasticizers to solutions
In order to properly prepare a solution for plastering, it is important to observe the proportions of the components. The table will tell you in what ratios to mix the main components.
This table clarifies how to calculate the amount of materials for plastering 1 square meter. m of surface depending on the thickness of the plaster layer.
PVA is added to solutions at the rate of 50–100 ml per 1 liter of mixing water; the working concentration of polyvinyl acetate emulsion in the solution can reach 20% by weight of dry cement.
Modern plasticizers are economical and easy to use.
Plasticizer consumption is 0.5–1% by weight of the binder (cement, gypsum or lime). When calculating the dosage of the additive, it should be taken into account that gypsum is more active than cement and the amount of the additive may differ from the dosage of the additive with cement, therefore it is recommended to carry out trial use in plaster mortars.
Plastering walls with cement mortar with your own hands - video and detailed instructions
Before starting work, surfaces should be primed to increase the adhesion characteristics of the finish. Plastering walls can be done mechanically or manually and includes several stages:
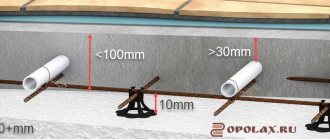
- Spray, layer thickness: on concrete - 5 mm, brick - 7 mm, wood - 1 mm. We wet the wall. We take a solution of medium consistency into a ladle or spray bottle, pour it onto the surface, level it with a rule or a trowel. If a layer of more than 50 mm is further required, we attach a reinforcing mesh.
Plastering walls with cement mortar with your own hands, the video shows detailed tips on how to spray.
- The soil is a thick solution, we scoop it up with a plaster falcon and apply it to the surface with a trowel. We wait 30 minutes, level it with a long rule, add solution to the holes, remove the bulging areas and straighten again.
- The covering is done with a liquid plaster mixture, layer thickness up to 4 mm. We moisten the previous layer, add the solution and carefully smooth it in a circular motion.
The materials in the video below will tell you the secrets of how to plaster walls with cement mortar, and the video instructions will help you figure out how to use the tool.
Plastering walls with cement mortar on beacons
We hang the walls, set up beacons: metal, plastic, wire, mortar or drywall. The distance between the guides is 150-300 mm less than the length of the rule. To increase the adhesion of the plaster to the surface, apply a primer.
Advice: It is better to cover an area of 2 m2 at a time; on average, such an area requires a bucket of solution.
Using a trowel, apply the solution from bottom to top, a little more than the required layer, there should be no gaps. As a rule, we carefully move it up and swing it slightly from side to side, and for the second pass we move the tool evenly. We apply a level; there should be no gaps between it and the surface. If necessary, add cement mortar again and repeat the procedure.
For details, watch the video on how to plaster walls with cement mortar using beacons; the video tutorial will help you understand all the nuances of the work.
How to properly install and care for a plaster figure
The durability and attractive appearance of figurines directly depend on the material from which they are made, as well as on how correctly they are located on the site.
Here are some recommendations to delay the repair of garden figures:
- Installation of garden figures: the bottom of the figure, or better yet the entire surface, needs to be coated with varnish, for example, car varnish. This advice applies to both new and refurbished figurines;
- It is advisable to place the product on some kind of pedestal to avoid contact with the ground or garden vegetation;
- Treat the hole in the bottom with ant repellent, as insects can take a liking to the decor and make an anthill out of it.
- regular washing (once a month) with a soft sponge to remove dirt. Dust absorbs oil and chemical compounds from the air, so if you rarely wipe it, it will be difficult to get rid of them;
- for the winter, the figures are brought into a dry, ventilated room without sudden changes in temperature;
Also, when purchasing, choose reputable manufacturers who use quality materials. Don’t skimp on quality, and your site will always be bright and unique!
What it is?
The plasticizer for gypsum mass is a special composition, which is most often made on a polycarboxylate base. The additive can significantly improve the properties of the material.
When using a plasticizer, the building composition will be highly volatile. It will be able to fill all elements of relief surfaces, while the number of bubbles is significantly reduced.
Currently, a large number of such additives are produced on different chemical bases.
As a rule, such powders are light in color (white, light yellow, light brown). The substance can significantly improve the quality of the finished gypsum product.
Leaves for decorating the yard
DIY plaster products are a great way to add variety to your garden decor. In addition to mushrooms and houses, you can make elegant leaves that will decorate any garden.
To create leaves you will need:
- Gypsum solution.
- Maple or other leaves.
- Rope.
- Wax paper.
- Hard brushes.
Green leaves are placed on wax paper. Each leaf is treated with a solution using hard brushes. A hole is made at the base of the leaf with a toothpick. Crafts are left to dry.
Finished products are hung on a string. Crafts can be painted with acrylic paints and decorated with sparkles.
Plaster sculpture is an endless field for creativity for children and adults. You can decorate both the interior of your home and your garden with crafts.
Concrete reinforcement
Concrete is a strong material comparable in strength to stone, but it does not withstand tensile loads well. An uneven load causes areas of tension to appear and cracks form. This can be avoided by additional strengthening of concrete - reinforcement.
Reinforcement is the “skeleton” of a structure, firmly connected to concrete. Concrete and reinforcement work synergistically: metal structures redistribute the load, protecting the concrete from stretching, and the concrete layer protects the metal from corrosion.
Gypsum with cement for the production of artificial stone and decor based on HCPV
Let us immediately note that the material is given on the basis of the practical experience of many craftsmen in the manufacture of gypsum products.
To strengthen the latter, cement is added to the mixture. But what do experts do to avoid the previously described problems?
To do this, pozzolans are included in the mixture.
Previously, the following active mineral additives were used: tripoli, opoka, diatomite, acidic slag and ash, volcanic ash, traces and others.
But their times have already passed and now the most modern pozzolan is used - highly active metakaolin (HMC).
Also today, many people use less active, but cheaper silica fume.
Their comparative characteristics were described in sufficient detail in the corresponding article on kamsaddeco.com.
The mixture, which includes gypsum, cement and pozzolans, is called gypsum cement pozzolanic binder.
The inclusion of cement in the gypsum base is associated not only with strengthening the product. Often pure gypsum castings warp when drying. They change their geometry.
The addition of cement compensates for the deformation. Expansion and contraction balance the material.
In addition, the surface of such a product the next day is much stronger than that made from pure plaster. It is drier and can be painted. This also speeds up the process.
Now in more detail about the composition of the GCPV
In addition to gypsum, cement and pozzolana, various plasticizers are added to the mixture.
Which plasticizer to use depends on the type of pozzolanic additive used.
Thus, the developers of the VMK, when using it, recommend including a plasticizer based on polycarboxylates in the HCPV composition.
The amount of pozzolana used in a mixture depends on its activity.
If we take ordinary natural pozzolans (for example, diatomite), then the amount of additive will be significantly greater than when using microsilica.
But even this cannot be increased beyond a certain value (20%). Large volumes begin to work not as active additives, but as a regular filler.
This may reduce the strength of the stone. This is due to the deterioration of the hydration process due to excess filler. Just like with too much dye.
When to slow down the setting
Slowing down the setting of alabaster is important when a large amount of work is being performed and there is no desire to dilute the plaster a hundred times in small portions. For example, you need to seal the grooves throughout the room, but Rotband (a gypsum mixture with polymer additives) is not at hand. You can dilute 100 grams of alabaster, but this volume will be enough for 5 minutes of work. If you use a retarder, then dilute 1-2 kg of material at once and perform a multiple greater amount of work in one approach.
So, the main task of slowing down the setting is to increase the volume of mixing the gypsum mixture and to complete a larger piece of work from one batch .
General rules
Before using retarders, we recommend that you follow the general rules for mixing alabaster, otherwise no additives will help. Here are tips that will come in handy when working with plaster:
- Knead only in clean plastic containers,
- Use a clean mixing tool
- First, water is poured into the container, then alabaster is poured.
If there are remnants of old mortar on the tool or in the mixing container, the plaster will set 2-3 times faster. If you first pour gypsum into the container and then pour water, the hardening will also go faster.