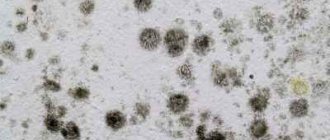
Mold easily grows in any basement or cellar. The reason for this is a favorable environment: high humidity, poor ventilation system or poor quality waterproofing.
To prevent this, you need to constantly perform preventive work. If the moldy fungus has already managed to penetrate into the cellar space and is quickly spreading there, folk methods or effective modern drugs will help get rid of it.
What is mold
This substance is a fungal colony. Its spores constantly hover in the air and, when a favorable environment arises, they attach themselves to a suitable surface and begin to quickly take over space and reproduce. To do this, the fungus needs high air temperature and high humidity.
The surfaces on which mold can live are very different. The colony will successfully develop on wood, concrete, brick and other materials. It gradually takes over walls and ceilings, moves to the ceiling and other building structures. Over time, the fungus penetrates the thickness of walls and ceilings and destroys the material. Therefore, if steps are not taken in time to destroy the colony, the house will soon need to be repaired or even rebuilt.
Important! Separate black, brown and white mold. The shade of the fungus indicates class and the age of the colony. Often the color of mold is influenced by the nature of the surface where it grows.
Molds do not develop on their own. Usually there are objective prerequisites for this. The causes of mold in the cellar are:
- insufficient supply of fresh air, poor operation of the ventilation system or its clogging;
- accumulation of condensation as a result of increased moisture or lack of ventilation;
- poor circulation and air stagnation in the cellar space;
- finding rotten foods in storage, which are an excellent breeding ground for the colony;
- use of wood affected by mold as a building material.
How to get rid of mold in your basement once and for all
If you simply use chemicals to eliminate mold in your home or basement, sooner or later the mold will come back because you haven't addressed the root cause of the problem in the first place.
The root cause of mold almost always lies in excess moisture in the basement, the root of which is water leaking into the basement or damp base of the walls or slab foundation. In order to get rid of mold once and for all, you need to eliminate existing leaks and reduce the humidity of the walls, foundation and basement floor to a minimum, and this is only possible when you protect all the structures of the underground room from possible exposure to water. This protection is called waterproofing.
Waterproofing can be done both from the inside and outside of the basement or basement.
External waterproofing:
To restore the external protection of an underground structure from water penetration, the following step-by-step actions must be performed:
- Dig out the building to the bottom of the foundation slab or strip;
- Remove the insulation and old waterproofing coating (if any);
- Clean the walls from dirt;
- Apply high-quality waterproofing to the slab, extending onto the walls 20cm above the ground level;
- Install the insulation using foam adhesive or other water-based adhesives;
- Backfill without damaging the insulation.
You can read more about waterproofing a basement from the outside in the article “How to properly waterproof a basement from the outside.”
Additionally recommended:
- Install a drainage membrane on the insulation - this measure will protect the work performed from damage during backfilling, and will also facilitate additional drainage of water from the house;
- Install a drainage system 30-50 cm below the foundation level - This measure will help drain both the water that approaches the building from the outside and the water that is located under the building, thereby reducing the water pressure on various building structures.
Diagram of the drainage system and external waterproofing
You can read more about the drainage system in the article - “Turnkey installation of drainage around a house: Proper drainage, its types, installation technologies, materials, diagrams and prices.”
Important: When performing waterproofing work on the outside, you solve the root of the problem, namely moisture getting into the walls, strip or foundation, and its impact on these elements.
Waterproofing from the inside:
If it is impossible to carry out work from the outside, you can always do it from the inside, but do not forget that in this situation you will not be able to solve the root of the problem and sooner or later it may return.
When installing waterproofing from the inside, you must perform the following steps:
- Repair existing cracks by jointing them, strengthening them with a special sealant and injection;
- Replenish the cut-off waterproofing of cold slab-to-wall joints by jointing them with layer-by-layer compaction of expanding sealant and injection. Seams are the weakest points of any structure, and it is there that water first begins to pass, and thanks to injection, it will not be able to pass either into the room or through capillaries up the walls;
- Apply a waterproofing compound that can withstand the negative effects of moisture from the outside to the inside.
Diagram of the waterproofing device from the inside
You can read more about waterproofing the basement from the inside in the article - “Waterproofing the basement from the inside: Methods, materials and stages of work.”
Additional events:
- Humidity control;
- Proper insulation;
- Adequate ventilation in your home.
Under what circumstances does fungus grow in the cellar?
Mold does not always appear in the basement. To do this, the following conditions must be simultaneously met:
- The appearance of mold spores in the airspace of the utility room. They can be carried along with food, on human skin or animal fur.
- Presence of a nutrient organic medium. This could be paper, wood fibers, peat pots, fertile soil.
- Microclimate with high humidity and temperature at +20 degrees. Stagnant air increases the likelihood of mold growth.
Not all types of mold require air heating above +20 degrees. There are fungi that successfully reproduce even at 0 degrees.
It is also necessary to note the quality of the ventilation system. The freely circulating air flow does not allow mold spores to gain a foothold on the surface. Therefore, where the air is stagnant, mold forms more often. The movement of air masses in the corners of the room is especially difficult. Therefore, mold grows there more often.
High-quality ventilation does not allow excess moisture to accumulate in the utility room, resulting from a significant difference in temperature between outside and inside or due to increased humidity. Spores are unable to take hold and germinate, even if they are present on structures, but there are no suitable conditions for development. Therefore, the main reason for the development of mold in the cellar is considered to be poor-quality ventilation.
Sulfur checker
The oldest, but no less effective way to destroy fungus in the cellar. Gas vapors spread throughout the entire infested area, which helps remove mold from the walls.
This method is prohibited for use in apartment buildings! May result in criminal liability as you are essentially spraying highly toxic carcinogens over a large area. Be careful!
Approach the matter with caution, guided by the following rules:
- Having a good ventilation system, you will need to tightly close the air shafts - old rags or foam rubber will do just fine. We carry out the same procedure with the basement exit.
- Then the checker is set on fire and remains inside for several hours (preferably from 8 to 12).
- After disinfection is completed, the room will need to be thoroughly dried and ventilated.
- Surfaces exposed to gas vapor will need to be treated with slaked lime.
- Before working with a saber, protect your respiratory organs, eyes, and skin. After setting it on fire, immediately leave the disinfection site. Smoke is POISON!
Health harm from mold
Not all people know why white mold in the basement is dangerous for building structures and for health. In addition to the danger of injury due to a floor or ceiling destroyed by fungus, mold causes many diseases. Contact with spores of a fungal colony is possible directly with the skin, after inhaling particles along with air, or through eating foods contaminated with the fungus.
Most types of mold reproduce at an incredible rate. After all, just 1 square meter of a colony throws over a billion spores into space. Because of this, after penetration into the body, the fungus provokes various diseases:
- dermatological diseases that develop as a consequence of an allergic reaction;
- diseases of the upper respiratory tract, including sinusitis, nosebleeds, difficulty breathing, chronic runny nose;
- headache and dizziness;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- anemia and exhaustion of the body.
When a person is constantly in contact with mold, serious diseases develop that lead to disability. Elderly people, those weakened by illness, and children are especially sensitive to such proximity.
Important! You can detect the presence of an allergic reaction to mold by passing the appropriate tests. If the diagnosis is confirmed, measures must be taken to destroy the fungal colony.
What to do with the foundation if groundwater passes nearby
Often the reason for the development of rot is groundwater penetrating into the underground, which is located quite close to the surface of the earth. This factor can be eliminated by a number of actions. If a drainage system was not provided outside, then there will be water on the floor in the basement .
The groundwater level under the foundation of a house can be artificially lowered by installing a drainage system outside. It should be buried below the expected groundwater level, while providing layering . This will prevent moisture from penetrating into the underground and will keep the ground around the house dry. Then fungus is unlikely to appear on the foundation.
Ways to fight
To completely destroy a mold colony, you need to put in a lot of effort and spend a lot of time. Before treating the room with special preparations, it is necessary to eliminate malfunctions in the ventilation system. Adjust the temperature and humidity levels. Otherwise, despite all efforts, the mold will grow again. Only an integrated approach will help destroy the enemy. The fight against mold in the basement is carried out in several stages.
Preparing the premises
Before getting rid of fungus in a cellar or basement, the room is completely cleared of the objects located there. They take out all products, tools and equipment. This will free up the work front and open access to possible places where fungus accumulates. Removed furniture is also treated with special preparations to avoid re-infection.
The cellar room is thoroughly cleaned and all mold is removed. If building structures are deeply affected by fungus, the parts are replaced with new ones. The earthen floor in the cellar is probably already contaminated with mold spores. Therefore, 20 cm of soil is removed and replaced with new one.
The cleaned cellar room is thoroughly dried. Only after this is it treated with special preparations to completely eliminate the fungus.
Destruction of a moldy colony
Simply removing visible mold and removing fungus in the cellar is not enough for complete destruction. Fungal spores have already penetrated into building structures and surfaces. Therefore, to combat mold in the cellar, they are treated with special antifungal and disinfectant preparations. You can purchase such products at construction and hardware stores. In this case, a good result can be achieved using folk recipes against mold. They are effective and do not harm human health.
Sulfur checker
This device kills mold with sulfur dioxide vapor. The device is very easy to use and effective, so it is recommended to use it first. Before processing, all ventilation holes in the cellar are closed to block air access. The checker is then placed in a metal container and set on fire. Immediately after this, the room is left and the entrance is tightly closed. After 5-6 hours, the cellar is ventilated to remove remaining vapors. Then the floor is covered with slaked lime to remove excess moisture.
Important! Sulfur dioxide is not only harmful to mold. It affects the health of humans and domestic animals. Therefore, they must leave home during treatment.
Vinegar
This product has good cleaning ability and destroys mold spores. White undiluted vinegar is poured into a convenient container. Then dip a brush in the liquid and treat all surfaces in the basement. There is no need to wash the substance with water. 12 hours after treatment, the entrance to the basement and ventilation are opened to get rid of the smell.
Bleaching
The method of getting rid of mold using preparations containing chlorine is comparable in its effectiveness to the action of a sulfur bomb. Any product that contains high concentrations of chlorine is suitable for this method. Inexpensive chlorine bleaches, such as Belizna, are usually used. It is diluted in water, adding 10 parts of water to 1 part of the active substance. Then the liquid is applied to all the walls, ceiling and surfaces of the shelving in the cellar.
Lime
Before using lime to remove mold, the cellar is treated with Dezaktin. It is diluted with water according to the instructions and applied to walls, ceilings and other surfaces. Lime is then applied in one of the following ways:
- 0.5 kg of bleach and 0.2 kg of formaldehyde are dissolved in 10 liters of water. All surfaces in the cellar are coated with this liquid. After this, dry the room and ventilate it.
- 0.5 kg of slaked lime and 50 g of copper sulfate are diluted in 10 liters of water. A spray bottle is used to distribute this solution.
Lemon acid
Using citric acid, you can successfully fight mold in the basement of a private house. To do this, dissolve 100 grams of crystals in 10 liters of water. The resulting solution is sprayed into the cellar. After this treatment, the room is simply dried.
Copper sulfate
Sometimes treating all surfaces with copper sulfate helps remove fungus in the basement of a wooden house. To do this, prepare a solution of 30 liters of water, 250 g of copper sulfate and 2 kg of quicklime. The liquid is applied to the walls, floor and ceiling in the cellar or basement using a paint roller or brush.
Borax
You can get rid of mold in the cellar, if it has appeared there, using borax powder. To do this, prepare a solution of 3 liters of water and 200 g of borax. All surfaces in the cellar are coated with the prepared liquid. It is suitable for treating an attic, shed, garage or basement. To make the result more effective, the solution is not washed off.
Important! When treating a room with a borax solution, wear rubber gloves, as the drug corrodes the skin.
Grapefruit Seed Extract
Treatment with this substance is more of a preventative measure and helps to avoid mold infection. To prepare the solution, take 0.5 liters of water and pour in 20 drops of grapefruit seed extract. The liquid is poured into a spray bottle and all surfaces in the treated area are sprayed. There is no need to rinse off the composition.
Tea tree oil
Tea tree has antibacterial properties. Therefore, its oil ester is able to remove mold. The product is mixed with water and sprayed throughout the cellar. After a few hours, the drug will take effect and the mold spores will die. There is no need to rinse this product off.
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide has good antifungal and antibacterial effects. Therefore, it is recommended to use it to clean a room of mold. You can use this tool in two ways:
- mix half and half with water and spray all surfaces in the basement;
- coat the walls, floor and ceiling, as well as shelving with undiluted peroxide.
Bleach with slaked lime
Another effective solution for removing mold is prepared from 1 liter of water, 3 tbsp. l. bleach and the same volume of slaked lime. The liquid is thoroughly mixed and applied to all surfaces in the cellar.
Boric acid
Another good way to solve the problem is to treat the cellar against mold and mildew with a solution containing boric acid. To do this, dissolve 1 kg of salt in 5 liters of warm water and add 100 g of boric acid. The ingredients are mixed until completely dissolved and sprayed throughout the room.
Using an ultraviolet lamp
Another way to remove mold in the cellar is exposure to ultraviolet rays. This treatment method will require a powerful quartz lamp or a bactericidal one. It is installed in the center of the cellar. If the infection is concentrated in one area, the lamp is directed towards this place. Then plug the device into the network and leave it for up to 12 hours.
Important! Ultraviolet rays are harmful to the eyes. Therefore, when working with a quartz lamp, they are protected with special glasses. Immediately after connecting the device to the network, they leave the room.
Cleaning the basement with a vacuum cleaner
To reduce the amount of mold and to prevent allergic diseases due to the impact of its spores, it is useful to clean the cellar room, as well as other rooms in the house, with a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter. The pores of such a filter are so small that they can retain not only ordinary dust, but also microscopic fungal spores. Therefore, preventive treatment with a HEPA filter helps get rid of allergens and maintain health.
Modern means
Dezaktin solution is one of the most effective disinfectants. After applying the solution, you need to clean up. It is carried out using a scraper or brush (metal). The fungus is scraped off from surfaces and objects.
Important! If there is rotting on the furniture, it is worth getting rid of things. Otherwise, there is a high probability of mold reoccurring.
Preparations with a high content of chlorine. These include sulfur bombs, acids and other substances.
Precautionary measures
Since most anti-mold products are quite dangerous if handled carelessly, basement treatment is carried out using personal protective equipment. To do this, before starting work, put on rubber gloves, a respirator or mask, and safety glasses. Exposed parts of the body are protected with a special suit.
Solutions prepared for treatment should not be touched or inhaled. After the antifungal solution is applied to the walls and other surfaces, the room must be left and the entrance closed for several hours.
Important! Do not eat foods contaminated with mold. They will definitely be thrown out.
Lime vapor
Any affected material is treated with lime. It is often used as a preventive measure against the settling of flowering spores. It can also be used in several ways: a mixture with formaldehyde or copper sulfate.
- In the first case, 200 grams of formaldehyde and 500 grams of bleach are diluted in a bucket of water. The resulting mixture is used to treat foci of infection.
- Mixing a kilogram of lime with 100 grams of copper sulfate produces slaked lime, which I use to treat the affected area with a spray bottle.
Prevention
After mold is removed from the cellar, it is important to create conditions under which re-infection of the room will be impossible. To do this, you need to maintain a certain microclimate:
- Check the quality of ventilation. If it does not work, troubleshoot. If there is no ventilation at all, it needs to be done.
- The basement is insulated and high-quality waterproofing is created from the outside. It is best to do this during the construction stage, but if desired, work can be carried out after its completion.
- They make a window that is periodically opened to let sunlight into the room.
There should be good air circulation in the cellar so that it does not stagnate. To do this, install open racks with lattice shelves. All products and things are laid out on these structures so that they do not come into contact with the walls.
It is important to monitor the humidity level. If condensation appears, the room is dried and the cause of its formation is eliminated. It is recommended to monitor temperature and humidity using a household thermometer and hygrometer.
Preparing the premises
Structures located underground are constantly in a humid environment. If the space around the basement is not drained, there is no waterproofing, and the groundwater level is close to the floor surface, it is not surprising that the air in the room is saturated with water vapor.
When converting an already built cellar, it is quite difficult to carry out extensive construction work. It is necessary to dig out the basement walls around the perimeter, lay a drainage pipe, waterproof and insulate the surface, and backfill.
If this is not possible, then the walls of the basement are coated from the inside with penetrating agents - Penetron, Hydrohit. They create an impenetrable barrier in the thickness of the concrete, preventing moisture from seeping through the walls.
In practice, liquid glass and plaster with waterproofing additives are often used to protect the internal surfaces of basement walls. All joints are carefully sealed. It is important that moisture does not find even the smallest hole.
Concrete additives that prevent the development of mold - Biolin and its analogues - have a good effect. This is not yet widespread in our country, but materials can be ordered online.
It is imperative to make drainage from the roof surface, insulate the blind area and basement.
Before treating the cellar for mold, remove everything that is possible from the basement. Wash shelves, furniture and utensils with detergents or vinegar and dry for two weeks in the sun.
Reviews
Pavel, 45 years old
I recently discovered black mold in the corners of my basement. It turned out that condensation was accumulating on the walls. We had to urgently dry the room, and we got rid of the mold with a sulfur bomb. A very effective remedy.
Igor, 37 years old
Mold developed on the potatoes in the cellar because it was too warm. We ventilated the cellar and adjusted the ventilation. Of course, I had to throw out some of the potatoes. For prevention, all the walls were coated with bleach.
Microwave method
This is one of the most convenient options for destroying microorganisms. Any dampness in the cellar will be eliminated. The process does not involve the use of chemicals that can harm human health. No matter the number of mushroom colonies, they will all be destroyed, and the spores floating in the air will not be able to settle on the walls.
The principle of operation is that a wall or any surface (floor, parquet, ceiling) is heated in sections of 50 by 50 cm to a temperature of 66-73 degrees Celsius in a very short time. It takes 5-10 minutes to get rid of mycelium at a depth of 30-37 cm.
The advantages of the microwave method directly prevail over other options. All types of small organisms are destroyed; due to the heating of the room to 60 degrees, any microorganisms die. If you have to work with a large quadrature, then it warms up in sections.
External waterproofing
First, you need to check the entire building from the outside, because very often the reason that the basement floods or it simply becomes damp is that the drainage system around the house is simply stupid.
It includes:
- slopes on the roof, windows, above the porch;
- “directional” drainpipes, that is, draining water into an underground storm drain funnel or at least into an above-ground gutter;
- drainage system around the walls of the house;
- blind areas.
If all these components or at least part of them are missing, then this deficiency must be eliminated. You should start from the top, that is, from the slopes and drainpipes.
Now you can move on to the next stage: protecting the underground part of the external walls. For this:
- We remove the old blind area.
- We dig a hole a little more than half a meter wide outside the outer walls of the basement (so that you can climb down into it and carry out work).
- Thoroughly dry the outer wall of the house (naturally or forcefully).
- We coat the wall with antifungal compounds (the choice in construction stores is simply endless).
- We coat the wall with bitumen mastic (you can use clay, concrete based on liquid glass, or with additives that reduce moisture absorption);
- Optional step: we make an underground blind area from a sheet of roofing felt. To do this, we fix it on the wall of the house 0.5 meters above ground level and move it beyond the edge of the outer wall of the basement.
- We fill the hole.
- We arrange a blind area (you can use any type of soft roof).
If serious excavation work is beyond your capabilities, then you can get by with only the last point for the first time.
In this case, the sheet of soft roofing should partially extend onto the wall of the building (about 50–70 cm), and it is important to secure it well, for example, with the same bitumen. The second edge should extend beyond the edge of the underground basement wall by the same 50–70 cm
Preventing dampness
As usual, this “disease” is easier (and cheaper) to prevent than to treat. Still being decided at the design stage:
- If groundwater is close or its level rises significantly in spring/autumn, external waterproofing is necessary. Liquid compounds are applied to the outside walls (better) or rolled ones are fused (cheaper, but less effective).
- If the cellar is being built on a slope, a drainage pipe must be laid in the ground above it, which will drain the precipitation flowing down the slope.
- A blind area is made around the cellar (or the building under which it is located), which removes precipitation flowing from the roof.
- Inside the cellar, in opposite corners, there must be two ventilation pipes with a diameter of at least 125 mm. One of them ends at floor level - 10 cm higher. Air from the street or room enters through it (supply pipe). The second ends almost at the ceiling - 10 cm below its level. This is a hood. Ventilation pipes on the street should be covered with umbrellas to prevent leaves and precipitation from getting into them. The exhaust pipe (the one that ends near the ceiling) should be higher and it is better to install a deflector on it to activate the draft. It can be painted black: due to heating from the sun, the draft should be better. Another subtlety: for good traction, ventilation ducts with natural air movement must be straight. If it is necessary to make a bend to the side, its angle of inclination must be at least 60° relative to the horizon, and the length of the inclined section should not exceed 100 cm.
- Between the room located above and the basement there should be a vapor barrier that prevents moisture from penetrating both from the basement and into the basement.
Inspecting the floor
Very often the floor in the cellar is made of earth. This is often the source of excess moisture. Through it, the moisture contained in the soil gets inside. To reduce humidity in the cellar, you need to level the earthen floor, compact it and cover it with thick plastic film. You can use roofing felt, but it breaks more often. Although it seems more durable, it breaks due to less elasticity.
There is no need to pour sand or soil on top of the film. Sometimes there is a large amount of water in the basement (accidental flooding). Then you simply remove the film, the water goes partly into the ground, partly evaporates through the ventilation. After the dampness has gone, you can re-cover the floor. If there is earth or sand on top, you will need to poke around in this slurry, extracting the film.
If the floor in the cellar is earthen, most of the moisture enters through it
If after laying the film the humidity level in the cellar has decreased, then you have found the reason. You can leave everything as is, just change the “flooring” periodically, or you can make a concrete floor with full waterproofing. The choice is yours. To prevent the film from tearing when people walk on it, knock down the wooden panels and throw them on the floor.
Improving waterproofing
The second reason why humidity increases in the basement is an insufficient degree of vapor barrier or waterproofing of the walls. This usually occurs if the cellar is lined with brick, especially silicate brick. The material is very hygroscopic and allows water vapor to pass through well. They settle in drops on the ceiling and all objects.
The problem can be solved if you make good external waterproofing: dig out the walls and apply bitumen mastic in two layers. Previously, they were coated with resin, but mastic is more effective and easier to handle.
Brick walls require additional waterproofing
But excavation work is not always a joy, and it’s not always possible to dig out the walls. In this case, you can make internal waterproofing of the cellar walls. For this purpose, there are cement-based impregnations: “Pnetron”, “Kalmatron”, “Hydrotex”, etc. They penetrate to a depth of up to half a meter into the thickness of the material (concrete, brick, etc.) and block the capillaries through which water seeps. Water permeability decreases significantly. Their only drawback is the price. But they are really effective.
All these measures will prevent the appearance of high humidity in the basement. But what to do if there is already moisture, how to dry the cellar? Next, we’ll look at ways to reduce humidity.
Preventive measures
The walls will need to be dried before storing food again. It would be a good idea to whitewash the ceiling, paint all surfaces, and treat the boards for shelving. Ventilation and waterproofing must be constantly checked for damage.
Prevention should be carried out annually exclusively in the summer. In this case, the air temperature should be without sudden changes that contribute to the formation of condensation. To avoid new fungal infections, wall waterproofing is always available.
Ventilation system
The microclimate in the cellar is very important for long-term storage of food and the prevention of mold, while ventilation will provide an integral part of the microclimate - air circulation. Depending on the size, type and purpose of the storage facility, natural or forced ventilation is installed with a different number of pipes. The simplest type of cellar ventilation is natural with an exhaust and supply pipe. For its correct installation and proper further functioning, several rules must be followed:
- Two pipes are installed in opposite corners of the room - exhaust and supply.
- The supply air supply will provide fresh air; its lower end is located at a height of half a meter from the floor, and its upper end is at a sufficient height above ground level.
- An exhaust pipe, designed to remove air from the storage, is installed in the upper corner of the cellar and protrudes half a meter above the ridge. It is insulated with mineral wool to prevent condensation from accumulating.
- The outer openings of the pipes are protected by canopies from snow and rain.
- The pipe material can be any - metal, plastic, reinforced concrete. Recently, PVC is often used, which is chosen because of its durability and lightness.
- The diameter of the pipes must be the same.
A properly equipped and well-maintained cellar will ensure long-term storage of supplies. If there is mold in the room, this problem can be dealt with using modern and proven means. Timely and thorough antifungal treatment of the cellar will not only preserve food, but also protect the health of its owner.
Share link: